
Data Science and Business Analytics: Key Differences
Mar 31, 2025 6 Min Read 2521 Views
(Last Updated)
Are you confused between data science and business analytics? Not sure what the difference is and what to pursue? We got you!
In this blog, we will provide you with a detailed explanation of data science, business analytics and their responsibilities. Moving with brief differences between data science and business analytics based on the process, tools and techniques, salary, education path, training and career opportunities.
After this blog, you will be able to pick up your domain and start focusing on developing your skills without any confusion. So, let’s get started!
Table of contents
- What is Data Science?
- Roles and Responsibilities
- What is Business Analytics?
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Data Science Vs Business Analytics
- Process
- Skills and Tools Required
- Salary
- Education Path and Training
- Career Opportunities and Job Market
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What are the primary differences between Data Science and Business Analytics?
- How do the skill sets required for Data Science and Business Analytics differ?
- What career paths can one pursue in Data Science and Business Analytics?
What is Data Science?
Data science is the study of data to extract meaningful information and insights. Data science is used to provide a data-driven solution to real-world problems. It includes maths, statistics, machine learning(ML) and artificial intelligence(AI).
Roles and Responsibilities
A data scientist is a person who is well-versed in data science. They are computer science disciplines. The responsibilities of a data scientist are as follows:
- Analyze the data and handle the missing data.
- Use algorithms and machine learning to find patterns and trends in data.
- Create predictive models to help guide business decisions.
- Ask and answer questions like what happened, why it happened, and what can be done with the results.
- Communicate their findings through reports, charts, and graphs.
What is Business Analytics?
Business Analytics is the process of improving business decisions by transforming data into insights. It includes data management, data visualization, predictive models, data mining and forecasting methods.
Roles and Responsibilities
A business analyst is a person who is an expert in using business analytical tools to understand the business needs, performance, identify problems and make better decisions to improve the business. The responsibilities of a business analyst include the following:
- Gather business requirements and data to provide solutions for the specific business problem.
- They communicate with stakeholders to gain a solid understanding of the business needs and convert them into clear actions.
- They create models to solve business problems and focus on the area for optimization.
- They test the built solution to ensure it meets the business requirements as intended.
- They document the business solution and monitor it closely to avoid any discrepancies.
- They work closely with stakeholders and developers to communicate the business needs and guide them to achieve them.
We have seen a brief description of both data science and business analytics, including their roles and responsibilities. Now, let’s jump into the differences based on various factors.
Data Science Vs Business Analytics
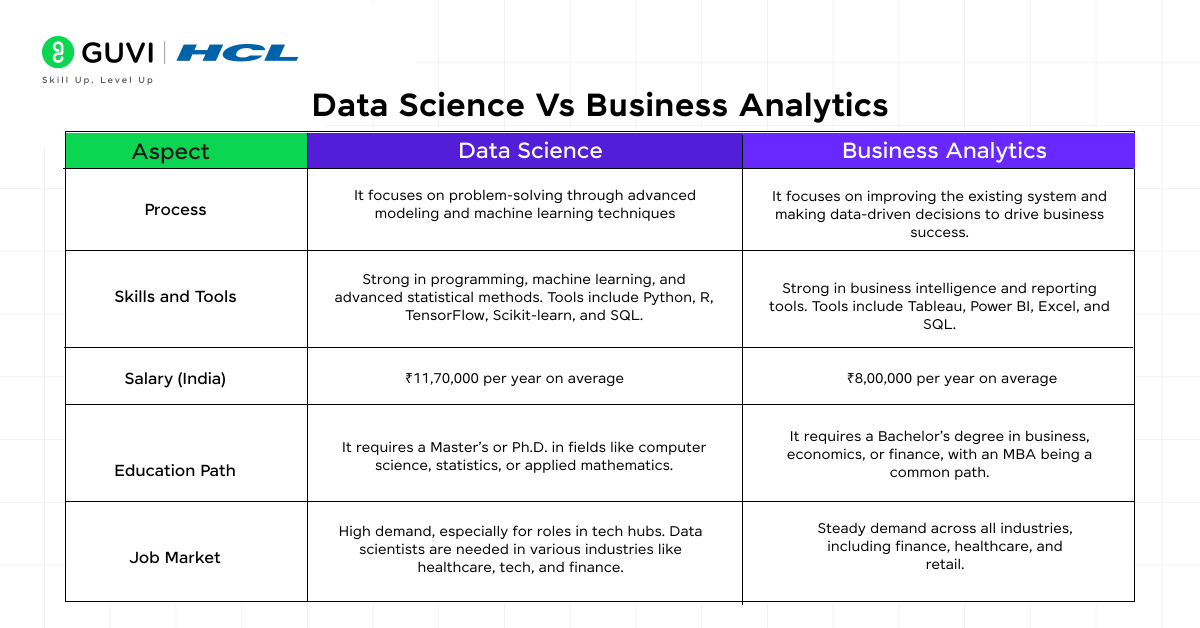
As a beginner, you will find that both data science and business analytics are the same. But, if you focus in depth on its processing and use cases, you will see the difference between them. In this section, we will see the differences by understanding various factors.
