
Data Science vs Computer Science: Which is the Right Path for You?
Mar 07, 2025 8 Min Read 2958 Views
(Last Updated)
If you’re here, I guess you’ve found yourself at a crossroads: data science vs computer science. Which path should you choose? Both fields offer exciting opportunities and have a significant impact on our digital landscape.
As you weigh your options, it’s crucial to understand the unique aspects of each discipline and how they align with your interests and career goals. This article aims to help you navigate the decision between data science and computer science.
We’ll explore the key differences in roles and responsibilities, required skills, typical salaries, and day-to-day activities. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of which field might be the right fit for your future in tech.
Table of contents
- What is Data Science?
- Definition and Scope
- Key Components
- Applications in Business
- What is Computer Science?
- Definition and Scope
- Core Areas of Study
- Industry Applications
- Data Science vs Computer Science
- Skill Sets and Knowledge Areas
- The Data Science Skillset
- The Computer Science Skillset
- Overlapping Skills
- Educational Pathways and Requirements
- Data Science and Computer Science Graduate Degrees
- Online Courses and Industry Certifications
- Job Roles, Responsibilities and Salaries
- A) Data Science
- B) Computer Science
- Data Science vs Computer Science: Choosing Your Career Path
- Assessing Your Interests
- Evaluating Your Strengths
- Long-term Career Goals
- Concluding Thoughts…
- FAQs
- Is data science a good alternative to computer science?
- Will AI replace data scientists?
- Will data science be in demand in 2030?
- Does data science pay more than computer science?
What is Data Science?
Definition and Scope
Data science is an interdisciplinary field that combines scientific methods, processes, algorithms, and systems to extract knowledge and insights from structured and unstructured data. It’s a powerful tool that helps you make sense of the vast amount of information available in today’s digital world.
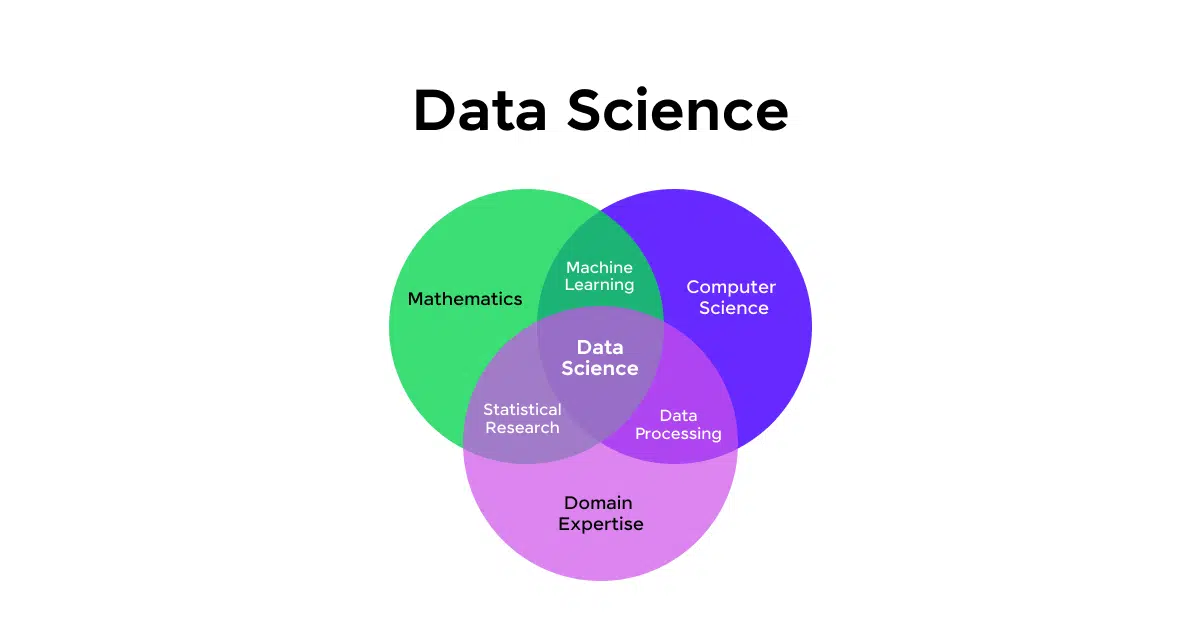
As a data scientist, you’ll be tasked with obtaining, processing, and analyzing data to gain valuable insights for various purposes.
The scope of data science is incredibly vast, encompassing different types of analytics and applications. It has emerged as a revolutionary field crucial for transforming businesses and industries. You’ll find that data science is not just about statistics; it’s a blend of mathematics, technology, and business acumen.
Key Components
To excel in data science, you’ll need to master several key components:
- Data Collection and Management: You’ll work with both structured and unstructured data, including numerical data, text, images, and videos.
- Programming: Proficiency in languages like Python and R is essential for data analysis, machine learning, and visualization.
- Statistical Analysis: This forms the backbone of data science, helping you interpret data and make predictions.
