
Digital Marketing Syllabus for Beginners: A Comprehensive Guide
Jan 16, 2025 13 Min Read 5288 Views
(Last Updated)
Digital marketing has become essential for businesses of all sizes. Understanding the fundamentals of digital marketing can open up a world of opportunities.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through a beginner-friendly digital marketing syllabus, covering all the important aspects you need to know to kickstart your journey in this dynamic field.
Table of contents
- What is Digital Marketing?
- Digital Marketing Syllabus for Beginners
- Building a Strong Foundation
- Website Optimization and SEO
- Content Marketing
- Social Media Marketing
- Email Marketing
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising
- Analytics and Data-Driven Marketing
- Affiliate Marketing
- Emerging Trends in Digital Marketing
- Artificial Intelligence in Marketing
- Video Marketing
- Influencer Marketing
- Developing a Comprehensive Digital Marketing Strategy
- Budgeting and Resource Allocation
- Creating a Digital Marketing Calendar
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is covered in a beginner's digital marketing syllabus?
- How long does it take to complete a digital marketing course for beginners?
- Do I need any prior experience to start learning digital marketing?
- Will I learn how to run ads on social media platforms?
- Is SEO included in the digital marketing syllabus for beginners?
What is Digital Marketing?

Digital marketing refers to all marketing efforts conducted through electronic devices or the Internet. It involves promoting products, services, or brands using various online platforms to connect with customers where they spend most of their time: the digital world. This marketing approach leverages channels like social media, search engines, email, websites, and mobile apps to reach a targeted audience, engage with them, and ultimately drive sales or conversions.
Types of Digital Marketing
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
SEO involves optimizing a website or content to improve its visibility on search engine results pages (SERPs) like Google. The goal is to rank higher for relevant keywords and attract more organic traffic.
- Content Marketing
This focuses on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and engage a specific audience. Blogs, videos, infographics, and ebooks are common examples.
- Social Media Marketing
Utilizing platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn to promote products, build brand awareness, and engage with customers through posts, ads, and influencer partnerships.
- Email Marketing

Email marketing involves sending targeted messages or newsletters to subscribers, nurturing leads, and keeping current customers informed about promotions or updates.
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising
PPC is a form of paid advertising where marketers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked. Platforms like Google Ads or social media networks allow for targeted ads based on user behavior, demographics, or search intent.
- Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing allows businesses to collaborate with third-party partners (affiliates) who promote their products in exchange for a commission on sales or leads. This performance-based model allows businesses to collaborate with affiliates who promote their products in exchange for a commission on generated sales.
- Influencer Marketing
Brands partner with influencers—people with a large online following—who promote their products through social media platforms, blogs, or other digital channels.
- Mobile Marketing
This involves reaching audiences through smartphones, tablets, or other mobile devices. Strategies include SMS marketing, mobile apps, and in-app advertising.
- Video Marketing
Platforms like YouTube, Vimeo, and social media provide an avenue for businesses to share video content to engage and inform their audience.
These types of digital marketing enable businesses to create more personalized, measurable, and scalable campaigns that cater to a digital-first audience.
Digital Marketing Syllabus for Beginners
| Module | Topics Covered |
| 1. Building a Strong Foundation | – Creating buyer personas – Conducting market research – Analyzing consumer behavior online – Identifying pain points and needs – Mapping the customer journey – Setting SMART goals – Understanding the Digital Marketing Funnel |
| 2. Website Optimization and SEO | – User-friendly website elements – On-page SEO – Off-page SEO – Technical SEO – Keyword Research – Content Optimization |
| 3. Content Marketing | – Types of Content – Content Strategy – Content Calendar – Topic Ideation – Content Repurposing – Distribution Channels – Measuring Content Success |
| 4. Social Media Marketing | – Understanding major platforms – Creating a Social Media Strategy – Building and Engaging Your Community – Social Media Advertising |
| 5. Email Marketing | – Building Your Email List – Email Campaign Types – Email Design and Copywriting – Email Marketing Metrics |
| 6. Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising | – PPC basics and platforms – Keyword Research for PPC – Creating Effective Ad Copy – Landing Page Optimization – PPC Campaign Management |
| 7. Analytics and Data-Driven Marketing | – Setting up Google Analytics – Key metrics to track – Conversion Tracking – A/B Testing – Data-Driven Decision Making – Affiliate Marketing: • Basics and program selection • Tracking and optimization • Compliance and best practices • Integration with other channels |
Here’s a beginner-friendly digital marketing syllabus to get started on your journey:
1. Building a Strong Foundation
Before diving into specific tactics, it’s crucial to understand who you’re marketing to:
- Creating buyer personas: Develop detailed profiles of your ideal customers, including demographics, psychographics, and behavior patterns.
- Conducting market research: Use surveys, interviews, and online tools to gather data about your target market.
- Analyzing consumer behavior online: Study how your audience interacts with digital platforms, including their preferred channels and content types.
- Identifying pain points and needs: Understand the challenges your audience faces and how your product or service can address them.
- Mapping the customer journey: Outline the steps your audience takes from awareness to purchase and beyond.
You can consider enrolling yourself in GUVI’s Business Analytics and Digital Marketing Course, which lets you gain practical experience by developing real-world projects and covers technologies including Power BI, Excel, SQL, Tableau, Data Visualization, etc.