Process
Let’s understand the process of both data science and business analytics separately.
Data Science Process
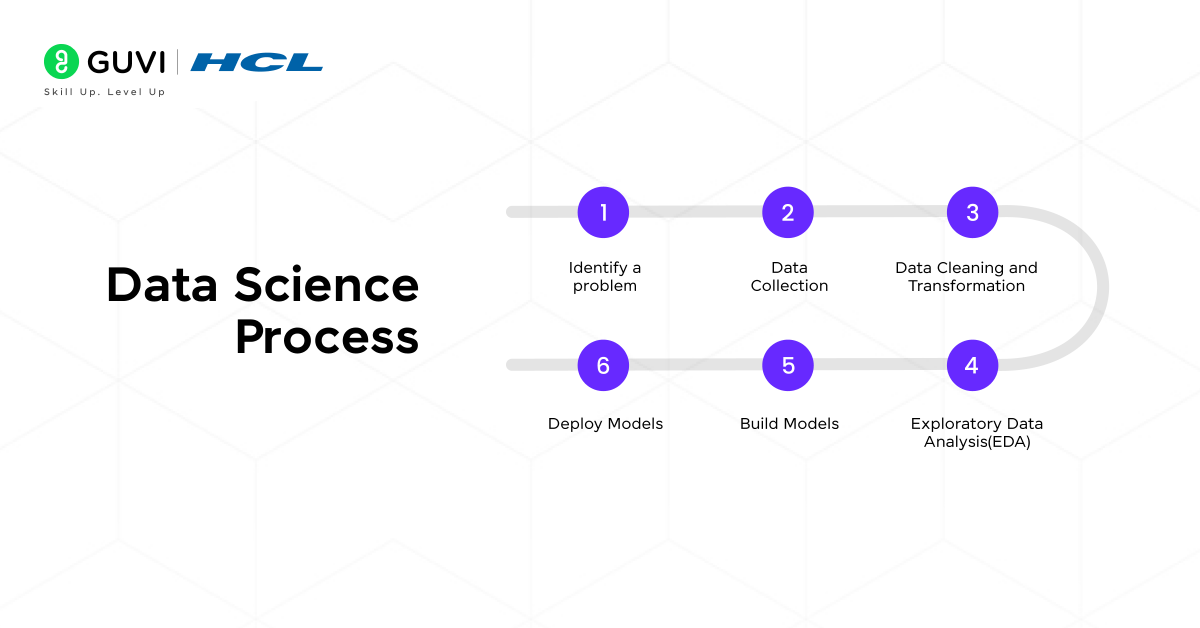
The Data Science process covers from finding the problem to deploying the solution for enterprise use. There are six steps in the data science process. The overview of each step is given below:
- Identify a problem: To identify the problem statement that can be solved using data science.
- Data Collection: Collect relevant data from various sources such as spreadsheets, databases and web scraping.
- Data Cleaning and Transformation: Clean and prepare the dataset for processing by removing duplicates, missing and inconsistent data.
- Exploratory Data Analysis(EDA): Identifying trends and patterns using visualization techniques like charts, plots, histograms and box plots.
- Build Models: Build predictive models using machine learning and deep learning algorithms to provide solutions to the problem statement.
- Deploy Models: The final step is to communicate the findings to the stakeholders and deploy the predictive models.