- Machine Learning: You’ll use algorithms and statistical models to enable computers to perform tasks without explicit instructions.
- Data Visualization: Creating visual representations of data helps communicate insights effectively.
Applications in Business
Data science has numerous applications in the business world:
- Improving Operations: From logistics to human resources, data science can optimize various business processes.
- Uncovering Insights: You will discover hidden patterns that provide companies with a competitive edge.
- Innovation: Data science drives the creation of new products and services based on customer needs and preferences.
- Predictive Analytics: You will help businesses anticipate market trends and stay ahead of the competition.
By leveraging these applications, you can significantly impact a company’s strategy and decision-making processes. As a data scientist, you’ll play a crucial role in helping businesses harness the power of data to drive growth and innovation.
What is Computer Science?
Definition and Scope
Computer science is the academic study of computers and computing, encompassing both theoretical and practical aspects. It’s a field that explores how to use technology to solve problems and create innovative solutions.
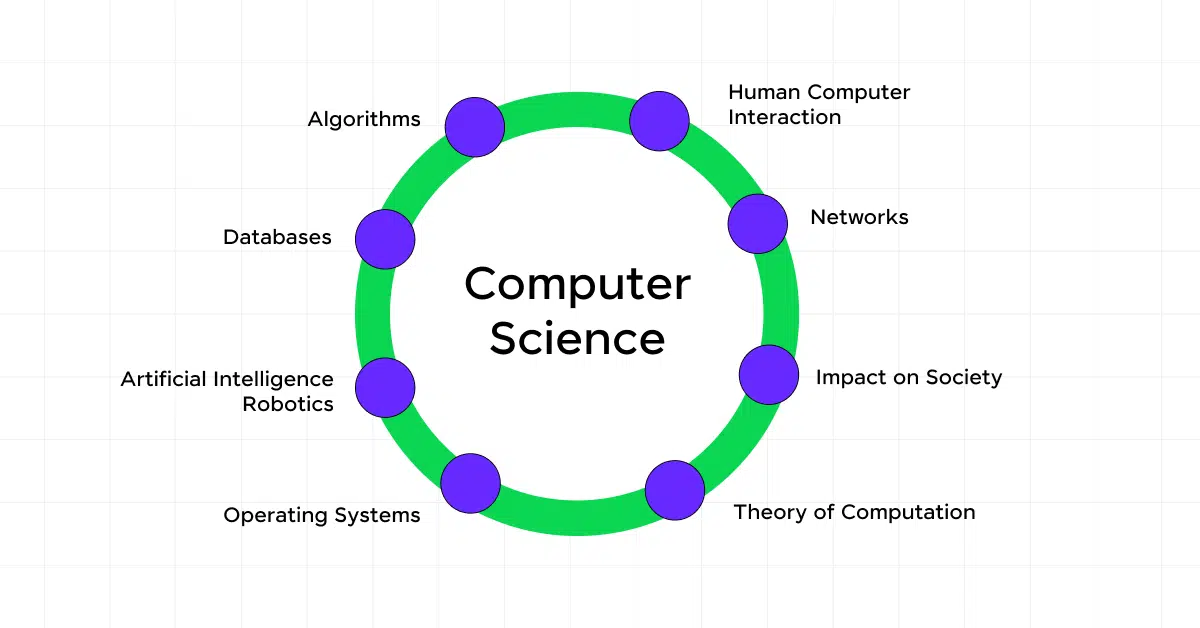
As a computer scientist, you’ll delve into subjects like algorithms, data structures, computer architecture, and artificial intelligence.
The scope of computer science is vast and continually expanding. It’s not just about programming; it’s a blend of mathematics, engineering, and even aspects of natural sciences. You’ll find that computer science has no geographical boundaries, with opportunities available worldwide.
Core Areas of Study
- Algorithms and Data Structures: These form the backbone of efficient problem-solving in computer science.
- Programming Languages: You’ll work with various languages, from low-level assembly to high-level languages like Python and Java.
- Computer Architecture: Understanding how computers are built and function is crucial.
- Artificial Intelligence: This rapidly growing field focuses on creating intelligent machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence.
- Software Engineering: You’ll learn how to design, develop, and maintain complex software systems.
Industry Applications
Computer science has numerous applications across industries:
- Information Technology: Developing and maintaining computer systems for businesses.
- Software Development: Creating applications for desktop, mobile, and web platforms.
- Data Science: Analyzing large datasets to extract valuable insights. Data Science is a subset of Computer Science.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting computer systems and networks from threats.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Developing systems that can learn and make decisions.
As the world becomes increasingly digital, the demand for computer science professionals continues to grow. You’ll find opportunities in various sectors, from tech giants to startups, and even in non-tech industries that rely on technology for their operations.
