
In the digital age, data collection is the cornerstone of informed decision-making, enabling organizations to harness the power of information to strategize, innovate, and personalize their services. As you understand this critical process, it’s important to recognize its role in enhancing data quality, guiding business intelligence, and fostering an environment of continuous improvement.
Data collection isn’t just about gathering information; it’s about doing it so effectively and ethically that the relevance, accuracy, and timeliness of the data collected is ensured.
This article will help you explore the depth of data collection, from its fundamental concepts to the intricate methods and types of data collection utilized across different sectors.
Table of contents
- What is Data Collection?
- The Importance of Data Collection
- 1) Improves Decision Making
- 2) Enhances Customer Understanding
- 3) Aids in Operational Efficiency
- Types of Data Collection Methods
- 1) Quantitative Methods
- 2) Qualitative Methods
- 3) Mixed Methods
- Key Steps in the Data Collection Process
- Step 1: Defining the Goal
- Step 2: Choosing Methods
- Step 3: Planning Procedures
- Step 4: Collecting Data
- Step 5: Cleaning and Organizing
- Common Challenges in Data Collection
- 1) Data Quality Issues
- 2) Incomplete Data
- 3) Choosing the Right Data
- 4) Low Response Rates
- Concluding Thoughts...
- FAQs
- What is data collection in definition?
- Why is data collected?
- What are the four types of data collection?
- What is data in simple words?
What is Data Collection?
Data collection is the systematic process of gathering information from various sources to gain insights and make informed decisions. It involves different methodologies like surveys, interviews, observations, and automated data logging, depending on the nature of the data and the desired outcome.
For instance, in healthcare, sensors and wearable devices collect real-time patient data to monitor vital signs, enabling timely interventions.
In the business sector, web analytics tools track user behavior on websites, providing valuable insights into consumer preferences and market trends. Effective data collection is crucial for accurate analysis, driving strategic decisions, and fostering innovation across various fields.
The Importance of Data Collection
Data collection is a pivotal function in today’s data-driven landscape, where making informed decisions is crucial for business success.
By gathering and analyzing relevant data, organizations can significantly enhance their decision-making processes, understand customer behaviors and preferences, and improve operational efficiency.
1) Improves Decision Making
Data collection empowers businesses to make decisions that are not just based on intuition but on solid, data-driven insights.
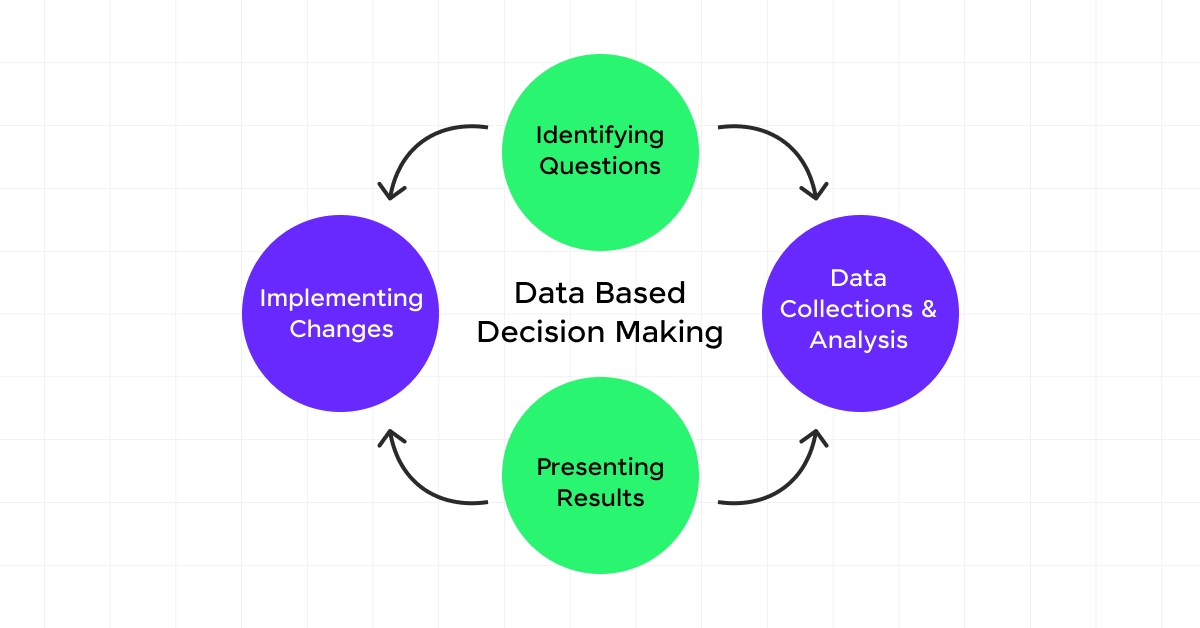
For instance, business analytics and big data can forecast customer behavior trends, market changes, and price fluctuations, aiding organizations in adapting to competitive environments effectively.