Business Analytics Process
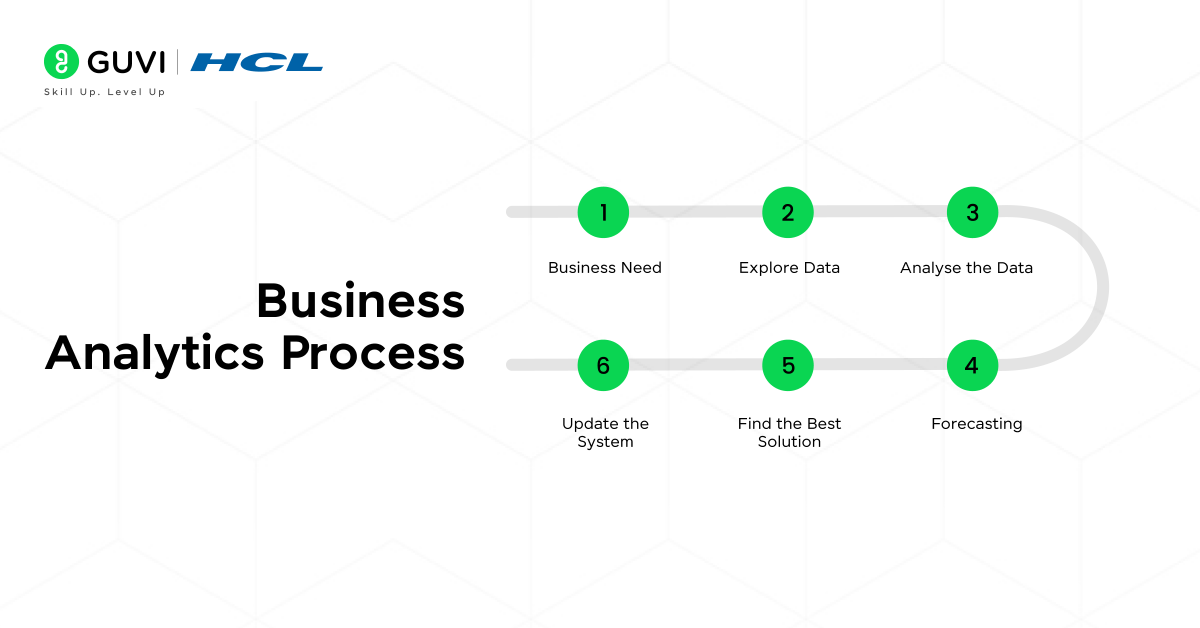
Similar to the data science process, the business analytics process also defines from problem statement to system update. There are 6 steps in the business analytics process. The overview of each step is given below.
- Business Need: Identify the business needs, similar to identifying problem statements in the data science process.
- Explore Data: Explore the data to make it compatible for processing and other steps by handling missing and incomplete data.
- Analyse the Data: Select features that are relevant to the business needs and try to find relationships between variables.
- Forecasting: With the help of collected data, try to predict the potential outcome and how it affects the business.
- Find the Best Solution: Discuss the forecasted result with stakeholders and analyse the outcome and choose the best suitable solution for the problem.
- Update the System: According to the proposed solution, update the system to handle the upcoming changes easily.
Difference
The data science process is purely focused on providing solutions that solve real-world problems such as fraud detection, cancer prediction and so on. Business analytics processes focus on improving the existing system to provide better results and revenue. Examples include sales analysis and prediction and stock market prediction.
Skills and Tools Required
Next up, let’s look into the tools and techniques of both data science and business analytics and understand the technological differences between them.