Setting SMART Goals
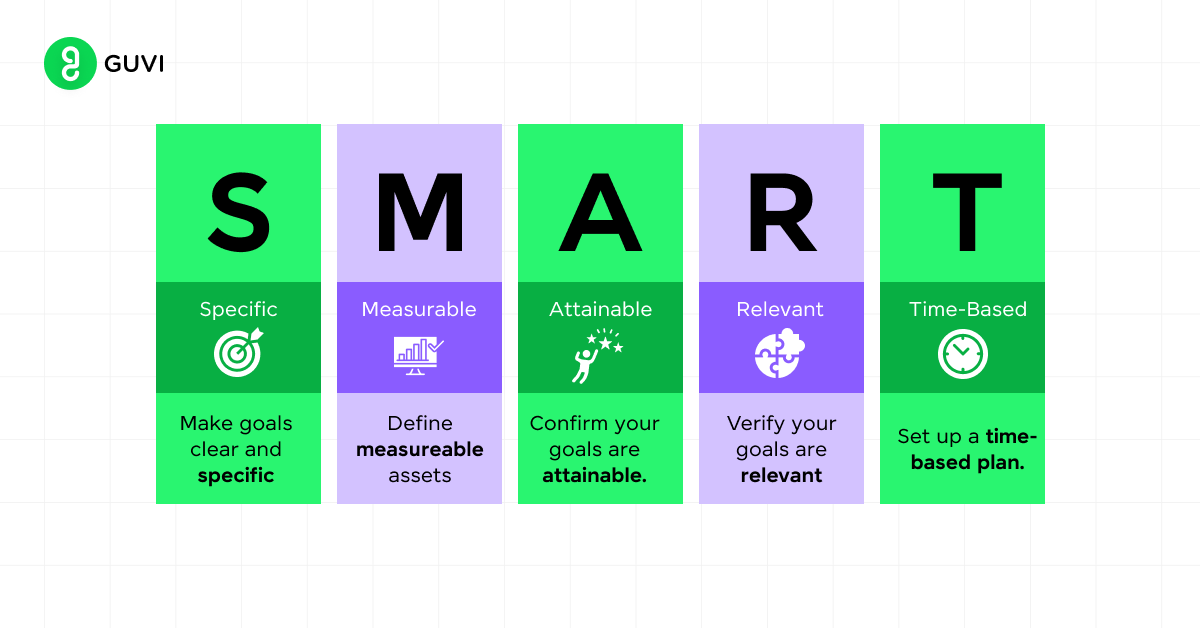
Effective digital marketing starts with clear objectives. Use the SMART framework to set goals that are:
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve (e.g., increase website traffic by 25%).
- Measurable: Ensure you can track progress using metrics and KPIs.
- Achievable: Set realistic goals based on your resources and market conditions.
- Relevant: Align your goals with overall business objectives.
- Time-bound: Set a deadline for achieving your goals.
Examples of SMART digital marketing goals:
- Increase organic search traffic by 30% within the next 6 months.
- Grow email subscriber list by 1000 new subscribers in Q3.
- Achieve a 10% conversion rate on landing pages by the end of the year.
The Digital Marketing Funnel
Understanding the customer journey is key to creating effective marketing strategies. The digital marketing funnel typically consists of the following stages:
- Awareness: Introduce your brand to potential customers.
Tactics: SEO, content marketing, social media advertising.
- Interest: Engage users and provide value to build interest in your offerings.
Tactics: Blog posts, videos, social media content.
- Consideration: Showcase your unique value proposition and differentiate it from competitors.
Tactics: Case studies, product comparisons, digital marketing webinars.
- Intent: Nurture leads who have shown interest in making a purchase.
Tactics: Email marketing, retargeting ads, free trials.
- Evaluation: Provide the information needed for prospects to make an informed decision.
Tactics: Customer reviews, detailed product information, FAQs.
- Purchase: Convert leads into customers.
Tactics: Clear CTAs, streamlined checkout process, abandoned cart emails.
- Loyalty: Retain customers and encourage repeat purchases.
Tactics: Loyalty programs, personalized offers, excellent customer service.
2. Website Optimization and SEO

Your website is often the first point of contact with potential customers. Key elements of a user-friendly website include:
- Responsive design: Ensure your site looks and functions well on all devices (desktop, tablet, mobile).
- Clear navigation: Create an intuitive menu structure and use breadcrumbs for easy navigation.
- Fast loading times: Optimize images, leverage browser caching, and use a content delivery network (CDN) to improve speed.
- Compelling content: Provide valuable, relevant information that addresses user needs and questions.
- Strong calls-to-action (CTAs): Guide users towards desired actions with clear, prominent CTAs.
- Accessibility: Ensure your site is usable by people with disabilities (e.g., alt text for images, keyboard navigation).
- Contact information: Make it easy for visitors to get in touch with you.
- Trust signals: Include customer testimonials, security badges, and privacy policies to build credibility.
SEO
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is crucial for visibility in search results. It encompasses:
- On-page SEO
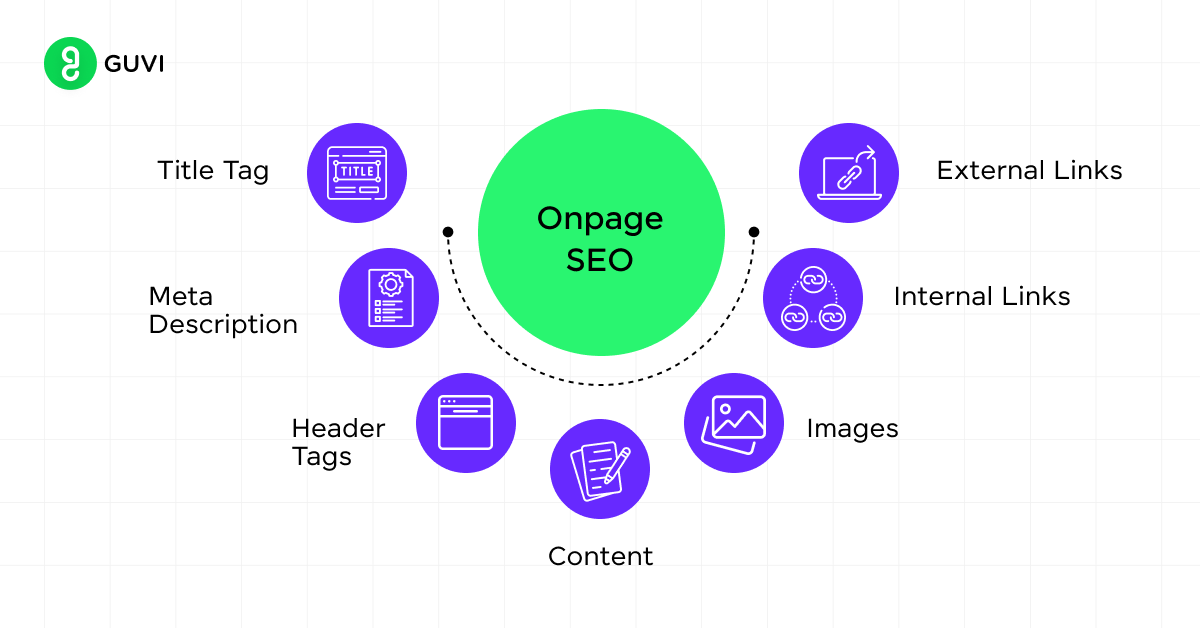
- Title tags: Craft compelling, keyword-rich titles for each page (50-60 characters).