This predictive analysis is crucial for achieving a perfect product-market fit, thereby improving decision-making at every organizational level.
2) Enhances Customer Understanding
Understanding your customers’ needs and behaviors is essential for tailoring products and services that meet their expectations.
Data collection methods, such as analyzing purchase histories and customer feedback, provide actionable insights into consumer behavior, preferences, and trends.
This data-driven approach not only boosts customer engagement but also enhances retention, giving businesses a competitive edge in the market.
3) Aids in Operational Efficiency
Operational efficiency is about maximizing productivity and reducing waste, and data collection plays a critical role in achieving these objectives.
By analyzing data from various sources, such as customer feedback and sales reports, companies can identify inefficiencies and optimize processes.
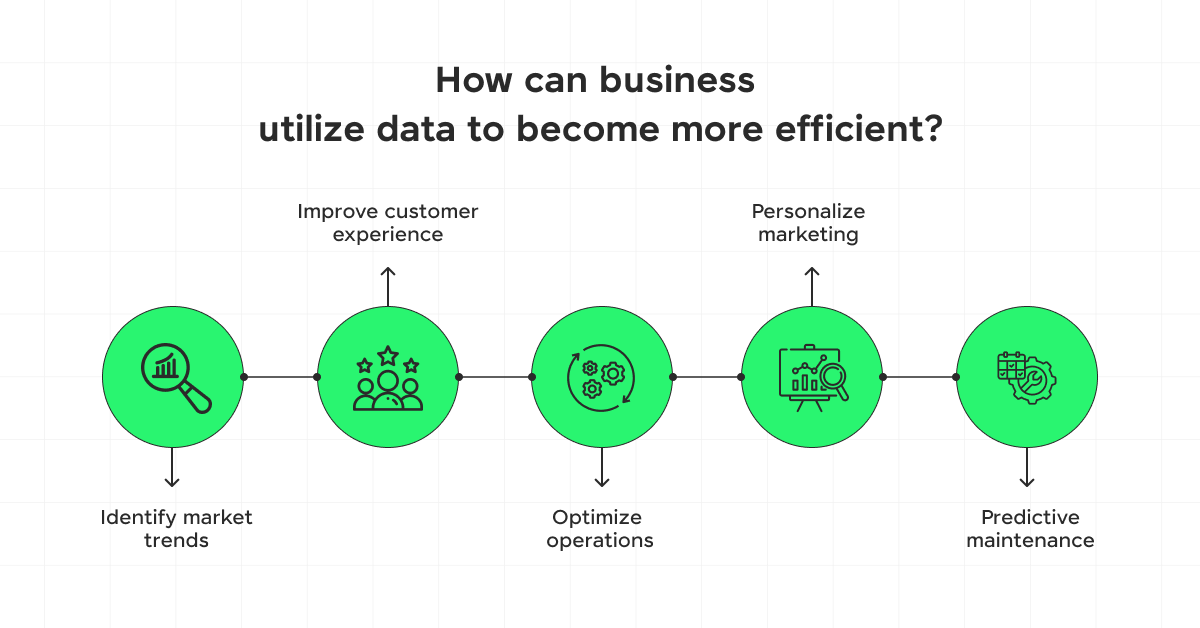
This not only helps in aligning every aspect of operations to enhance performance but also reduces operational costs and improves customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, data collection is indispensable for businesses aiming to thrive in a dynamic market. It supports informed decision-making, enhances customer understanding, and aids in operational efficiency, making it a cornerstone of modern business strategy.