Data Science
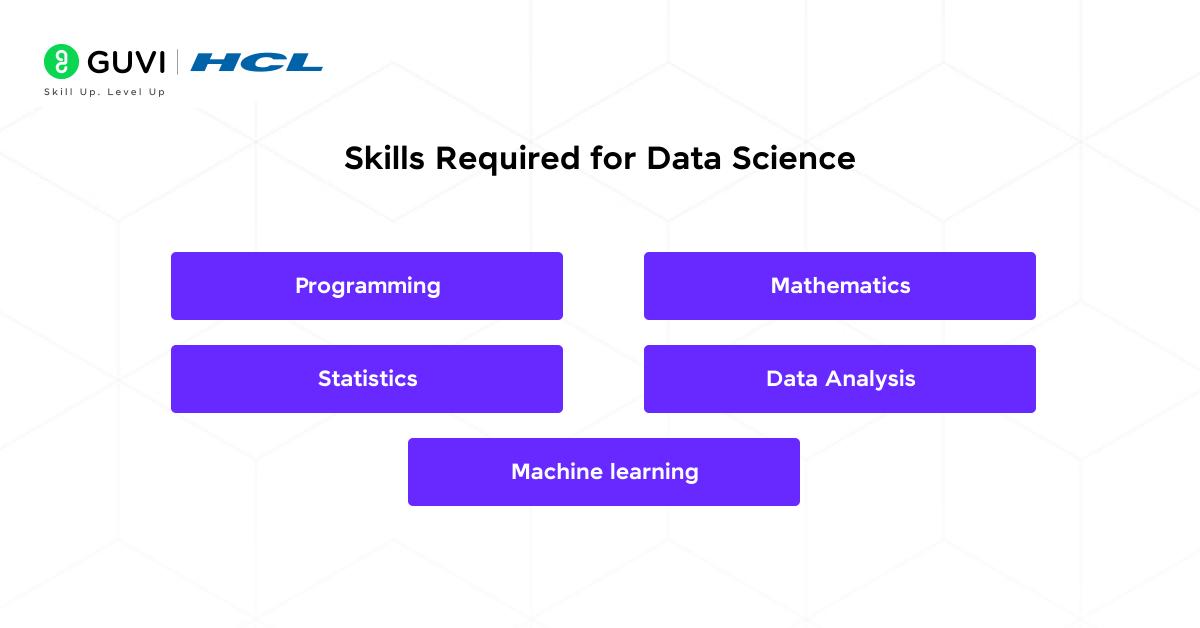
As we discussed earlier, data science is a combination of statistics, mathematics, machine learning and data visualization. The following are the tools and skills required for data science.
Skills
- Programming: Focus on fundamental concepts of programming languages such as variable declarations, functions, classes, objects and other pillars of object-oriented programming.
- Mathematics: To excel in mathematics, focus on key concepts such as linear algebra, calculus, and probability theory.
- Statistics: As for statistics, focus on Statistical theories such as hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and data distribution is essential for analysing data and drawing meaningful conclusions.
- Data Analysis: This involves data cleaning, exploration, processing, model building and visualization.
- Machine learning: Understanding the different types of machine learning algorithms, such as supervised(trained on the labeled dataset), unsupervised(trained on the unlabeled dataset), and reinforcement learning and their applications is mandatory.
Tools
- Data Cleaning and Processing: Nltk, SpaCy in Python.
- Data Manipulation and Analysis: Pandas, NumPy in Python language.
- Data Visualization: Matplotlib, Seaborn, Plotly in Python and tools like Tableau and Power BI.
- Machine Learning: Scikit-learn, Tensorflow, Keras in Python.
- Model Evaluation: GridSearchCV, RandomizedSearchCV in Python.
- Version Control: Git and GitHub.
- Databases: SQL and NoSQL.
- Model Deployment: Flask and FastAPI in Python.
Business Analytics
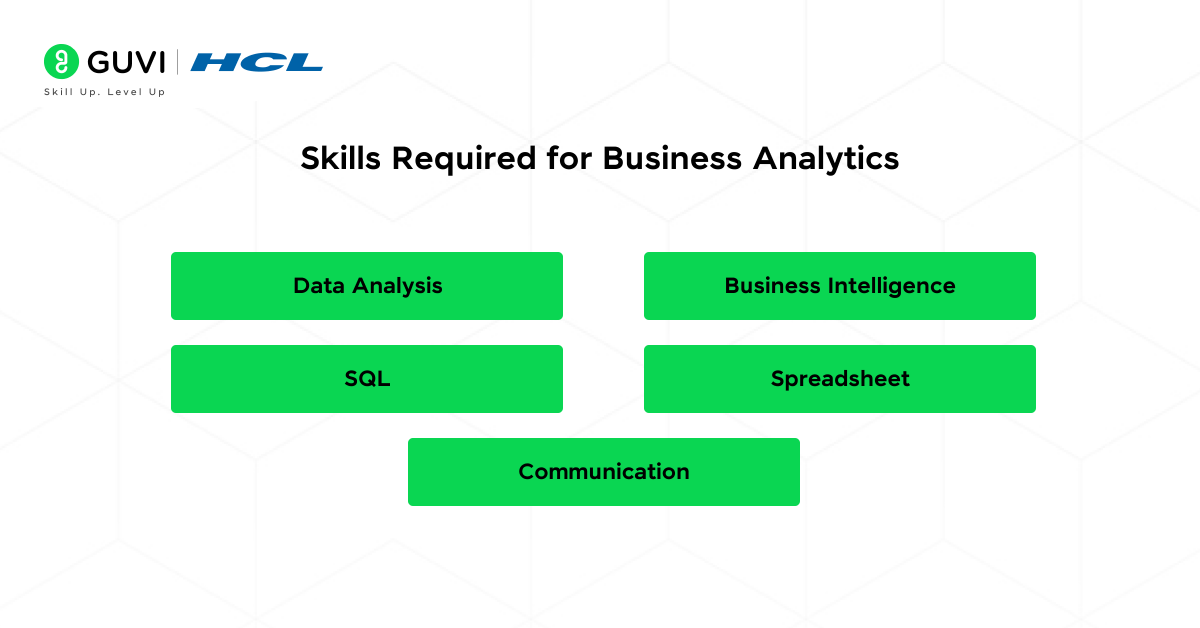
Similar to data science, business analytics also requires a strong analytical mind. It focuses more on business intelligence and less on advanced programming or machine learning. The following are the tools and skills required for business analytics.
