What Are the Different Roles in a Product-Based Company?
Oct 03, 2024 5 Min Read 3489 Views
(Last Updated)
As we go about our daily routines, we interact with different products that have become integral to our lives. From our smartphones to the cars we drive, these products result from the hard work and dedication of product-based companies. But what exactly goes into making these products a reality?
It’s not just about innovation and technology but also the different roles in a product-based company that works tirelessly to bring these products to fruition. Let’s explore.
Table of contents
- What is a Product-based Company?
- Understanding the Different Roles in a Product-based Company
- What is a Product Team?
- Steering the Vision: Product Management
- Creating the User Experience: Product Design
- Building the Product: Product Development
- Bringing the Product to the Market: Product Marketing
- Helping the Customers: Customer Support
- Operational Backbone: Product Operations
- Leveraging Data for Insights: Data Scientists and Analysts
- Pioneering Future Innovations: Research and Development
- Ensuring Product Delivery: eCommerce
- Overseeing Economic and Lawful Aspects: Finance and Legal
- Conclusion
- Frequently asked questions
- What legal challenges do product companies face, and how do they address them?
- How do product companies balance between innovation and established products?
- How will AI and automation change the demands of product companies?
What is a Product-based Company?

Contrary to service-based businesses, product-based companies focus on creating, refining, and distributing tangible or intangible goods with a clear value proposition that can resonate with millions of customers.
These initiatives, however, are seen as riskier due to heavy investments in research, design, prototyping, testing, and marketing. Yet, companies like Apple, Tesla, and Netflix have transformed how we live, work, and play by taking bold forays into the market.
Creating these products requires a complex network of professionals, each playing a unique role. These roles include business leaders who envision the roadmap, product managers who navigate the journey, marketers who entice the masses, and engineers who lay the bricks and mortar. Together, they form the nucleus of action in a product-based company, where ideas grow and are nurtured to completion.
Understanding the Different Roles in a Product-based Company
In a product-based company, each role is like a thread in a tapestry, adding its own unique shade and texture. It’s the combination of these roles and their collaboration that creates a great product.
Let’s explore all the different roles in a product-based company:
What is a Product Team?

The product team is the beating heart of a product-based company where ideas are turned into reality. They are a collective of business leaders, product managers, marketers, and engineers who work together to create products that are not just tangible objects but experiences.
The modern product team is a confluence of diverse skills where technology meets aesthetics and market trends meet innovative solutions. They set trends rather than follow them by fusing user-centric designs, technologically feasible strategies, and business-viable solutions.
The success of a product-based company depends on the weight and responsibility each role in the product team carries to achieve the vision.
Steering the Vision: Product Management
At the top of the funnel is product management, which isn’t just about managing the product but also guiding the vision of the company.
The primary roles in product management include:
Product Manager (PM)

In a product-based company, the product manager is equal parts an administrator, a visionary, a strategist, a communicator, and, more often than not, the beating heart of the company.
The product manager navigates through the turbulent waters of market trends, customer feedback, and organizational objectives. Their role is to shape these disparate elements into one cohesive product strategy.
Every decision product managers make, from the color of a button to the launch of a new feature, bears their imprint. They act as a bridge between what’s ideal and what’s feasible, ensuring that a product not only shines in a boardroom presentation but also thrives in the real world.
Product Owner (PO)
Often misconstrued as interchangeable with the product manager, the product owner (or PO) is a distinct entity. Operating predominantly in agile environments, the product owner is the custodian of the product backlog.
Product owners prioritize, refine, and ensure the development team has clarity on what needs to be built. While the product managers might be looking at the broader horizon, the product owner is zoomed in, ensuring every sprint, every iteration moves the product closer to perfection.
Creating the User Experience: Product Design

Beyond marketing and branding lies user experience, which genuinely decides the fate of a product. Let’s explore the roles that fall under product design.
UX Designer
The product designer or UX designer is the architect of experiences. They don’t just craft interfaces; they shape user journeys.
Their canvas? Every interaction, every touchpoint a user has with the product.
By fusing empathy with creativity, they anticipate user needs, eliminating friction and sculpting experiences that are intuitive and delightful. Their tools aren’t just colors and graphics; it’s a deep understanding of human behavior.
UI Designer
While the UX Designer plots the journey, the UI Designer colors the scenery. They’re the visual artists of the product world, painting pixels to create interfaces that are not just functional but aesthetically mesmerizing.
Every gradient, every icon, and every animation bears their signature touch. But their role isn’t just about beauty; it’s about communicating the product’s essence through visual language.
Building the Product: Product Development