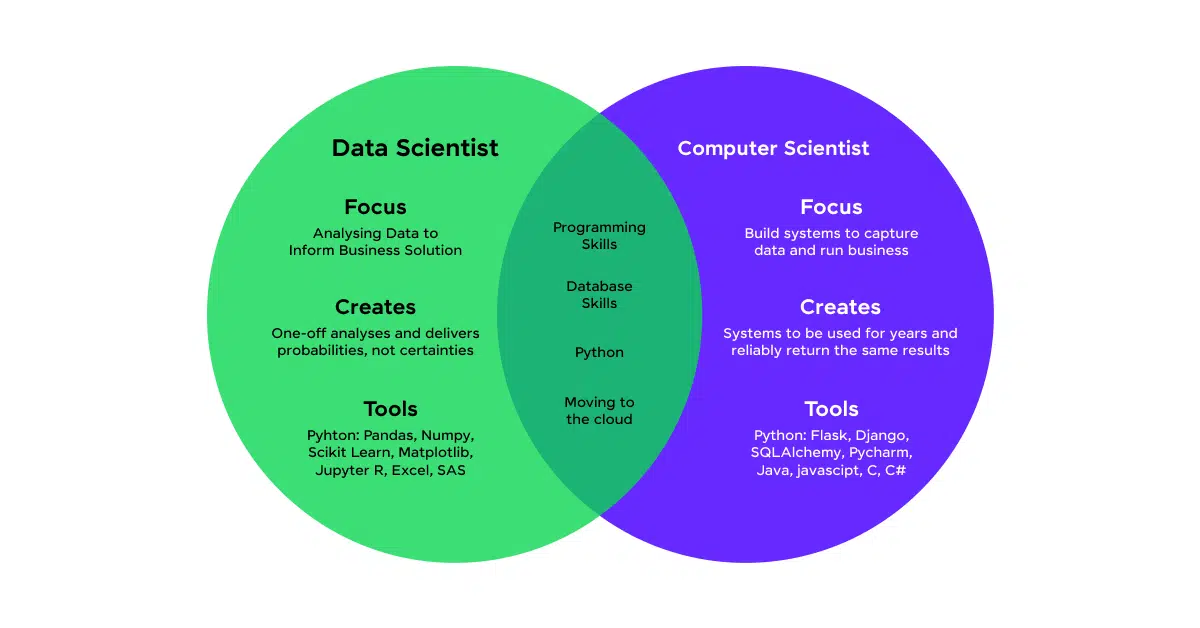
Data Science vs Computer Science
| Aspect | Data Science | Computer Science |
| Focus and Objectives | Extracting insights from data, using statistical methods and machine learning to make data-driven decisions | Study of computation, information, and technology; designing and implementing software and hardware solutions |
| Core Skills and Tools | Statistics, mathematics, data visualization, machine learning, Python, R, SQL, Tableau | Programming languages (Java, C++), algorithms, software design, computer systems, Git, Docker |
| Educational Background | Bachelor’s or master’s in data science, statistics, mathematics, or related fields | Bachelor’s or master’s in computer science, software engineering, or related fields |
| Career Paths | Data analyst, data scientist, machine learning engineer | Software developer, IT consultant, cybersecurity specialist, systems engineer |
| Average Salary in India | ₹8L – ₹20L per annum (for roles like Data Scientist, Machine Learning Engineer) | ₹5L – ₹15L per annum (for roles like Software Developer, Systems Architect, Cybersecurity Analyst) |
| Industry Applications | Finance, healthcare, marketing, technology; focus on data-driven decision making | Software development, IT, cybersecurity, gaming; focus on creating and improving tech products |
Data science emphasizes extracting insights from data, while computer science covers a broader scope of computing and digital innovation.