- Meta descriptions: Write concise, appealing summaries of page content (150-160 characters).
- Header tags (H1, H2, H3): Use a logical hierarchy to structure content and include relevant keywords.
- URL structure: Create clean, descriptive URLs that include target keywords.
- Image optimization: Use descriptive file names and alt text for images.
- Off-page SEO
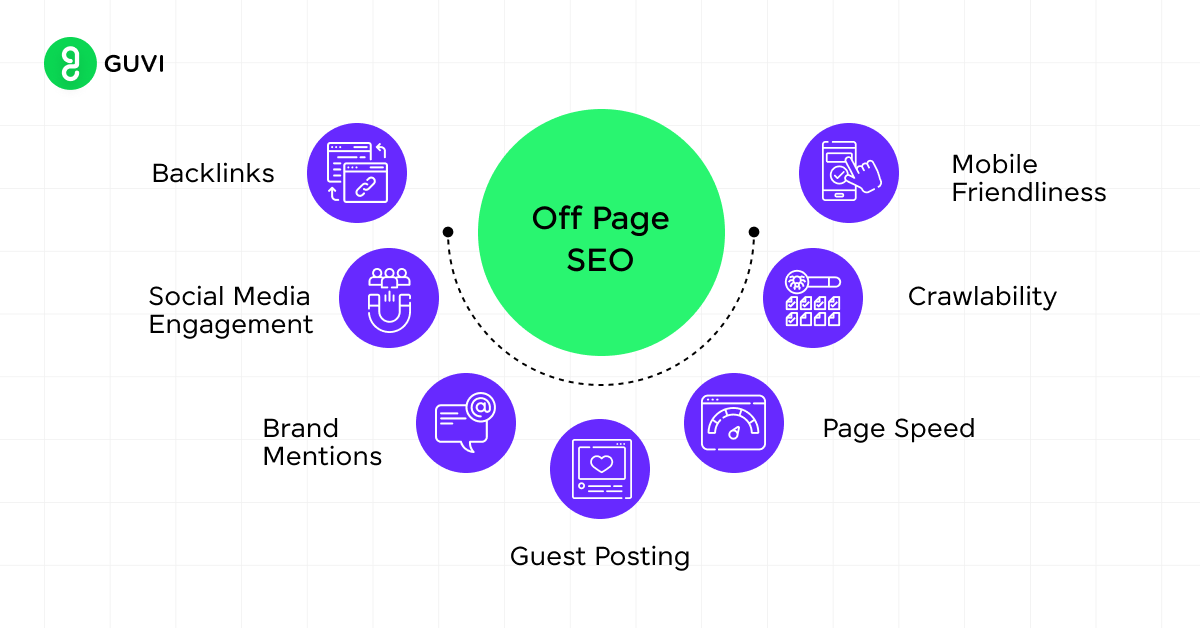
- Backlinks: Earn high-quality, relevant links from reputable websites.
- Social signals: Encourage social sharing and engagement with your content.
- Online directories and citations: Ensure consistent NAP (Name, Address, Phone) information across the web.
- Technical SEO
- Site structure: Create a logical, easy-to-crawl website architecture.
- XML sitemaps: Submit a sitemap to search engines to aid in indexing.
- Robots.txt: Guide search engine crawlers on which pages to index or ignore.
- Page speed: Optimize loading times for better user experience and search rankings.
- Mobile-friendliness: Ensure your site performs well on mobile devices.
- Schema markup: Implement structured data to help search engines understand your content.
Keyword Research
Understanding what your audience is searching for is crucial for effective SEO:
- Long-tail vs. short-tail keywords
- Short-tail: Broader terms with high search volume and competition (e.g., “digital marketing”).
- Long-tail: More specific phrases with lower volume but higher intent (e.g., “beginner digital marketing course online”).
- Keyword intent
- Informational: Users seeking information or answers (e.g., “What is digital marketing”).
- Navigational: Users looking for a specific website or page (e.g., “GUVI digital marketing”).
- Transactional: Users ready to make a purchase or take action (e.g., “buy digital marketing course”).
- Commercial investigation: Users research before making a purchase decision (e.g., “best digital marketing courses”).
- Using keyword research tools
- Google Keyword Planner: Free tool for search volume and competition data.
- SEMrush: Comprehensive tool for keyword research and competitor analysis.
- Ahrefs: Powerful tool for backlink analysis and keyword difficulty assessment.
- Answer the Public: Generates question-based keywords and content ideas.
Content Optimization
Creating content that ranks and engages involves:
- Keyword placement: Naturally incorporate target keywords in titles, headings, first paragraph, and throughout the content.