Skills
- Data Analysis: Similar to data science, you should be proficient in processes such as data cleaning, data exploration, processing and data visualization.
- Business Intelligence: Understanding of tools like Tableau, Power BI to create detailed reports and dashboards.
- SQL: Database querying skills are essential for extracting and manipulating data.
- Spreadsheet: Advanced Excel skills are necessary for performing pivot tables, macros and data modelling in Excel tools.
- Communication: Business analysts are required to communicate a lot with stakeholders to discuss the business needs and the solutions.
Tools
- Business Intelligence platforms: Tableau, Power BI, QlikView
- Spreadsheet software: Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets
- Database management systems: MySQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server
- Statistical software: SPSS, SAS
- Project management tools: JIRA, Trello, Microsoft Project
From these tools and techniques definition, you can clearly spot the difference. Business analysts require communication a lot whereas data scientists don’t. Also, there are other differences too.
Salary
In this section, we will discuss the salaries of both data scientists and business analysts in India and see how they differ from one another. Both fields offer competitive salaries, while data scientists often command higher pay for senior positions.
According to Glassdoor, the average base salary for a Data Scientist in India is around ₹11,70,000 per year, with potential increases based on experience and expertise. According to Glassdoor, the average base salary for a Business Analyst is approximately ₹8,00,000 per year, with variations depending on the specific industry and location.
Education Path and Training
Let’s look into the educational path and training requirements for both a data scientist and a business analyst. By the end of this section, you should be able to pick up your own training path for your desired role.
Data Science
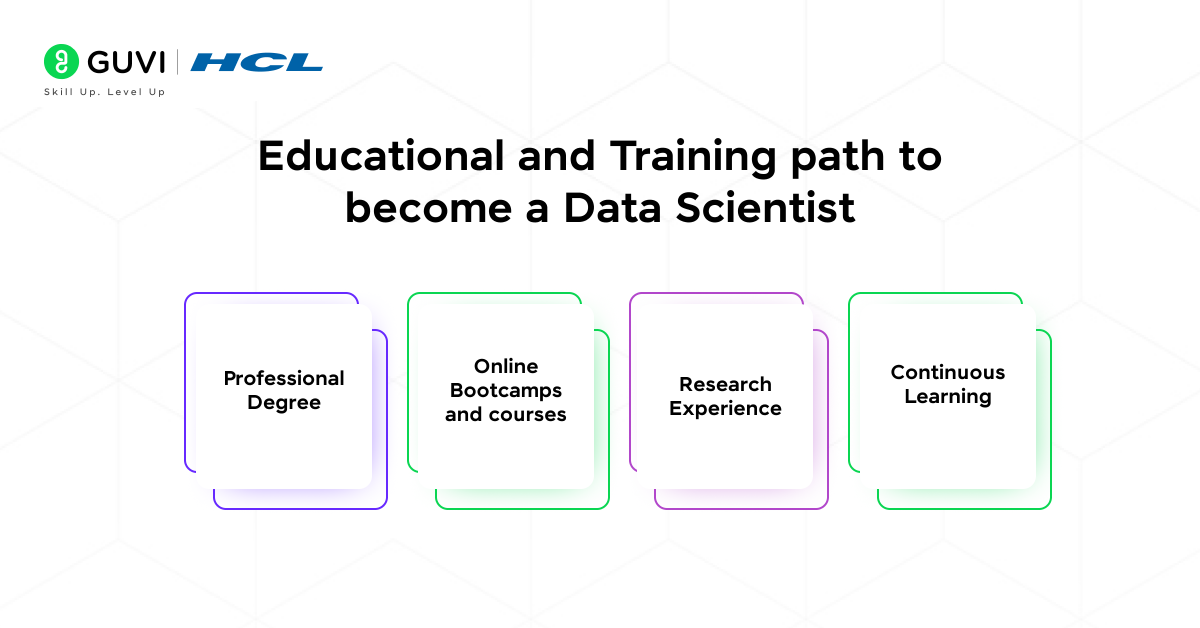
The educational and training path to become a data scientist includes the following.