Skill Sets and Knowledge Areas
The Data Science Skillset
To excel in data science, you need a diverse set of skills:
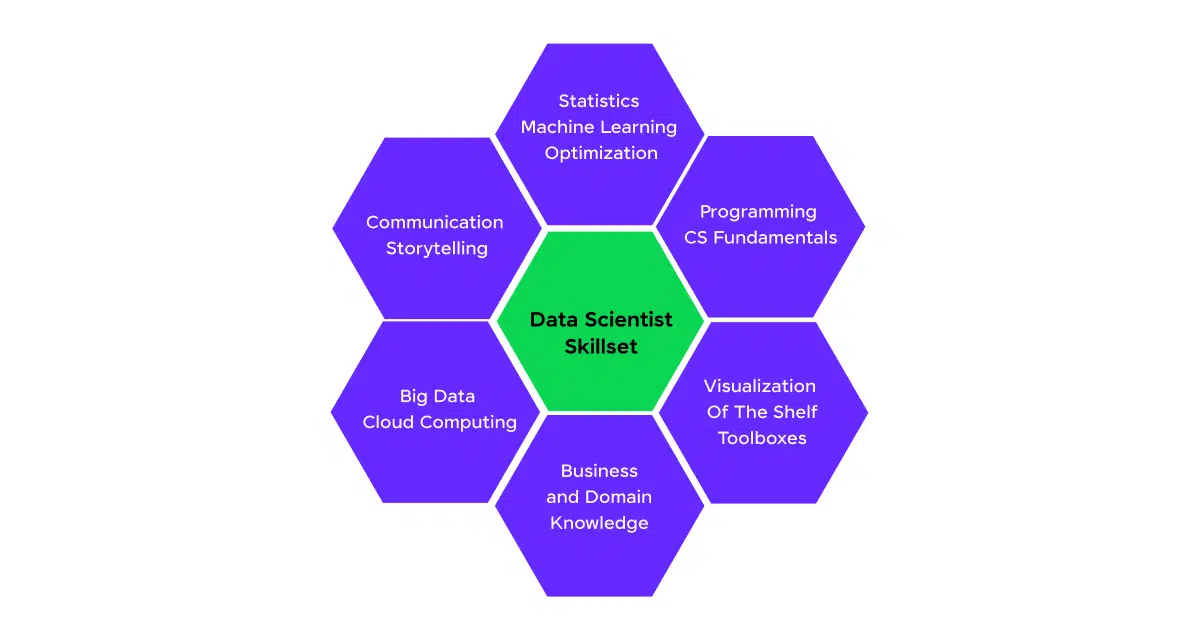
- Statistical Analysis and Mathematics: This involves understanding statistical methods, probability theory, and linear algebra to analyze data and draw meaningful inferences.
These skills are fundamental for developing models, conducting hypothesis testing, and making data-driven decisions. They help you understand data patterns, correlations, and predictions.
- Programming (Python, R): Proficiency in programming languages like Python and R, which are widely used for data manipulation, analysis, and machine learning.
Programming skills allow you to automate data processing, build machine learning models, and perform complex statistical computations. Python’s libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and Scikit-learn are essential tools for any data scientist.
- Data Wrangling and Cleaning: The process of cleaning, transforming, and organizing raw data into a usable format.
Data wrangling is critical because real-world data is often messy and incomplete. This skill ensures that data is accurate and ready for analysis, which is crucial for building reliable models.
- Machine Learning: This is the study and application of algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make predictions based on data.
Machine learning is at the heart of data science, enabling the creation of predictive models, recommendation systems, and automated decision-making processes.
- Data Visualization (Tableau, Power BI): The ability to create graphical representations of data to help communicate findings to stakeholders.
Visualization helps in understanding complex data sets and presenting insights in a way that is accessible and actionable for non-technical audiences. Tools like Tableau and Power BI are commonly used in the industry.
- Big Data Tools (Hadoop, Spark): Technologies for processing and analyzing large data sets that exceed the capacity of traditional databases.
As the volume of data grows, proficiency in big data tools like Hadoop and Spark is essential for efficiently handling and analyzing massive data sets.
- Domain Knowledge: Understanding the specific industry or field where data science is applied, such as finance, healthcare, or e-commerce.
Domain knowledge allows data scientists to apply their technical skills more effectively by understanding the context and relevance of the data they are working with.
The Computer Science Skillset
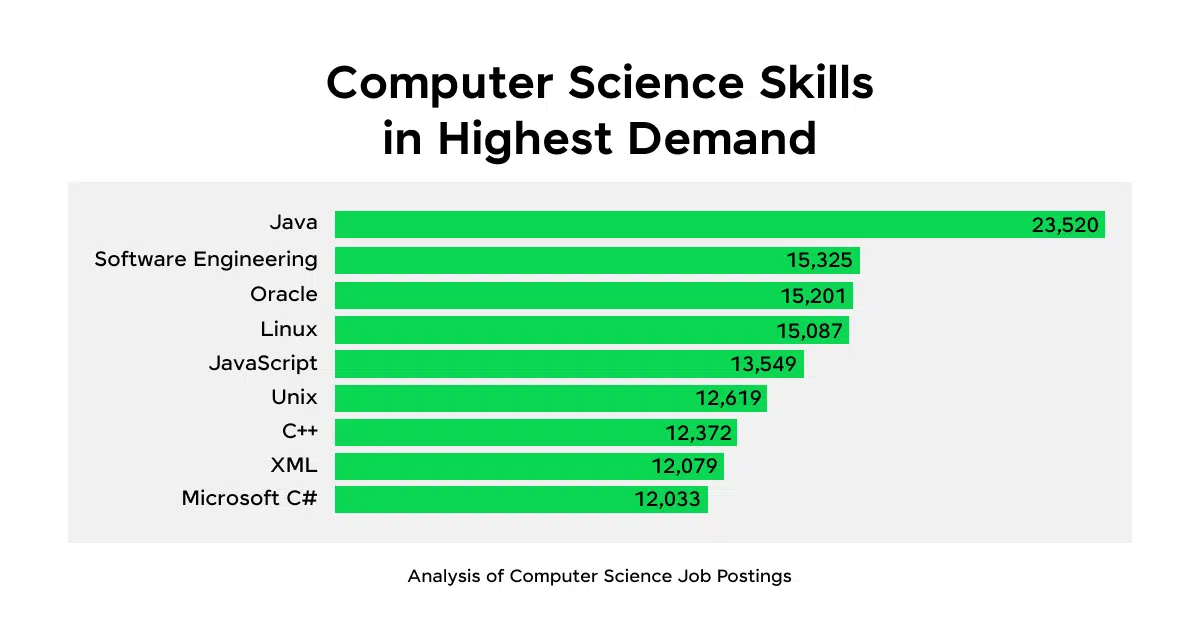
- Programming (C++, Java, Python): Mastery of programming languages such as C++, Java, and Python, which are essential for software development and system design.