- Quality and relevance: Produce in-depth, valuable content that addresses user intent and questions.
- User experience: Format content for readability (short paragraphs, bullet points, subheadings).
- Multimedia integration: Enhance content with images, videos, and infographics to increase engagement.
- Internal linking: Connect related content within your site to improve navigation and distribute link equity.
- External linking: Link to reputable sources to provide additional value and context.
- Content freshness: Regularly update and improve existing content to maintain relevance.
- Semantic SEO: Use related terms and concepts to provide comprehensive coverage of a topic.
3. Content Marketing
Content is the fuel that drives digital marketing:
- Building brand awareness: Consistently publishing valuable content helps establish your brand as a thought leader in your industry.
- Establishing authority: High-quality, informative content demonstrates expertise and builds trust with your audience.
- Driving traffic and leads: Well-optimized content attracts organic search traffic and encourages social sharing.
- Supporting other marketing efforts: Content fuels email marketing, social media, and paid advertising campaigns.
- Educating customers: Helpful content can guide prospects through the buyer’s journey and address common questions or objections.
- Fostering community: Engaging content encourages discussion and builds a loyal following around your brand.
Types of Content

Exploring various content formats to diversify your strategy:
- Blog posts: Regular articles on topics relevant to your audience (how-to guides, industry news, etc.).
- Infographics: Visual representations of data or concepts for easy consumption.
- Videos: Engaging visual content (tutorials, product demos, digital marketing interviews, etc.).
- Podcasts: Audio content for on-the-go consumption (industry discussions, interviews, storytelling).
- Ebooks and whitepapers: In-depth, downloadable resources that provide comprehensive information on a topic.
- Case studies: Real-world examples of how your product or service has helped customers.
- Webinars: Live or recorded online presentations or workshops on relevant topics.
- Social media posts: Short-form content tailored to each platform (tweets, LinkedIn articles, Instagram stories).
- User-generated content: Encourage and showcase content created by your customers or community.
Content Strategy
Developing a cohesive content plan:
- Content calendar: Plan and schedule content creation and publication in advance.
- Topic ideation: Use keyword research, customer questions, and industry trends to generate content ideas.
- Content repurposing: Adapt existing content into different formats to maximize reach and efficiency.
- Distribution channels: Identify the best platforms to share your content based on your target audience.
- Content gaps analysis: Identify topics or formats that are missing from your current strategy.
- Competitor analysis: Study successful content from competitors for inspiration and to find opportunities.
- Evergreen vs. timely content: Balance long-lasting, foundational content with timely, trending topics.
- Content promotion: Develop a digital marketing plan to amplify your content through various channels (social media, email, paid advertising).
Measuring Content Success
Key metrics to track the performance of your content marketing efforts:
- Traffic: Monitor overall website traffic and traffic to specific pieces of content.
- Engagement: Measure time on page, bounce rate, comments, and social shares.
- Lead generation: Track how many leads are generated through content (e.g., ebook downloads, webinar sign-ups).
- Conversion rates: Measure the percentage of visitors who take desired actions after consuming your content.
- SEO performance: Monitor keyword rankings and organic search visibility.
- Brand awareness: Track mentions, backlinks, and overall online visibility.
- Customer feedback: Collect and analyze qualitative feedback on your content.
- ROI: Calculate the return on investment for your content marketing efforts.
4. Social Media Marketing
Understanding the major players and their unique characteristics:
- Facebook
- Largest user base with diverse demographics
- Ideal for building community and sharing various content types
- Powerful advertising platform with detailed targeting options
- Instagram
- Visual-centric platform popular among younger audiences
- Great for showcasing products, behind-the-scenes content, and influencer partnerships
- Features like Stories and Reels offer creative ways to engage audiences
- Twitter
- Real-time conversation and news sharing
- Excellent for customer service and engaging with industry trends
- Short-form content and hashtags are key
- LinkedIn
- Professional networking and B2B marketing
- Ideal for thought leadership content and industry insights
- Targeted advertising for professional audiences
- Pinterest
- Visual discovery platform often used for product inspiration and DIY ideas
- Excellent for driving traffic to e-commerce sites
- Long-lasting content potential compared to other platforms
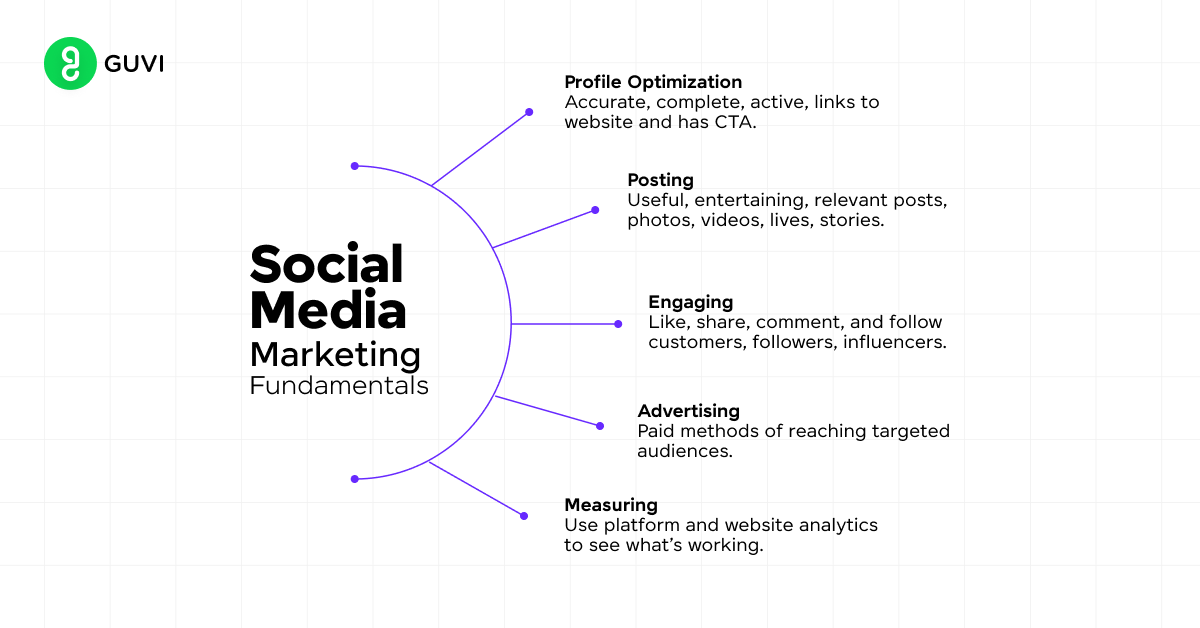
Creating a Social Media Strategy
Developing a plan for social success:
- Setting platform-specific goals: Tailor objectives to each platform’s strengths (e.g., brand awareness on Instagram, lead generation on LinkedIn).