Before we move into the next section, ensure you have a good grip on data science essentials like Python, MongoDB, Pandas, NumPy, Tableau & PowerBI Data Methods. If you are looking for a detailed course on Data Science, you can join GUVI’s Data Science Course with Placement Assistance. You’ll also learn about the trending tools and technologies and work on some real-time projects.
Additionally, if you want to explore Python through a self-paced course, try GUVI’s Python course.
Types of Data Collection Methods
Exploring the different types of data collection methods is essential for harnessing the full potential of your analytical endeavors.
These methods fall into three primary categories: Quantitative Methods, Qualitative Methods, and Mixed Methods. Each type has its unique applications and is chosen based on the specific needs of the research or data collection initiative.
1) Quantitative Methods
Quantitative data collection involves structured techniques such as surveys, questionnaires, and experiments that yield numerical data. This data can be easily quantified and subjected to statistical analysis, making it invaluable for testing hypotheses and making predictions.
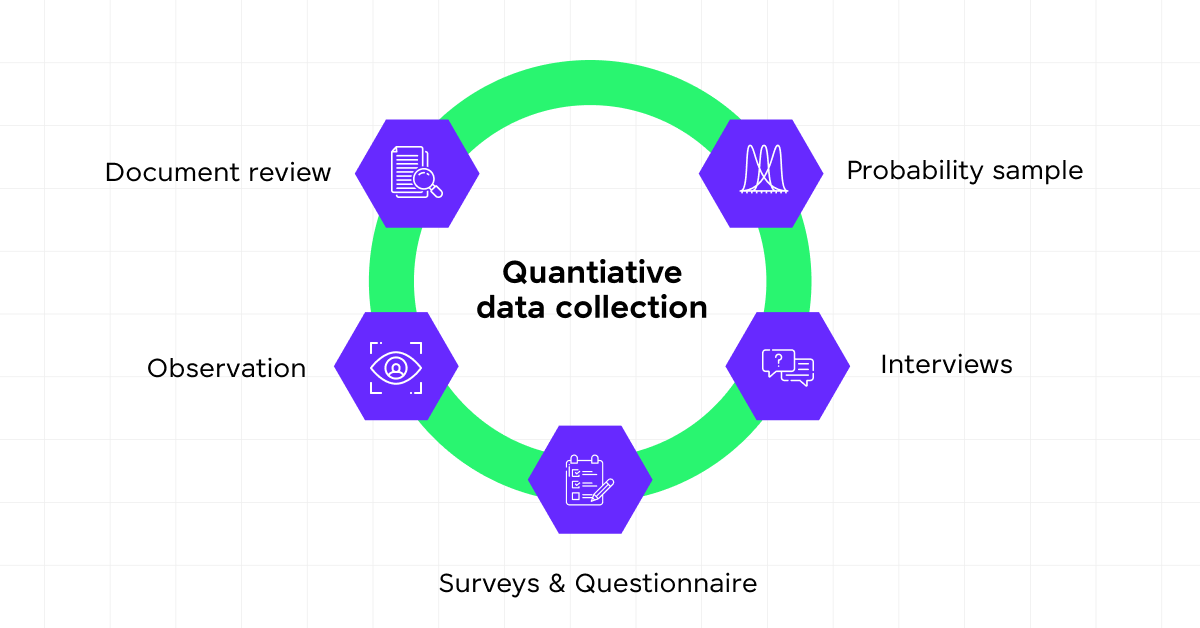
You’ll find these methods particularly useful when you need to measure variables numerically and assess relationships between them. For instance, using online surveys to gather customer feedback on product satisfaction allows for quick aggregation and analysis of large data sets to identify trends and patterns.
Master Your Basics: Understanding the Data Science Process: A Useful Guide!
2) Qualitative Methods
In contrast, qualitative data collection methods focus on descriptive data that can be observed but not measured. Techniques like interviews, focus groups, and observations are typical methods that provide depth and detail through direct quotes and comprehensive narratives.