- Professional Degree: Most of the data scientists hold master’s or Ph.D degrees in either of the fields, such as computer science, statistics, Applied mathematics, or specialized data science programs.
- Online Bootcamps and courses: People from different fields, such as computer science, mechanical engineering and others, take online courses and bootcamps to learn about data science.
- Research Experience: Many data scientists, especially those with Ph. D.s, have experience conducting original research and publishing papers in their field.
- Continuous Learning: Due to the rapid development in AI, keeping up-to-date with recent developments and their implementation in data science is mandatory. This can be done by participating in hackathons and workshops.
If you want to learn the necessary skills required for a data science starting from scratch to advance from India’s top Industry Instructors, consider enrolling in GUVI’s Zen class course “Become a Data Science Professional with IIT-M Pravarta” that not only teaches you everything about data science, but also provides you with hands-on project experience an industry-grade certificate!
Business Analytics
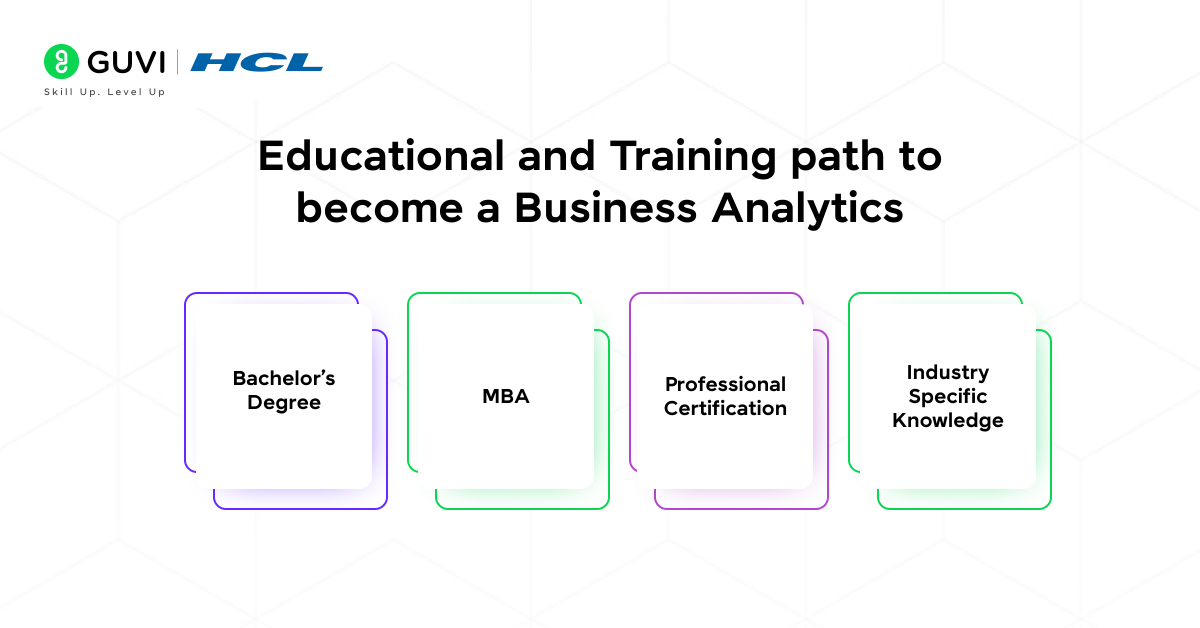
The educational and training path of business analytics is more focused on business. Let’s look into it deeper.
- Bachelor’s Degree: Most of the business analysts hold bachelor’s degrees in fields such as business administration, economics or finance.
- MBA: MBA programs are focused on analytics, especially for businesses.