- Defining your brand voice: Establish a consistent tone and personality across platforms while adapting to each platform’s culture.
- Content mix: Balance different types of content:
- Promotional (20%): Showcase products, services, and offers
- Educational (30%): Share industry insights, how-to guides, and tips
- Entertaining (30%): Engage the audience with fun, relatable content
- Curated (20%): Share relevant third-party content to provide value
- Posting frequency and timing: Determine optimal posting schedules for each platform based on audience behavior and platform norms.
- Visual branding: Develop consistent visual elements (color schemes, fonts, image styles) across platforms.
- Hashtag strategy: Research and use relevant hashtags to increase discoverability.
- Influencer collaboration: Identify and partner with influencers who align with your brand values.
- Cross-promotion: Encourage followers to connect with your brand across multiple platforms.
Building and Engaging Your Community
Growing your social presence and fostering meaningful connections:
- Organic growth tactics
- Consistently post high-quality, relevant content
- Engage with followers by responding to comments and messages
- Participate in relevant conversations and communities
- Use platform-specific features (e.g., Instagram Reels, Twitter Spaces)
- Collaborate with other brands or influencers for cross-promotion
- Community management
- Develop guidelines for engaging with followers
- Monitor mentions and tags of your brand
- Address customer service issues promptly and professionally
- Create and moderate branded hashtags
- Host Q&A sessions or live events to interact with your audience
- Responding to comments and messages
- Set response time goals (e.g., within 24 hours)
- Personalize responses when possible
- Use a friendly, approachable tone
- Address negative feedback constructively and take conversations private when necessary
- User-generated content
- Encourage customers to share their experiences with your brand
- Create branded hashtags for UGC campaigns
- Feature UGC on your profiles and website (with permission)
- Run contests or challenges to incentivize content creation
Social Media Advertising
Leveraging paid social for greater reach and targeted results:
- Ad formats across platforms
- Facebook/Instagram: Image ads, video ads, carousel ads, stories ads, collection ads
- Twitter: Promoted tweets, follower ads, Twitter Amplify
- LinkedIn: Sponsored content, sponsored InMail, text ads
- TikTok: In-feed ads, branded hashtag challenges, branded effects
- Targeting options
- Demographics: Age, gender, location, education, job title
- Interests and behaviors: Hobbies, purchase behavior, device usage
- Custom audiences: Retarget website visitors, email subscribers, or customer lists
- Lookalike audiences: Reach new users similar to your existing customers
- Budget allocation
- Start small and scale based on performance
- Allocate budget across platforms based on your target audience and goals
- Consider seasonal social media trends and peak times for your industry
- A/B testing
- Test different ad elements: Headlines, images, videos, ad copy, CTAs
- Experiment with various targeting options and audience segments
- Compare the performance of different ad formats
- Use platform-specific tools (e.g., Facebook’s A/B testing feature) for controlled experiments
- Performance measurement
- Track key metrics: Click-through rate (CTR), cost per click (CPC), conversion rate, return on ad spend (ROAS)
- Use platform analytics tools and integrate with Google Analytics for comprehensive reporting
- Regularly review and optimize campaigns based on performance data
5. Email Marketing
Understanding why email remains a powerful marketing tool:
- Direct communication: Reach your audience directly in their inbox
- Personalization capabilities: Tailor content to individual subscribers’ preferences and behaviors
- Cost-effectiveness: High ROI compared to many other marketing channels
- Ownership of the channel: Unlike social media, you own your email list
- Versatility: Suitable for various purposes (newsletters, promotions, transactional emails)
- Automation potential: Set up triggered emails based on user actions or time intervals
- Measurability: Track opens, clicks, conversions, and other key metrics
Building Your Email List
Ethically growing your subscriber base:
- Lead magnets: Offer valuable content (e.g., ebooks, webinars, discount codes) in exchange for email addresses
- Sign-up forms: Place strategically on your website (homepage, blog, footer)
- Landing pages: Create dedicated pages for specific offers or campaigns
- Double opt-in process: Ensure subscribers confirm their email address to maintain list quality
- Social media integration: Promote your email list and offers on social platforms
- Offline collection: Gather emails at events or in-store with proper consent
- Referral programs: Encourage existing subscribers to refer friends
- Content upgrades: Offer additional, related content within blog posts in exchange for emails
Email Campaign Types
Different emails for different purposes:
- Welcome series: Introduce new subscribers to your brand and set expectations
- Newsletters: Regular updates with company news, industry insights, and valuable content