Programming is the backbone of Computer Science. These languages are used for building applications, writing algorithms, and solving complex computational problems. Python is also versatile for scripting and data processing.
- Data Structures and Algorithms: Understanding and implementing data structures (e.g., arrays, linked lists, trees) and algorithms (e.g., sorting, searching).
Efficient data structures and algorithms are crucial for optimizing software performance and solving computational problems. This knowledge is fundamental in developing scalable and efficient software.
- Software Development and Engineering: The process of designing, coding, testing, and maintaining software applications.
Proficiency in software development ensures that you can create reliable, maintainable, and user-friendly applications. Knowledge of version control, agile methodologies, and testing frameworks is also essential.
- Systems Design and Architecture: Designing the structure of complex software systems, including the integration of various components and ensuring system scalability.
Good system design is critical for building software that is scalable, efficient, and easy to maintain. It involves understanding how different parts of a system interact and ensuring that they work together seamlessly.
- Operating Systems and Networking: Knowledge of how operating systems work, including memory management, process scheduling, and network communication.
Understanding operating systems and networking is essential for developing and managing software that interacts with hardware and other software across networks.
- Database Management (SQL, NoSQL): The ability to design, implement, and manage databases, both relational (SQL) and non-relational (NoSQL).
Efficient data storage and retrieval are key to software performance. Knowing how to work with databases ensures that applications can handle data effectively and scale as needed.
- Cybersecurity: The practice of protecting systems, networks, and data from digital attacks.
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, understanding cybersecurity principles is crucial for safeguarding software and data integrity.
Overlapping Skills
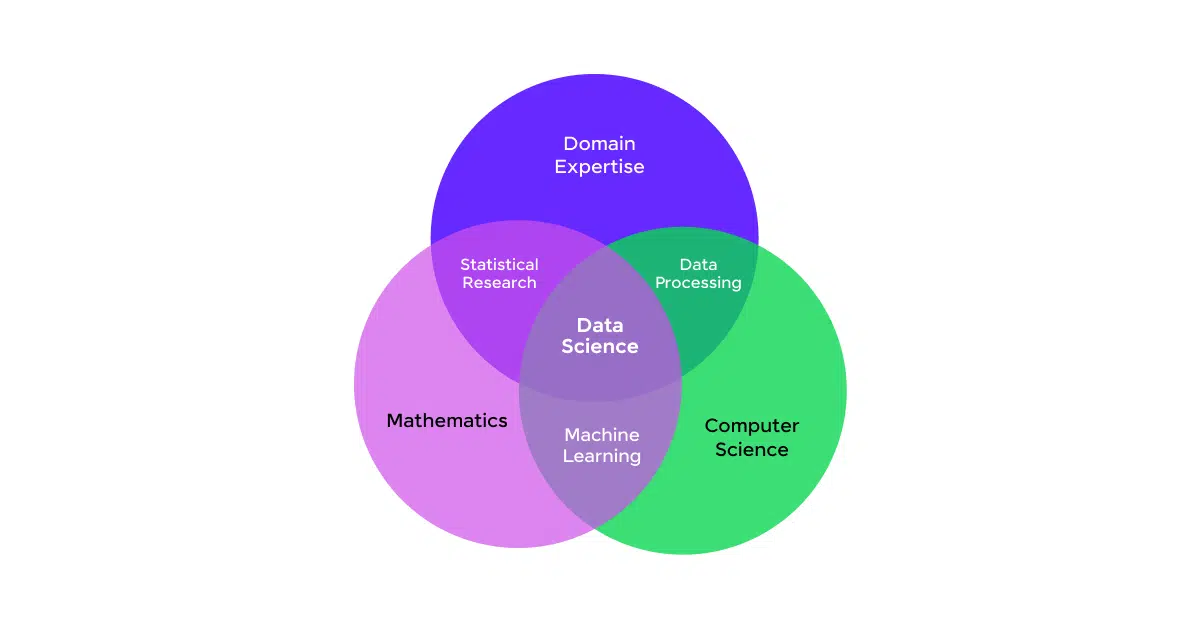
- Programming: Both Data Science and Computer Science heavily rely on programming. Data Scientists use Python and R for data analysis, while Computer Scientists use languages like C++ and Java for system development.
