
Data Scientist or Data Engineer: Which Path Is Right for You
Mar 21, 2025 6 Min Read 2831 Views
(Last Updated)
When it comes to data, there are two key professions which people often might be confused about. Know that they are? It’s the role of data scientist and data engineer. Pretty sure that you also might be confused about what these two are.
As data shapes more of our world, knowing the differences between these two fields is key for people who want to start a good career in any one of them.
In this article, we will discuss whether you should become a data scientist or data engineer and learn all the important aspects of both of these interesting fields. Hopefully, you’ll find the right career path for you!
Table of contents
- What is Data Science?
- Data Science Life Cycle
- The Key Skills of a Data Scientist
- A Day in the Life of a Data Scientist
- What is Data Engineering?
- The Key Skills of a Data Engineer
- A Look into the Life of a Data Engineer
- Data Science vs. Data Engineering: What's the Difference?
- Things to Consider When Choosing Your Career
- What You Love and Find Interesting
- Salary Comparison
- Skill Alignment
- Career Goals and Opportunities
- Learning Preferences
- Data Engineer and Data Scientist – Who Gets Hired More?
- Companies Hiring Data Scientists
- Companies Hiring Data Engineers
- Startups & Mid-Sized Companies Hiring
- Data Scientist vs. Data Engineer: Which Is Best for You?
- Choose Data Science if you:
- Choose Data Engineering if you:
- Can You Switch Between the Two?
- Takeaways…
- FAQ’s
- Is it better to be a data engineer or a data scientist?
- Do data scientists earn more than data engineers?
- Is it easy to switch from data engineer to data scientist?
- Can a data engineer become a data scientist?
What is Data Science?
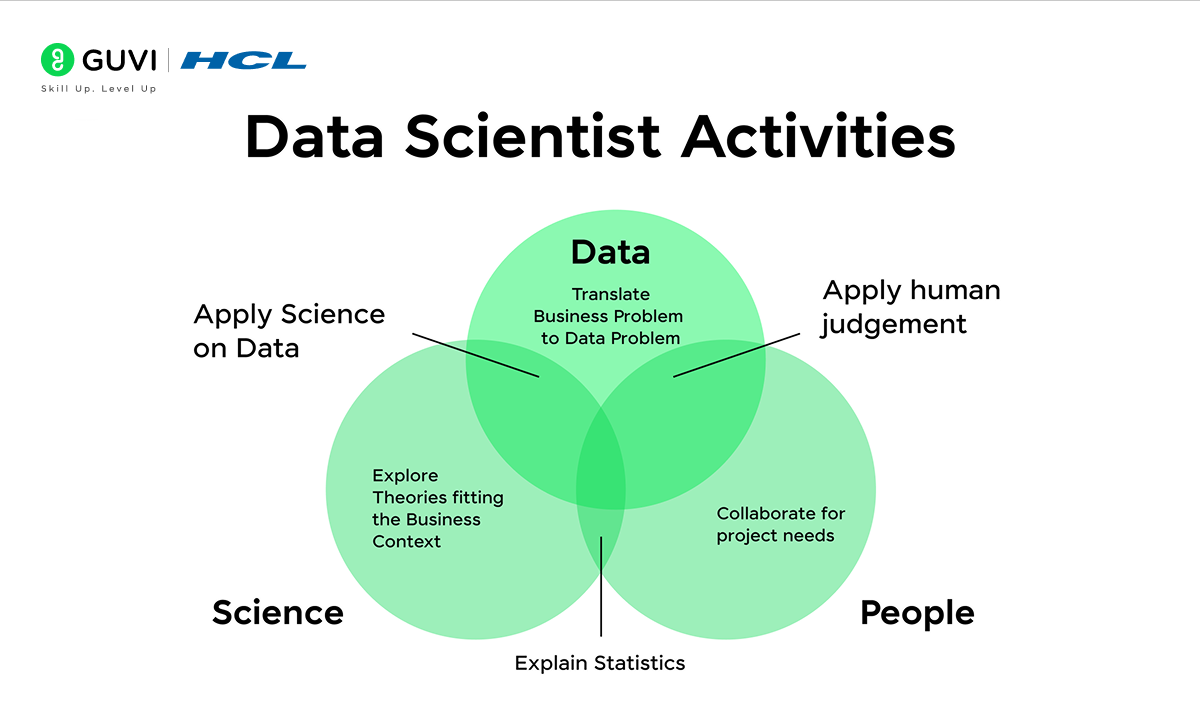
Data Science involves getting useful insights from tonnes of data. It uses a mix of computer science, math, machine learning, and data management methods to find hidden patterns, trends, and links.