- Promotional emails: Announce sales, new products, or special offers
- Automated sequences
- Drip campaigns: Nurture leads with a series of pre-planned emails
- Abandoned cart reminders: Encourage users to complete their purchase
- Re-engagement campaigns: Win back inactive subscribers
- Transactional emails: Order confirmations, shipping notifications, password resets
- Event invitations: Promote webinars, workshops, or in-person events
- Seasonal campaigns: Holiday promotions or industry-specific seasonal content
- Milestone emails: Celebrate subscriber anniversaries or birthdays
Email Design and Copywriting
Crafting emails that convert:
- Subject lines that grab attention
- Keep it concise (40-50 characters)
- Create urgency or curiosity
- Use personalization when appropriate
- A/B test different subject lines
- Compelling copy
- Focus on benefits rather than features
- Use a conversational tone
- Keep paragraphs short and scannable
- Include social proof (testimonials, reviews)
- Clear call-to-actions (CTAs)
- Use action-oriented language
- Make CTAs prominent and easy to click
- Limit the number of CTAs per email
- Consider using buttons for primary CTAs
- Mobile-responsive design
- Use a single-column layout for easy mobile reading
- Ensure text is large enough to read on small screens
- Make CTAs touch-friendly (minimum 44×44 pixels)
- Test emails on various devices and email clients
- Visual elements
- Use high-quality, relevant images
- Maintain a consistent brand aesthetic
- Consider using GIFs or videos to increase engagement
- Ensure proper image-to-text ratio to avoid spam filters
Email Marketing Metrics
Measuring the success of your campaigns:
- Open rates: Percentage of recipients who open your email
- Benchmark: 15-25% is considered good for most industries
- Improve by optimizing subject lines and sending times
- Click-through rates (CTR): Percentage of recipients who click on a link in your email
- Benchmark: 2-5% is average across industries
- Improve with compelling CTAs and relevant content
- Conversion rates: Percentage of recipients who complete a desired action (e.g., make a purchase, fill out a form)
- Benchmark varies by industry and campaign type
- Improve by aligning email content with landing pages and optimizing the user journey
- Bounce rates: Percentage of emails that weren’t delivered
- Soft bounces: Temporary issues (full inbox, server down)
- Hard bounces: Permanent issues (invalid email address)
- Keep bounce rates under 2% to maintain good sender reputation
- Unsubscribe rates: Percentage of recipients who opt out of your emails
- Benchmark: Keep under 0.5% per campaign
- High unsubscribe rates may indicate irrelevant content or too frequent sending
- List growth rate: Net growth of your email list over time
- Calculate: (New subscribers – Unsubscribes) / Total subscribers
- Aim for steady, organic growth
- Email forwarding rate: How often your emails are shared
- Indicates highly engaging content
- Encourage sharing with “Forward to a Friend” links
- Overall ROI: Revenue generated compared to the cost of your email marketing efforts
- Calculate: (Revenue from email – Cost of email marketing) / Cost of email marketing
- Email marketing typically has a high ROI compared to other channels
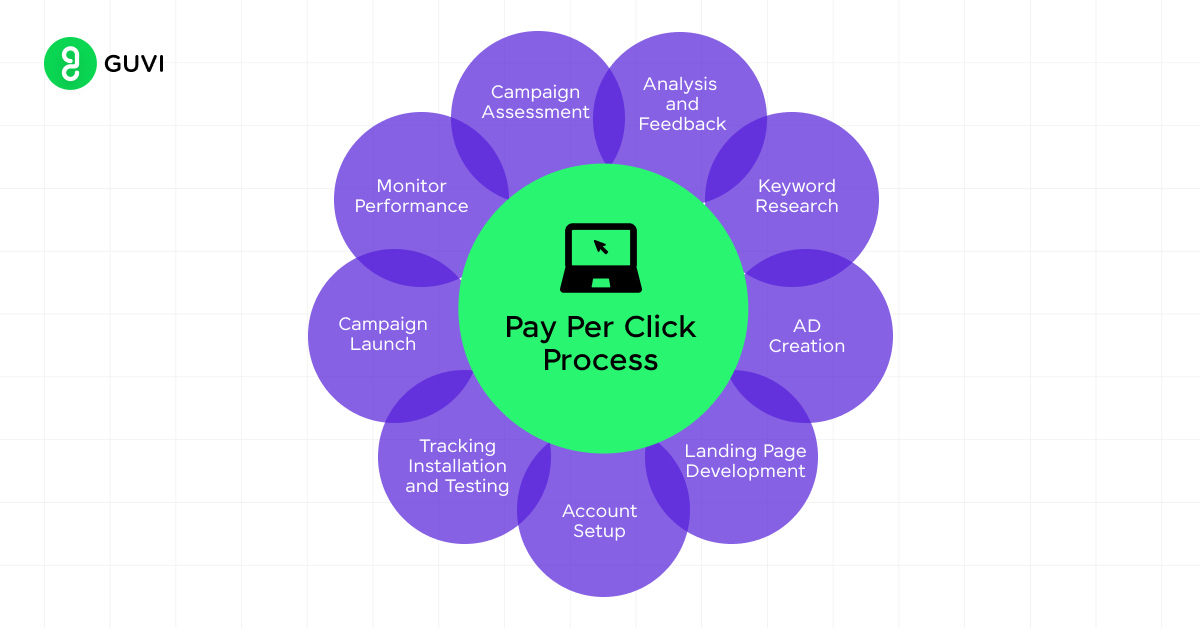
6. Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising
Understanding the basics of paid search:
- How PPC works: Advertisers bid on keywords and pay when their ad is clicked
- Major platforms
- Google Ads: Largest PPC platform, includes Search, Display, and Video ads
- Bing Ads: Smaller audience but often less competition
- Social media platforms: Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Twitter offer PPC options
- The auction system
- Ad Rank: Determined by bid amount and quality score
- Quality Score: Based on ad relevance, expected CTR, and landing page experience
Keyword Research for PPC
Selecting the right keywords for your campaigns:
- Search volume: Balance between high volume and relevance
- Competition: Consider bidding on less competitive long-tail keywords
- Cost-per-click (CPC): Estimate potential costs and ROI
- Keyword match types
- Broad match: Widest reach, but less targeted
- Phrase match: Ads show for searches that include your keyword phrase
- Exact match: Most targeted, but limited reach
- Negative keywords: Exclude irrelevant searches to improve ad relevance and reduce wasted spend
Creating Effective Ad Copy
Writing ads that drive clicks:
- Headline best practices
- Include primary keyword
- Highlight unique selling propositions
- Create urgency or offer solutions
- Description line tips
- Focus on benefits and features
- Include a clear call-to-action
- Use power words to evoke emotion
- Using ad extensions
- Sitelink extensions: Additional links to relevant pages
- Callout extensions: Highlight key features or offers
- Structured snippet extensions: Showcase specific aspects of your products or services
- Location extensions: Display your business address
- Call extensions: Add a phone number to your ad
Landing Page Optimization
Ensuring your ads lead to conversions:
- Relevance to ad copy: Maintain consistency between ad and landing page messaging
- Clear value proposition: Communicate benefits clearly above the fold
- Strong CTAs: Use action-oriented buttons that stand out