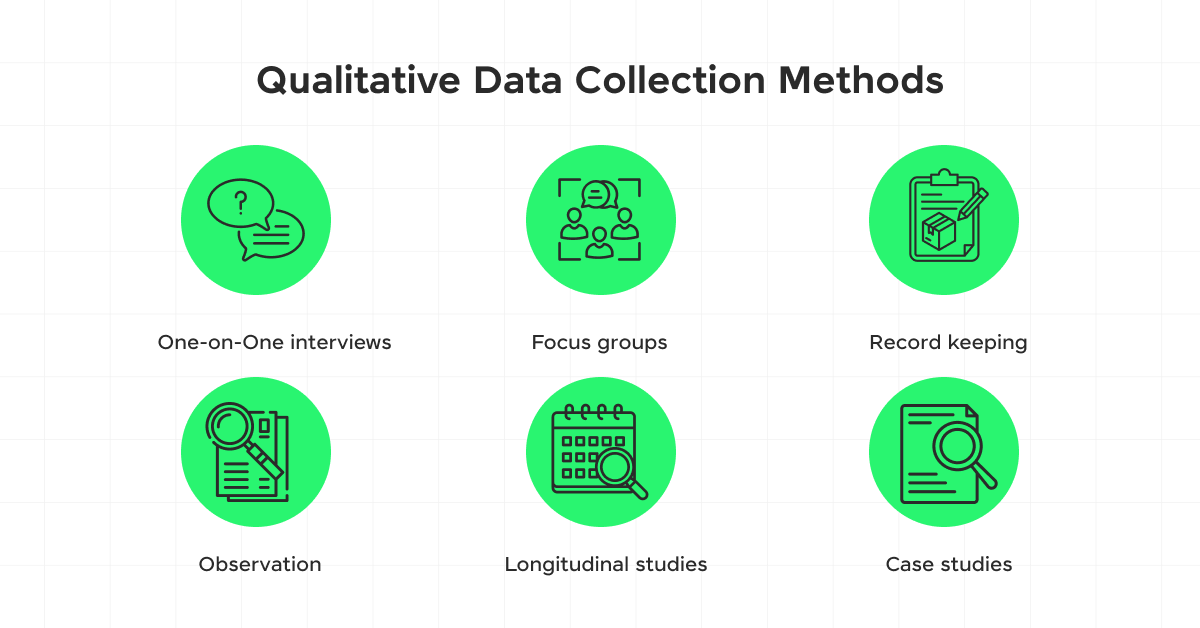
These methods are pivotal when you aim to understand concepts, thoughts, or experiences from a personal perspective. For example, conducting in-depth interviews can uncover why customers prefer one product over another, providing insights that are not attainable through numerical data alone.
3) Mixed Methods
Mixed methods combine elements of both quantitative and qualitative data collection. This approach allows for a comprehensive analysis that leverages the strengths of both types of data.
By integrating quantitative surveys with qualitative interviews, you can enrich your understanding of a research topic, providing a more complete picture of the phenomena under study.
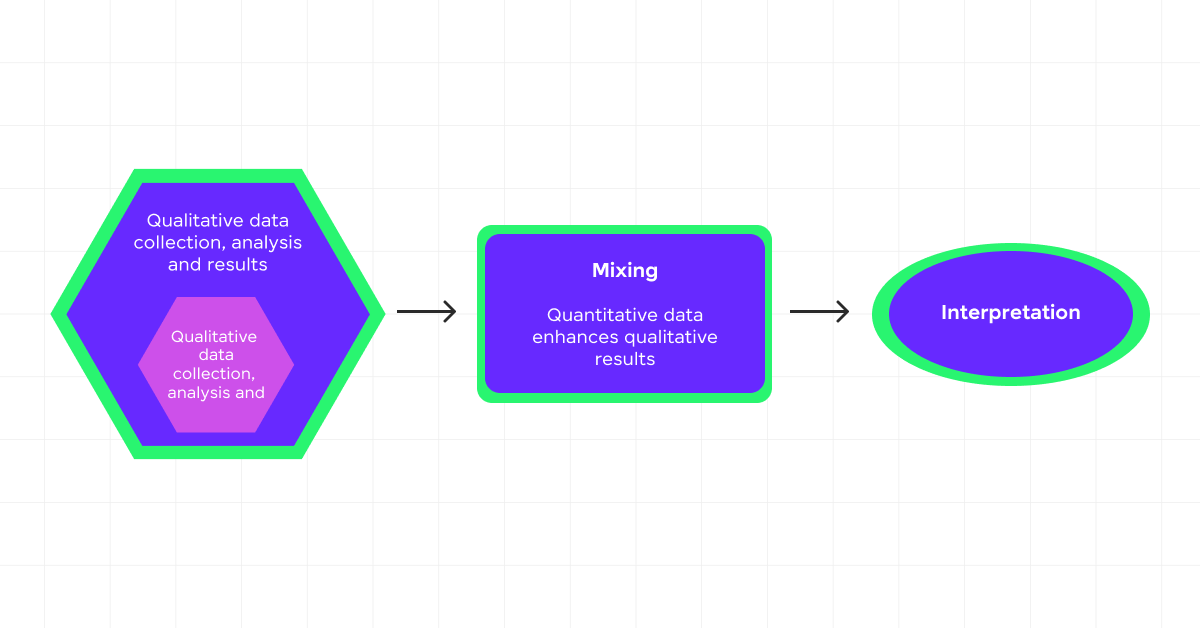
This method is particularly beneficial when addressing complex research questions that require multiple perspectives to uncover the nuances of the subject matter.