- SQL and Data Management: Managing and querying databases is a shared skill. Data Scientists use SQL for data extraction, while Computer Scientists use it to manage and integrate data within applications.
- Problem-Solving and Analytical Thinking: Both fields require strong problem-solving skills. Data Scientists analyze data to solve business problems, while Computer Scientists solve technical challenges in software and systems design.
- Cloud Computing (AWS, Azure): Knowledge of cloud platforms is valuable in both fields for deploying applications (Computer Science) and managing big data or machine learning models (Data Science).
Educational Pathways and Requirements
Now that we’ve covered what skills you need for both data science and computer science, let’s learn about the ways through which you can master them:
1. Data Science and Computer Science Graduate Degrees
- In Data Science focused graduate degrees such as BSc. Data Science/Big Data Analytics and MSc. Data Science, students focus on learning how to extract valuable insights from large datasets. This involves studying statistical methods, machine learning algorithms, and data visualization techniques.
You will learn programming languages such as Python and R, as well as tools like SQL for database management. Students also gain experience with big data technologies like Hadoop and cloud computing platforms.
The curriculum is designed to build skills in data analysis, predictive modeling, and data-driven decision-making, with opportunities to specialize in areas like deep learning or natural language processing (NLP).
- A Computer Science degree such as BSc. Computer Science or B. Tech Computer Science Engineering, on the other hand, covers a broader range of computing and software development topics. You will learn the core principles of algorithms, data structures, and system architecture.
Programming languages such as Java, C++, and Python are emphasized, along with courses in software engineering, operating systems, and database management. The program also teaches networking, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence, comprehensively understanding how software and hardware systems work together.
Graduates are equipped with skills to design, develop, and optimize complex software systems, making them versatile in various tech roles.
2. Online Courses and Industry Certifications
Online courses and certifications offer a flexible, fast-tracked alternative to traditional degree programs, making them ideal for those looking to quickly acquire new skills or shift careers.
- In Data Science, online courses you will learn essentials like data manipulation, machine learning, and statistical analysis. You’ll gain hands-on experience with tools such as Python, R, and SQL, and develop projects that help build a strong portfolio. And, a course that offers all the core concepts with career guidance is GUVI’s Data Science Course.
- For Computer Science, courses focus on programming languages (Java, C++, Python), algorithms, and software engineering principles. You’ll also learn about systems architecture, databases, and emerging fields like cybersecurity and cloud computing, all through practical, real-world coding projects. Learn all about advanced programming and full-stack development with GUVI’s Full Stack Development Course.
- Certifications: Certifications offer a targeted way to demonstrate expertise in specific areas. For Data Science, certifications like Certified Analytics Professional (CAP) and AWS Certified Data Analytics emphasize data handling and cloud computing. In Computer Science, certifications like CompTIA Security+ and AWS Certified Solutions Architect focus on cybersecurity and system design.
Online courses and certifications are perfect for those who need flexibility, such as working professionals or those looking to switch fields. They provide industry-relevant skills, updated to reflect current trends, and allow you to build a portfolio that showcases your expertise.
Job Roles, Responsibilities and Salaries
A) Data Science
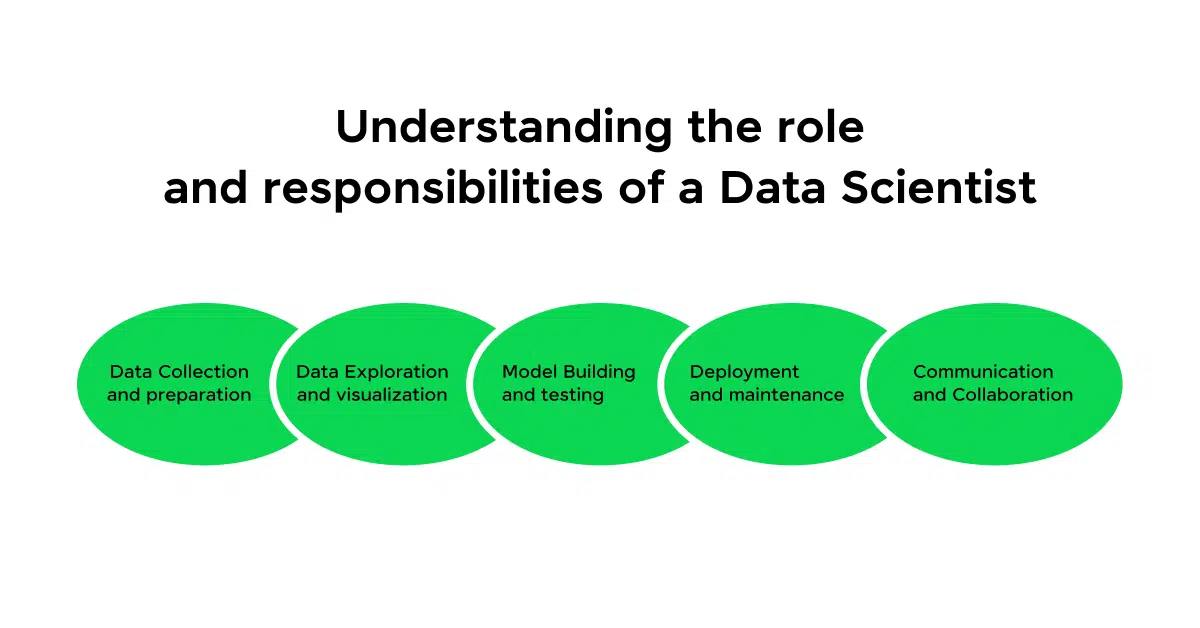
- Data Scientist
- Responsibilities: Analyze large datasets, build predictive models, and generate insights for decision-making.