- A/B testing: Continuously test and improve landing page elements
- Mobile optimization: Ensure a seamless experience on all devices
- Page load speed: Optimize images and code for fast loading
- Trust signals: Include testimonials, reviews, or security badges
- Minimal distractions: Focus the page on the primary conversion goal
PPC Campaign Management
Ongoing optimization for better results:
- Budget management
- Set daily or lifetime budgets
- Allocate budget based on campaign performance
- Use automated bidding strategies when appropriate
- Bid adjustments
- Adjust bids based on device, location, time of day, or audience
- Use bid modifiers to increase or decrease bids for specific scenarios
- Ad scheduling
- Show ads during peak performance times
- Adjust bids during high-converting hours
- Device targeting
- Optimize campaigns for desktop, mobile, and tablet users
- Create device-specific ads and landing pages
- Geographic targeting
- Focus on locations that drive the most conversions
- Use location bid adjustments to optimize spend
- Audience targeting
- Utilize remarketing lists for search ads (RLSA)
- Create custom audiences based on website behavior or customer data
- Regular account audits
- Review account structure and campaign settings
- Identify and pause underperforming keywords or ads
- Look for new keyword opportunities
- Conversion tracking
- Set up proper tracking for all conversion actions
- Use cross-device conversion tracking when possible
- Attribute conversions accurately (e.g., first-click vs. last-click)
7. Analytics and Data-Driven Marketing
Understanding the importance of data:
- Setting up Google Analytics
- Create a Google Analytics account
- Install tracking code on your website
- Set up views and filters for clean data
- Key metrics to track
- Traffic: Users, sessions, pageviews
- Engagement: Bounce rate, time on site, pages per session
- Conversions: Goal completions, e-commerce transactions
- Acquisition: Traffic sources, channels, campaigns
- Creating custom reports
- Combine relevant metrics and dimensions
- Use segments to analyze specific user groups
- Set up automated email reports for stakeholders
Conversion Tracking
Measuring the actions that matter:
- Setting up goals in Google Analytics
- Destination goals: Reaching a specific page (e.g., thank you page)
- Duration goals: Sessions lasting a minimum amount of time
- Pages/screens per session goals: Viewing a minimum number of pages
- Event goals: Specific interactions (e.g., video plays, form submissions)
- Tracking e-commerce transactions
- Implement e-commerce tracking code
- Monitor product performance, average order value, and revenue
- Attribution modeling
- Last-click attribution: Gives credit to the final touchpoint
- First-click attribution: Gives credit to the initial touchpoint
- Linear attribution: Distributes credit evenly across all touchpoints
- Time decay: Gives more credit to touchpoints closer to conversion
- Data-driven attribution: Uses machine learning to determine credit
A/B Testing
Continuously improving your marketing efforts:
- What to test
- Headlines and copy
- CTAs (text, color, placement)
- Images and videos
- Page layouts
- Pricing and offers
- Tools for A/B testing
- Google Optimize: Free tool integrated with Google Analytics
- Optimizely: Enterprise-level experimentation platform
- VWO: Visual Website Optimizer for website and mobile app testing
- Interpreting test results
- Statistical significance: Ensure results are not due to chance
- Sample size: Run tests long enough to gather sufficient data
- Segmentation: Analyze results for different user groups
- Secondary metrics: Consider the impact on related metrics
Data-Driven Decision Making
Using insights to inform strategy:
- Identifying trends and patterns
- Use historical data to predict future performance
- Look for seasonal trends or recurring patterns
- Monitor industry benchmarks and competitor performance
- Segmenting your audience
- Create segments based on demographics, behavior, or value
- Analyze how different segments interact with your marketing efforts
- Tailor strategies to each segment’s preferences and needs
- Personalizing marketing efforts
- Use data to create targeted content and offers
- Implement dynamic website content based on user behavior
- Develop personalized email campaigns using subscriber data
- Predictive analytics
- Use machine learning to forecast future outcomes
- Identify high-value customers or those at risk of churning
- Optimize marketing spend based on predicted ROI
8. Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing is a performance-based strategy where affiliates promote products or services in exchange for commissions. It benefits businesses by increasing visibility and sales, while affiliates can earn passive income through successful referrals.
- Choosing Affiliate Programs
When selecting an affiliate program, evaluate its quality and relevance to your audience. Consider different commission structures, such as cost per acquisition (CPA), cost per click (CPC), or revenue share, to determine the best fit for your goals.
- Tracking Affiliate Performance
Using affiliate tracking software and implementing tracking links and cookies is essential to monitor performance. These tools help measure sales, leads, and overall engagement from affiliate referrals.