Ideas, no matter how powerful, remain ethereal until given form. Product development is the department of engineers who translate visions into tangible realities.
The prominent roles in product development include:
Product Engineer
Call them product developers or product engineers; they are critical to the development of any product.
Through lines of code, frameworks, and algorithms, they build the edifice of the product. It’s a role of precision, innovation, and relentless problem-solving.
QA Engineer
Once the product is developed comes the phase of testing. QA testers or QA engineers are the gatekeepers of quality. Their role is of meticulous scrutiny, always on the lookout for the slightest glitch or anomaly.
They poke, prod, and push the product to its limits, ensuring that when it reaches the user, it’s not just functional but flawless.
Bringing the Product to the Market: Product Marketing
The completion of the product leads to a more significantly challenging journey – introducing the product to its target audience and ensuring its success by all means.
The key roles that fall under product marketing include:
Sales and Business Development
The sales and business development teams are always at the forefront of business. They are not just selling a product; they are narrating its story and potential.
With a mixture of charisma, strategy, and insight, they find opportunities, forge partnerships, and open doors that were previously closed. Their goal is not just revenue but creating resonance in the market.
Marketing Manager
The sales team speaks directly to customers, while the marketing manager communicates to a larger audience. They create the story, develop the brand, and amplify the product’s voice in the crowded market.
With campaigns, content, and creative efforts, they make sure that the product not only reaches its target audience but also captivates them.
Helping the Customers: Customer Support
Selling a product is half the battle. The real test lies in post-sale engagement, ensuring the user’s journey with the product is smooth, enriching, and long-lasting.
The support team, as a result, plays a critical role.
Customer Support
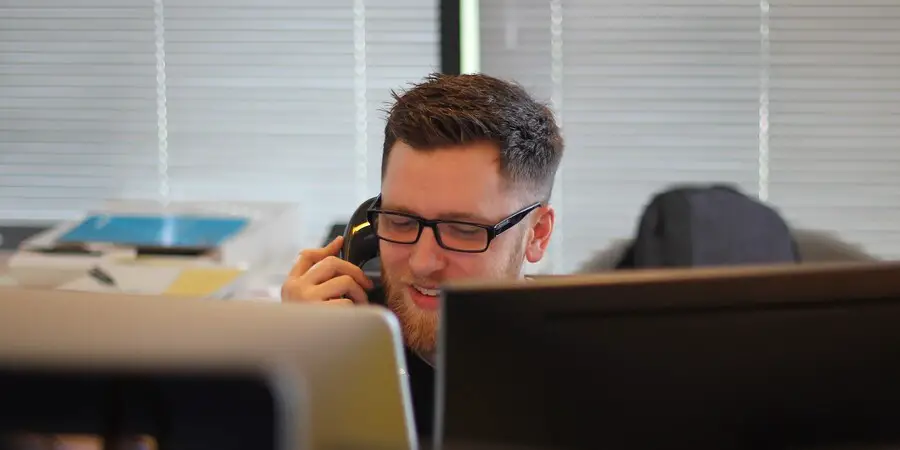