- Must Know: Proficiency in Python, R, machine learning algorithms, statistics, and data visualization tools like Tableau or Power BI.
- Salary: ₹4L – ₹20L per annum
- Data Analyst
- Responsibilities: Interpret data to identify trends, create reports, and assist in strategic decision-making.
- Must Know: Strong skills in SQL, Excel, data visualization, and basic statistical analysis.
- Salary: ₹4L – ₹13L per annum
- Machine Learning Engineer
- Responsibilities: Develop and deploy machine learning models, optimize algorithms, and work on AI-driven applications.
- Must Know: Deep understanding of machine learning frameworks like TensorFlow, and PyTorch, programming in Python, and experience with big data tools such as Hadoop or Spark.
- Salary: ₹3L – ₹22.5L per annum
- Business Intelligence Analyst
- Responsibilities: Design and implement BI solutions, create dashboards, and report on business performance metrics.
- Must Know: Knowledge of BI tools like Power BI, Tableau, SQL, and an understanding of business operations.
- Salary: ₹3L – ₹18L per annum
- Data Engineer
- Responsibilities: Develop, construct, test, and maintain data architectures such as databases and large-scale processing systems.
- Must Know: Expertise in SQL, Python, ETL tools, cloud platforms (e.g., AWS, Google Cloud), and data pipeline frameworks like Apache Kafka.
- Salary: ₹4L – ₹21L per annum
B) Computer Science
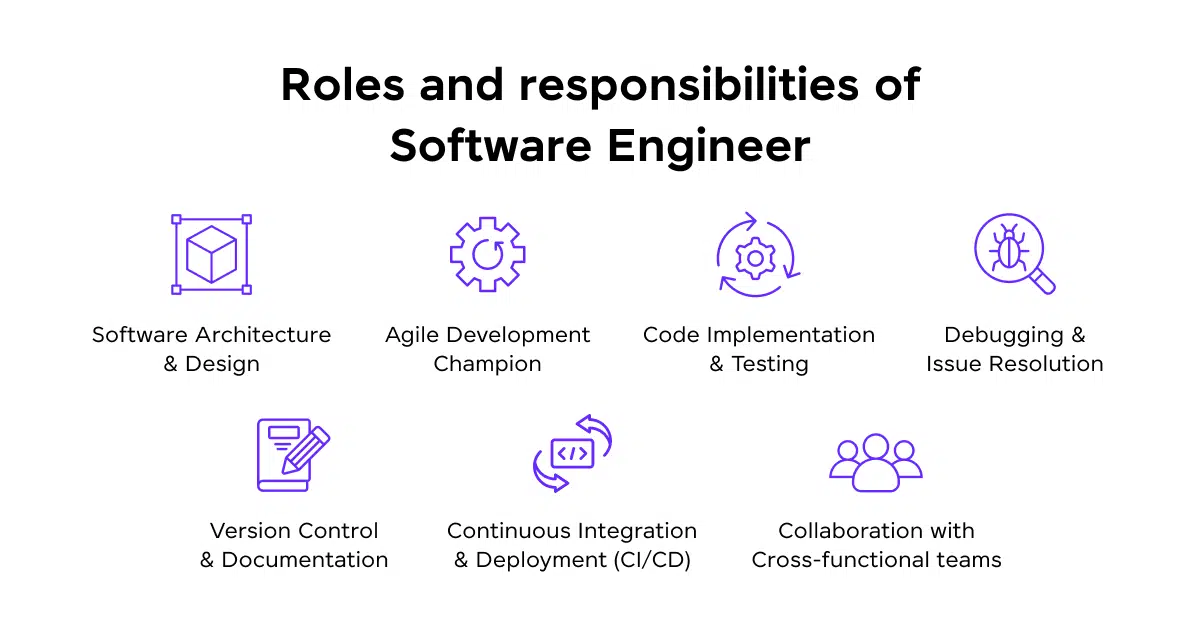
- Software Engineer
- Responsibilities: Design, develop, and maintain software applications, work on debugging, and ensure code efficiency.
- Must Know: Proficiency in programming languages like Java, C++, or Python, knowledge of software development lifecycle (SDLC), and version control systems like Git.