Each of these methods plays a crucial role in data collection, and selecting the appropriate type depends on your specific research goals and the nature of the information you seek. By understanding these differences and applying the right techniques, you can ensure high-quality data collection that supports informed decision-making.
Key Steps in the Data Collection Process
Step 1: Defining the Goal
- Before you begin collecting data, it’s essential to clearly define what you aim to achieve.
- This involves engaging stakeholders to establish clear objectives and key questions.
- Understanding the purpose of your project—whether solving a problem or making informed decisions—guides the entire data collection process.
- Consider the long-term impact and how you will measure success, using historical data if available to refine your approach.
Step 2: Choosing Methods
- Selecting the right data collection methods is crucial and should align with your goals.
- Data collection isn’t limited to surveys and interviews; it extends to automated methods like sensor data or web scraping.
- Evaluate each method’s strengths and limitations, ensuring they match the nature of the data you need.
- This step ensures the data collected is relevant and sufficient for your analysis needs.
Step 3: Planning Procedures
- Develop a detailed plan that outlines how data will be collected.
- This includes deciding on the tools and technologies to be used, the timeline for the collection process, and the personnel involved.
- Establish protocols for each method, whether it involves direct observations, digital tools, or personal interviews.
- Planning also involves setting up quality control measures to ensure data accuracy and reliability from the start.
Step 4: Collecting Data
- With your plan in place, begin the actual data collection.
- Ensure that every member of your team is clear on their roles and the methods to be used.
- Data should be collected systematically to maintain consistency and prevent errors.
- It’s also vital to monitor the collection process closely to make adjustments as needed and to ensure compliance with ethical standards, particularly when human subjects are involved.
Step 5: Cleaning and Organizing
- After data collection, the next crucial step is data cleaning and organizing.
- This involves removing any inaccurate or irrelevant data, correcting errors, and ensuring all data is in a consistent format.
- Organizing your data effectively allows for easier analysis and helps maintain the integrity of your data set.
- Use appropriate software tools to assist in this process, ensuring that your data is ready for analysis.
By following these steps, you ensure that your data collection process is robust, efficient, and tailored to meet your specific research goals, ultimately leading to more accurate and reliable outcomes.
Common Challenges in Data Collection
1) Data Quality Issues
Ensuring data quality is a significant challenge during data collection. The initial data gathered often requires extensive pre-processing and annotation, which are labor-intensive and prone to errors.