- Optimizing Affiliate Campaigns
To maximize success, provide affiliates with resources like creatives and detailed product information. Setting up performance incentives can further motivate affiliates to drive more conversions.
- Compliance and Best Practices
Ensure compliance with FTC disclosure guidelines to maintain transparency. Protect your brand by avoiding fraud and managing affiliates carefully.
- Integrating Affiliate Data with Other Marketing Channels
Incorporate affiliate insights into your overall marketing strategy. Cross-channel attribution can help understand how affiliate marketing influences other channels and improve campaign effectiveness.
Emerging Trends in Digital Marketing
Preparing for the rise of voice-activated devices:
- Long-tail keyword optimization: Focus on natural language phrases
- Featured snippets: Optimize content to appear in “position zero”
- Local SEO for voice search: Ensure NAP consistency and optimize for “near me” searches
- Conversational content: Create content that answers specific questions
- Structured data markup: Implement schema to help search engines understand your content
Artificial Intelligence in Marketing
Leveraging AI for better results:
- Chatbots for customer service: Provide 24/7 support and instant responses
- Predictive analytics: Forecast customer behavior and optimize digital marketing strategies
- Personalized recommendations: Use AI to suggest relevant products or content
- Ad optimization: Automatically adjust bids and targeting for best performance
- Content creation: Use AI tools to generate or optimize marketing copy
Video Marketing
Capitalizing on the growing popularity of video:
- Live streaming: Engage with audiences in real-time on platforms like Facebook Live, Instagram Live, or YouTube Live
- Short-form video: Create engaging content for platforms like Instagram Reels, and YouTube Shorts
- Video SEO: Optimize video titles, descriptions, and tags for search engines
- Interactive videos: Use shoppable videos or interactive elements to boost engagement
- Video advertising: Leverage pre-roll, mid-roll, and post-roll ad placements
Influencer Marketing
Partnering with influencers to extend reach:
- Identifying relevant influencers: Use tools to find influencers in your niche
- Micro-influencers vs. macro-influencers: Consider working with niche influencers for higher engagement
- Negotiating partnerships: Develop mutually beneficial relationships with influencers
- FTC compliance: Ensure proper disclosure of sponsored content
- Measuring influencer campaign success: Track engagement, reach, and conversions attributed to influencer partnerships
Developing a Comprehensive Digital Marketing Strategy
Creating a cohesive online presence:
- Cross-channel consistency: Maintain consistent messaging and branding across all platforms
- Leveraging each channel’s strengths: Use each platform for its unique advantages
- Omnichannel marketing approach: Provide a seamless experience across all touchpoints
- Customer journey mapping: Understand how different channels contribute to the overall customer experience
- Cross-promotion: Use one channel to drive traffic and engagement on others
Budgeting and Resource Allocation
Making the most of your marketing budget:
- Determining your digital marketing budget: Consider industry benchmarks and business goals
- Allocating resources across channels: Distribute budget based on performance and strategic priorities
- ROI-based decision-making: Invest more in channels and tactics with proven returns
- Testing and experimentation budget: Set aside funds for trying new strategies and platforms
- Scaling successful campaigns: Be prepared to increase spend on high-performing initiatives
Creating a Digital Marketing Calendar
Planning for success:
- Seasonal campaigns: Align marketing efforts with holidays and industry-specific seasons
- Product launches: Coordinate marketing activities to support new product releases
- Content publication schedule: Plan and organize content creation and distribution
- Social media posting calendar: Maintain a consistent presence across social platforms
- Email marketing timeline: Schedule regular newsletters and promotional campaigns
- Advertising flight dates: Plan start and end dates for paid advertising campaigns
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Staying ahead in the ever-evolving digital landscape:
- Following industry blogs and thought leaders: Stay informed about the latest trends and best practices in digital marketing
- Attending webinars and conferences: Gain insights from experts and network with other professionals
- Experimenting with new platforms and tactics: Be an early adopter of emerging technologies and strategies
- Online courses and certifications: Invest in ongoing education to deepen your skills
- Analyzing competitors: Stay aware of what others in your industry are doing
- Subscribing to industry newsletters: Receive regular updates on digital marketing trends
- Joining professional groups: Participate in discussions and share knowledge with peers
- Testing and iterating: Continuously refine your strategies based on performance data
- Staying updated on platform changes: Keep abreast of updates to major platforms like Google, Facebook, and LinkedIn
Kickstart your career by enrolling in GUVI’s Business Analytics and Digital Marketing Course where you will master technologies including Power BI, Excel, SQL, Tableau, and Data Visualization, and build interesting real-life business-analytics projects.
Conclusion
As you continue your learning journey, consider exploring specific areas that interest you most or align closely with your goals. You might find that you have a particular affinity for content creation, data analysis, or perhaps the creative aspects of social media marketing.
Lastly, always keep the end user in mind. At the heart of all these strategies and tactics is the goal of providing value to your audience and solving their problems. By maintaining this customer-centric approach, you’ll be well on your way to digital marketing success.
FAQs
What is covered in a beginner’s digital marketing syllabus?
A beginner’s syllabus typically includes SEO, social media marketing, email marketing, content marketing, Google Ads, and analytics basics.
How long does it take to complete a digital marketing course for beginners?
Most beginner courses take 6-12 weeks, depending on the intensity and depth of the course.
Do I need any prior experience to start learning digital marketing?
No prior experience is required. Beginner courses are designed to teach you the fundamentals from scratch.
Will I learn how to run ads on social media platforms?
Yes, social media advertising, including platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn, is a key part of most beginner syllabi.
Is SEO included in the digital marketing syllabus for beginners?
Absolutely! SEO is a crucial part of any digital marketing course and is usually one of the first modules covered.




























Did you enjoy this article?