- Salary: ₹3L – ₹16L per annum
- Systems Architect
- Responsibilities: Design and manage complex IT systems, ensure scalability and integrate new technologies into existing frameworks.
- Must Know: Deep knowledge of system architecture, cloud computing, networking, and an understanding of various operating systems.
- Salary: ₹6L – ₹47.2L per annum
- Database Administrator
- Responsibilities: Manage, back up, and ensure the security of databases, optimize database performance, and handle disaster recovery.
- Must Know: Expertise in SQL, knowledge of database management systems like MySQL, Oracle, or MongoDB, and experience with database tuning.
- Salary: ₹4.6L – ₹24L per annum
- Cybersecurity Analyst
- Responsibilities: Protect organizational data, monitor security breaches, and develop strategies to prevent cyberattacks.
- Must Know: In-depth knowledge of security protocols, encryption techniques, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and experience with tools like Wireshark or Splunk.
- Salary: ₹3L – ₹11.5L per annum
- AI Engineer
- Responsibilities: Design and implement AI models, integrate AI systems into applications and work on NLP, computer vision, or robotics.
- Must Know: Strong understanding of machine learning, neural networks, Python, and experience with AI frameworks like TensorFlow or Keras.
- Salary: ₹3L – ₹22L per annum
Data Science vs Computer Science: Choosing Your Career Path
Assessing Your Interests
- Self-Assessment: Reflect on your personal interests. Do you enjoy solving complex puzzles and coding (Computer Science), or are you more fascinated by analyzing data and deriving actionable insights (Data Science)?
Interest in software development or systems architecture often leads to a Computer Science career, whereas a passion for statistical analysis and working with data tends to guide you towards Data Science.
- Hands-On Experience: Try out introductory courses or projects in both fields to get a practical sense of what each discipline entails.
Gaining experience through projects or internships can help clarify your preference, whether it’s building applications (Computer Science) or creating data-driven solutions (Data Science).
Evaluating Your Strengths
- Technical Aptitude: Evaluate your strengths in areas like mathematics, logic, and problem-solving.
Strong mathematical and analytical skills are crucial in Data Science, while logical reasoning and a knack for programming are essential in Computer Science.
- Skill Development: Identify which skills you’re naturally inclined towards—statistical analysis, programming, data management, or system design—and focus on honing them.
Enhancing your strengths in data analysis and statistics will gear you towards roles like Data Scientist or Machine Learning Engineer. Conversely, excelling in programming and algorithms prepares you for Software Engineering or Systems Architecture.
Long-term Career Goals
- Career Vision: Think about where you want to be in the next 5-10 years. Are you aiming for a role in a high-growth field like AI or big data, or are you more interested in a traditional tech role with stability and a clear growth path?
Aiming for roles in emerging technologies like AI and data Science might be more suitable, while those seeking to contribute to foundational technology development might find a better fit in Computer Science.
- Specialization vs. Generalization: Decide if you want to specialize in a niche area like AI, cybersecurity, or big data, or if you prefer a broader scope in technology development.
Specializing in areas like AI or machine learning is more aligned with Data Science, while a broader tech role, such as full-stack development, typically requires a Computer Science background.
Kickstart your Data Science journey by enrolling in GUVI’s Data Science Course where you will master technologies like MongoDB, Tableau, PowerBI, Pandas, etc., and build interesting real-life projects.
Alternatively, if you would like to explore Python through a Self-paced course, try GUVI’s Python certification course.
Concluding Thoughts…
Choosing between data science and computer science is a significant decision and choosing the right one for YOU is important as it can make or break your career. Both fields offer exciting opportunities and have the potential to cause a revolution in various industries.
If you’re interested in dealing with data manipulation and analysis, you must go for data science as a career, whereas if you’re interested in programming or coding, playing with codes and machines, then you can choose computer science as a career.
Your choice should align with your interests, strengths, and long-term goals while considering the current and future trends in the tech industry.
FAQs
Yes, data science is a good alternative to computer science if you’re interested in data analysis, machine learning, and statistics rather than traditional programming and software development. It offers lucrative career opportunities in fields like AI, business analytics, and research.
AI is unlikely to replace data scientists entirely but will automate routine tasks. Data scientists will still be needed for complex problem-solving, interpreting AI outputs, and developing new models.
Yes, data science is expected to be in high demand in 2030 due to the growing reliance on data-driven decision-making across industries. The need for skilled professionals to analyze and interpret data will continue to rise.
Yes, data science often pays more than traditional computer science roles, especially in specialized positions like machine learning engineers(₹3L- ₹22.5L) or data scientists(₹4L – ₹20L), due to the high demand for advanced data analytics and AI skills.


















![Top 10 Mistakes to Avoid in Your Data Science Career [2025] 10 data science](https://www.guvi.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Beginner-mistakes-in-data-science-career.webp)





Did you enjoy this article?