- Professional Certification: It is valuable to have certifications such as Certified Analytics Professional(CAP) or IIBA Certification in Business Data Analytics.
- Industry Specific Knowledge: You should be an expert in particular industries such as healthcare, finance or retail.
Are you interested in the awesome works by business analytics professionals? Learn those skills starting from today by enrolling in Guvi’s course on Business and Marketing Analytics Course with AI tools. This course covers everything you need to know to become an expert in business analytics. You can gain industry certifications and real-time experience by building the projects.
Career Opportunities and Job Market
The last and most important factor is career opportunities and the job market. Let’s dive deeper into the job market of both data science and business analytics.
Data Science
Career Path
a) Entry-level: Junior Data Scientist or Data Analyst roles, often requiring strong technical skills and a relevant degree.
b) Mid-level: Senior Data Scientist positions, typically involving more complex projects and team leadership.
c) Advanced: Lead Data Scientist or Principal Data Scientist roles, often steering the overall data strategy of an organization. To learn more about data-driven insights, read the important roles and responsibilities of a data scientist.
d) Management: Chief Data Officer or Director of Data Science, overseeing entire data teams and aligning data initiatives with business goals.
e) Specialization: Some data scientists specialize in areas like machine learning engineering, AI research, or data architecture.
Job Market
According to Nasscom, the demand for data scientists in today’s digital world is increasing tremendously. Generally, data scientists receive competitive salaries, especially in tech hubs and for those with advanced skills. Many of the companies nowadays provide remote work options, broadening the job opportunities globally. There are more than 10,000 jobs listed currently on LinkedIn. This field requires you to learn continuously and master trending skills to stay up to date with technology.
Business Analytics
Career Path
a) Entry-level: Business Analyst or Junior Analytics Consultant roles, often requiring a bachelor’s degree and strong analytical skills.
b) Mid-level: Senior Business Analyst or Analytics Manager positions, involving more complex analyses and project leadership.
c) Advanced: Director of Business Analytics or Head of Business Intelligence, overseeing analytics strategy and teams.
d) Executive: Chief Analytics Officer or VP of Analytics, driving data-driven decision-making at the highest levels of an organization.
e) Specialization: Some analysts specialize in areas like marketing analytics, financial analytics, or operations research.
Job Market
The demand for business analytics continues to grow steadily as more companies recognize the importance of data-driven decisions. On LinkedIn, nearly 20,000 jobs are available for a business analyst to apply for. Business analysts are needed across the globe in all industries, from healthcare to finance and retail. Most companies also provide remote options to expand their region. It emphasizes more on soft skills such as communication and presentation than technical skills. Many organizations seek analysts to bridge the gap between business needs and technological solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both data science and business analytics offer rewarding career opportunities, competitive salaries and training opportunities. The data science role is ideal for those who are interested in exploring complex algorithms, machine learning and artificial intelligence. On the other hand, business analytics is perfect for those who want to use data to drive business decisions and strategy.
At last, the choice between data science and business analytics is purely based on your interest and skillset. If you are not much of a technical person, you can go with business analytics and vice versa.
Remember to stay consistent and up to date with recent developments in both fields if you don’t want to leave behind what the market needs. Happy Learning!
FAQs
Data Science uses complex algorithms and statistical models to extract insights and make predictions from large datasets. It involves advanced techniques like machine learning and deep learning to uncover patterns and trends for future predictions.
On the other hand, Business Analytics emphasizes using historical data to drive current business decisions through descriptive and diagnostic analytics.
Data Scientists typically need strong programming skills (Python, R), proficiency in statistical analysis, and knowledge of machine learning algorithms. They also require a solid understanding of data manipulation and visualization techniques.
In contrast, Business Analysts require skills in data querying (SQL), data visualization tools (Tableau, Power BI), and domain-specific knowledge in areas like finance or marketing.
In Data Science, career paths include roles such as Data Scientist, Machine Learning Engineer, and AI Specialist. These roles involve developing predictive models, designing algorithms, and applying advanced statistical techniques to solve complex problems across various industries. In Business Analytics, career paths include roles like Business Analyst, Data Analyst, and Business Intelligence Analyst.
















![Top 10 Mistakes to Avoid in Your Data Science Career [2025] 9 data science](https://www.guvi.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Beginner-mistakes-in-data-science-career.webp)







Did you enjoy this article?