They are the champions of post-sale engagement and, frankly, the unsung heroes of a product-based company. They’re the empathetic ears, the problem solvers, ensuring that every hiccup, every query of the user, is addressed with care and precision.
Their metric isn’t just problem resolution; it’s customer delight. Any product-based company that has a robust customer support system is bound to be victorious.
Operational Backbone: Product Operations
While not always in the limelight, product operations or product ops team is the silent engine that takes a product-based company forward. The key role in this department includes:
Product Operations Manager
A product operations manager helps in providing a stable platform for creating product masterpieces. They ensure that resources are allocated, processes are streamlined, and every cog in the machine functions harmoniously.
From logistics to administration, they’re the caretakers of maximum efficiency.
Leveraging Data for Insights: Data Scientists and Analysts
In this digital age, products generate a goldmine of data. But raw data is like uncut diamonds; its true value emerges only when processed and analyzed by skilled data scientists and analysts.
Data Scientist
Data scientists dive into vast oceans of data, extracting actionable insights. They use algorithms to identify patterns and provide a compass for future product strategies.
Their role is a perfect blend of art and science, where they translate numbers into narratives that everyone can easily understand.
Data Analyst
Complementing the data scientists, the data analysts fine-tune data comprehension.
They dissect metrics, generate reports, and ensure that every stakeholder, from the CEO to the Product Manager, has a clear, quantifiable pulse on the product’s performance.
Pioneering Future Innovations: Research and Development
A product-based company’s growth isn’t just linear; it’s evolutionary. To evolve, one must innovate, which leads us to the visionary arm of a business: the research and development team.
Researcher and Developer (R&D)
The role of the research and development team is not limited to just thinking about the next version of the product but constantly envisioning its next revolution.
Through experiments, prototypes, and relentless curiosity, they chart the course for the product’s future.
Ensuring Product Delivery: eCommerce
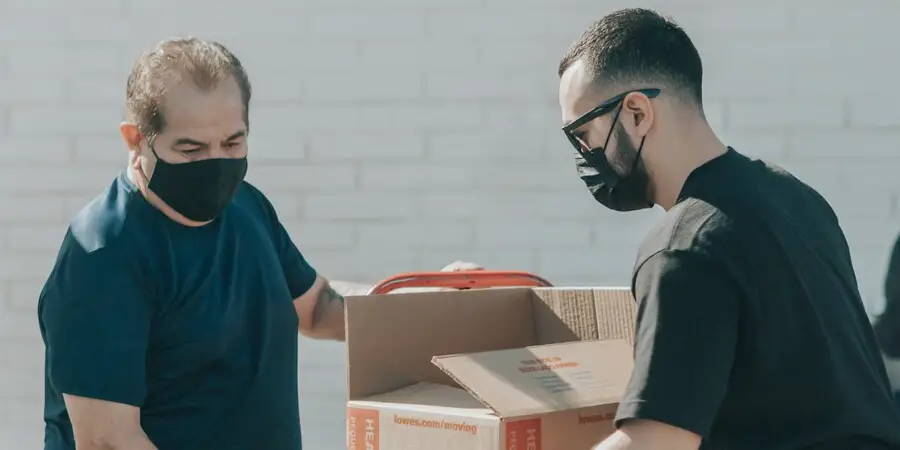

The last leg of a product’s journey provided it is tangible, lies in its smooth delivery. It has to reach the consumer, and this delivery is a mammoth task in itself. And this is where the eCommerce team comes to the rescue.
The top roles in the eCommerce division of a product-based company include:
Supply Chain Manager
Supply chain managers oversee and manage the entire supply chain, from sourcing to final delivery. They ensure efficient operations, reduce costs, and optimize the flow of products to guarantee timely delivery to consumers.
Logistics Coordinator
Logistics coordinators handle the intricacies of shipment, working with carriers and ensuring products are delivered in the stipulated time frame. They track shipments and resolve any issues related to transportation or customs.
Inventory Specialist
Warehouse or inventory specialists monitor stock levels, forecast demand, and ensure the right products are available for shipment. Their role is crucial in preventing stockouts and overstock scenarios balancing inventory with sales demands.
Overseeing Economic and Lawful Aspects: Finance and Legal
Navigating the complicated landscape of finance and legalities is crucial for ensuring a product’s success in the market. The top roles for finance and legal teams include:
Financial Analyst
These professionals scrutinize financial data, discerning trends and proposing actionable insights to augment the company’s fiscal decisions, strengthening profitability and growth.
Accountant
Equipped with the meticulous task of ensuring every financial transaction is accurately recorded and reconciled, accountants play an instrumental role in maintaining fiscal transparency and integrity.
Intellectual Property (IP) Attorney
Guiding the realms of patents, trademarks, and copyrights, the IP Attorney safeguards the company’s innovative assets, ensuring they remain protected from potential infringements and unauthorized use.
Contract Manager
Contract managers delve into the creation, review, and administration of contracts with partners, vendors, and customers. They ensure that agreements are fair, transparent, and enforceable, mitigating risks and potential disputes.
Conclusion
The different roles in a product-based company form a cohesive network where a diverse range of professionals come together to transform ideas into tangible realities.
From a visionary product manager steering the company’s course to careful QA engineers ensuring flawless execution, each role is indispensable.
In your quest to explore the different roles in a product-based company, remember that each role contributes to the success of the whole, creating products that not only meet customers’ needs but also shape how we live and interact with the world.
Frequently asked questions
What legal challenges do product companies face, and how do they address them?
Legal teams address intellectual property, contracts, compliance, and regulatory challenges, safeguarding the company’s interests and innovation.
How do product companies balance between innovation and established products?
Product-based companies often maintain a balance by investing in research and development to innovate while continuing to support and improve existing products to meet customer needs.
How will AI and automation change the demands of product companies?
The future of different roles in product-based companies may involve greater integration of AI for tasks like data analysis, process optimization, and even product development, leading to increased efficiency and innovation.





























Did you enjoy this article?