These findings can help make vital choices, boost research and new ideas, and even lead to new products and services.
Data Science Life Cycle
The data science life cycle is a systematic process used to extract knowledge and insights from data. Here are the key steps involved:
- Problem Definition: Identify and understand the problem or question to be addressed.
- Data Collection: Gather relevant data from various sources.
- Data Cleaning: Preprocess and clean the data to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): Analyze the data to discover patterns, trends, and relationships.
- Feature Engineering: Create and select relevant features that will be used in modeling.
- Model Building: Develop machine learning models to make predictions or classify data.
- Model Evaluation: Assess the performance of the models using appropriate metrics.
- Model Deployment: Implement the model in a real-world environment.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Continuously monitor the model’s performance and make necessary updates.
The Key Skills of a Data Scientist
To succeed as a Data Scientist, you need a wide range of abilities:
- Computer Science: To excel in data science, you must know how to code in SQL, Python, and R. You should also understand software design and engineering principles.
- Mathematics: Data analysis relies on a strong foundation in applied math. This includes knowledge of stats, probability, and linear algebra.
- Machine Learning: You must be familiar with different machine learning methods. These include unsupervised learning, supervised learning, reinforcement learning, and deep learning with neural networks. It’s also crucial to know how to use machine learning libraries like Pandas.
- Managing Data: A Data Scientist’s toolkit must include abilities to wrangle and mine data, keep databases in good shape, query and manipulate data, clean it up, and handle big data.
- Data Visualization: A key skill is a knack for turning complex data insights into eye-catching visuals using tools like Matplotlib and Tableau.
A Day in the Life of a Data Scientist
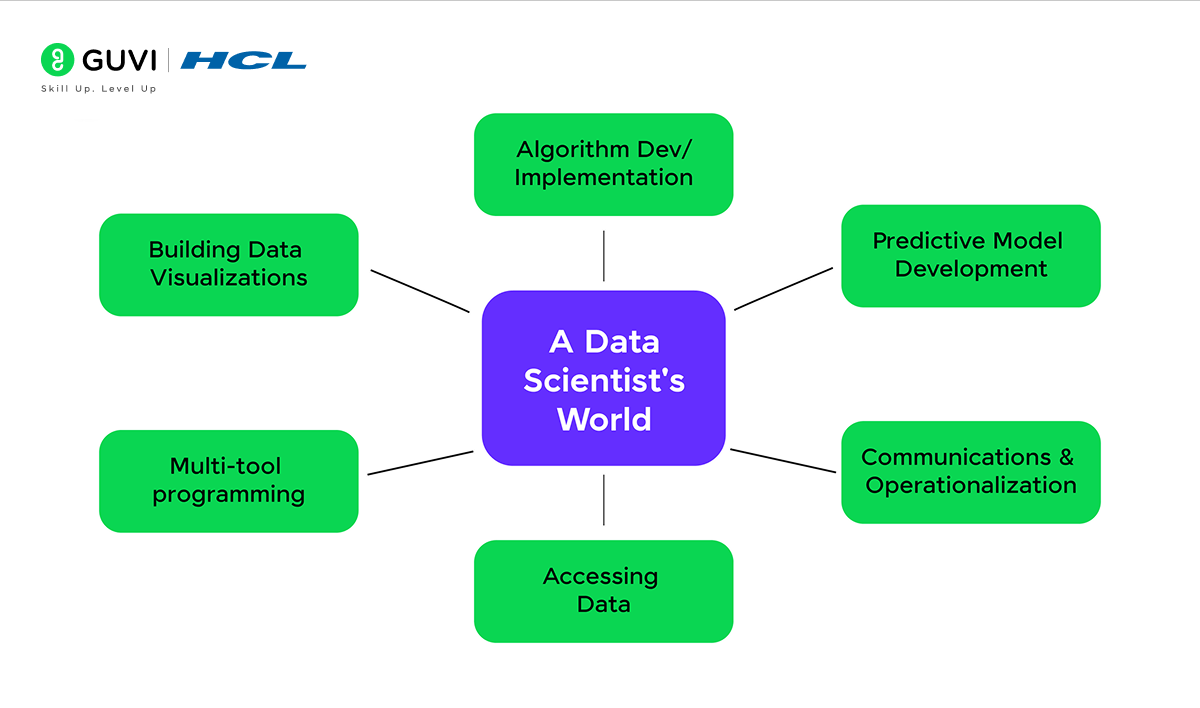
Being a Data Scientist means having a wide range of daily tasks, just like the key skills you need. These pros develop and push forward analytics projects, write code, train machine learning models, make sense of analysis results, and share insights with key people.