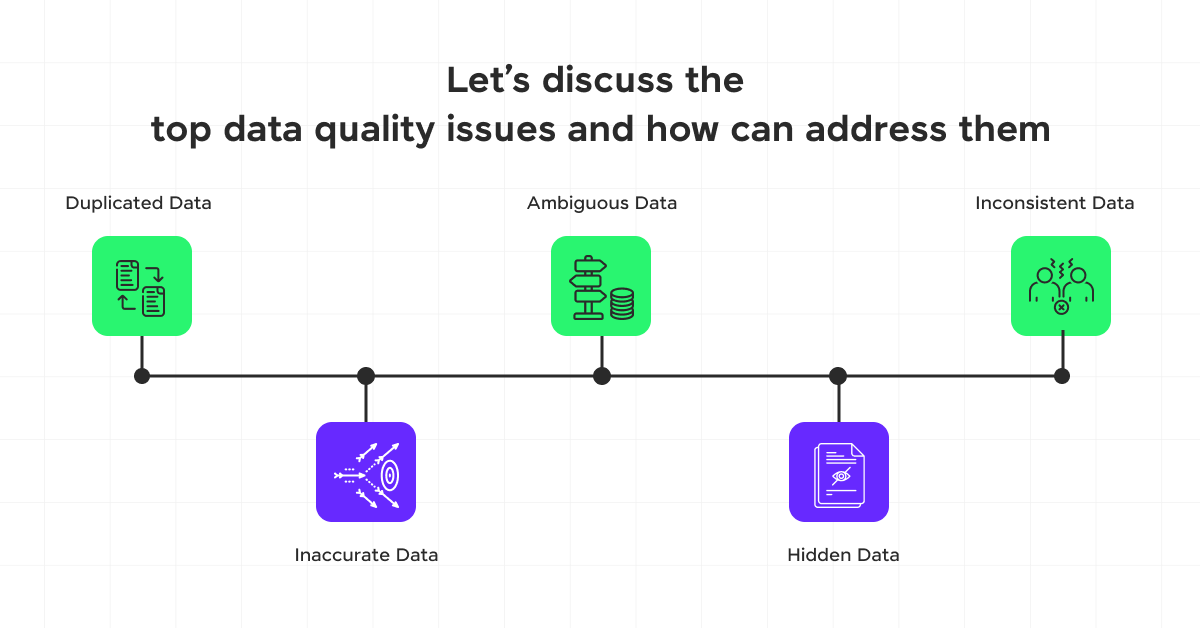
To address these issues, leveraging data preprocessing tools and implementing rigorous quality assurance practices are essential. These measures help verify data integrity and reduce data redundancy, ensuring the reliability of the data used for analysis.
2) Incomplete Data
Missing data is a pervasive issue that can undermine the statistical power of research and lead to biased results. Techniques like imputation, where missing values are replaced with estimated ones, and data removal, where incomplete data points are excluded, are commonly used.
However, these methods need careful application to avoid introducing further bias into the analysis.
3) Choosing the Right Data
Selecting appropriate data sets is crucial for the success of data projects. Often, data sets do not fully represent the scope of the project or align with real-world conditions, leading to inaccurate results.
It’s vital to ensure the data covers the full project scope and to consider all available data collection methods to gather the most relevant data.
4) Low Response Rates
Low response rates in surveys and studies can significantly affect the quality of data, introducing bias and reducing the representability of the sample.
Strategies to improve response rates include designing engaging and concise surveys, offering incentives, and employing multiple recruitment methods to ensure a diverse and representative sample.
Kickstart your Data Science journey by enrolling in GUVI’s Data Science Course where you will master technologies like MongoDB, Tableau, PowerBI, Pandas, etc., and build interesting real-life projects.
Alternatively, if you want to explore Python through a self-paced course, try GUVI’s Python course.
Concluding Thoughts…
The fundamental importance of data collection in the digital age has been thoroughly established, highlighting how it empowers organizations to make informed decisions, understand customer behaviors, and drive operational efficiency.
We learned quite a bit, right from the initial steps of defining goals to the meticulous processes of choosing methods, planning, collecting, and organizing data, and addressing common challenges along the way.
Given the comprehensive analysis of data collection methods, challenges, and best practices, it is evident that adept handling of the data collection process is paramount, not to mention how beneficial it is for businesses.
FAQs
Data collection is the process of gathering and measuring information on variables of interest in an organized and systematic way to answer research questions, test hypotheses, and evaluate outcomes.
Data is collected to gain insights, make informed decisions, identify trends, improve processes, and support research and development across various fields and industries.
The four main types of data collection are observational, experimental, simulation, and derived.
Data is information that is collected and used for reference or analysis. It can be numbers, words, measurements, observations, or descriptions of things.















![Top 10 Mistakes to Avoid in Your Data Science Career [2025] 9 data science](https://www.guvi.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Beginner-mistakes-in-data-science-career.webp)








Did you enjoy this article?