Take, for example, a Data Scientist working on sales analytics for Reality Labs at a company like Meta (Facebook). Their job would include:
- Partnering with Product, Engineering, and other teams to lead analytics projects from start to finish. These projects have an influence on product strategy and investment choices.
- Shaping product direction through clear persuasive talks to leadership.
- Tackling a wide range of tough problems using various analytical and statistical methods, while handling big complex datasets.
What is Data Engineering?
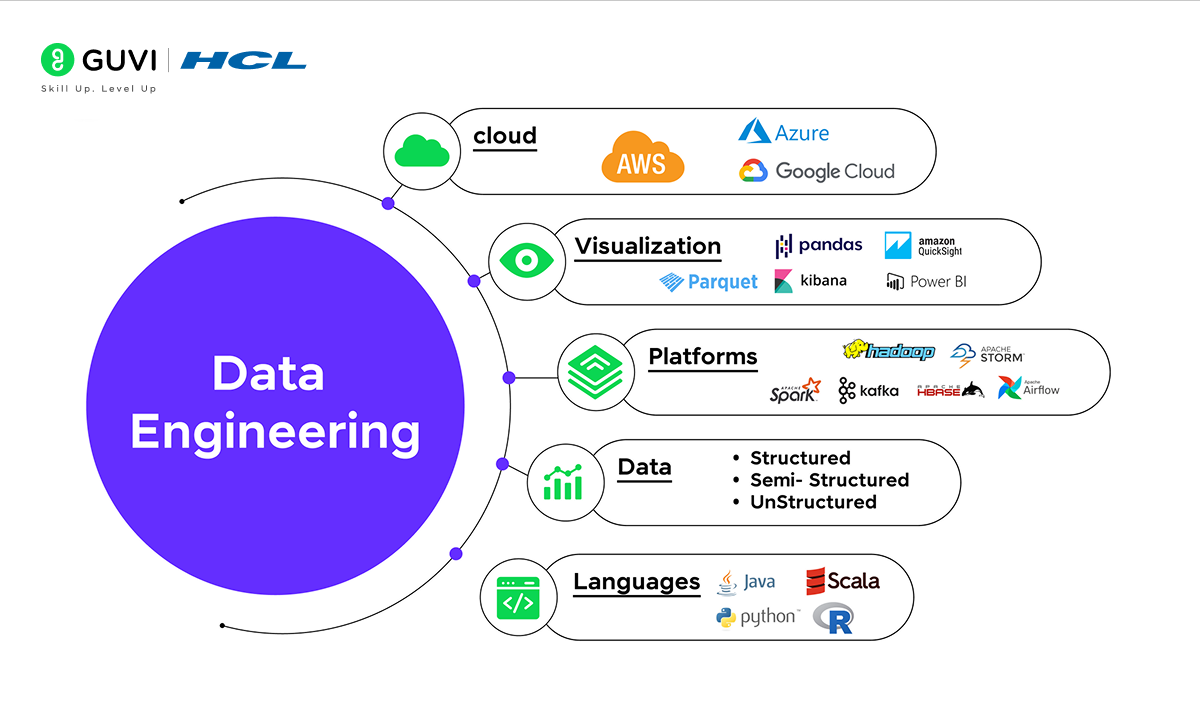
Data Engineering, in contrast, aims to put into action, assess, and keep up data structures, like data pipelines, databases, and other systems to process data.
It serves as the foundation to ensure easy access to data for various uses such as machine learning projects and automated factory production methods.
The Key Skills of a Data Engineer
While some skills overlap with those needed for Data Science, Data Engineers rely more on know-how in computer science and how to manage data:
- Computer Science: Deep knowledge of SQL, Python, R, C, C++, and Java programming languages, along with a thorough grasp of operating systems (Linux, Unix, Windows macOS), and software development principles.
- Data Management: Skill in tools to manage databases, transform data, mine data, create data pipelines, and use cloud computing is key.
- Analytical Acumen: A basic grasp of data analytics, including statistical analysis and the basics of artificial intelligence and machine learning, is needed.
- Visualization: Knowledge of tools like Matplotlib and Tableau is crucial to visualize data well.
A Look into the Life of a Data Engineer
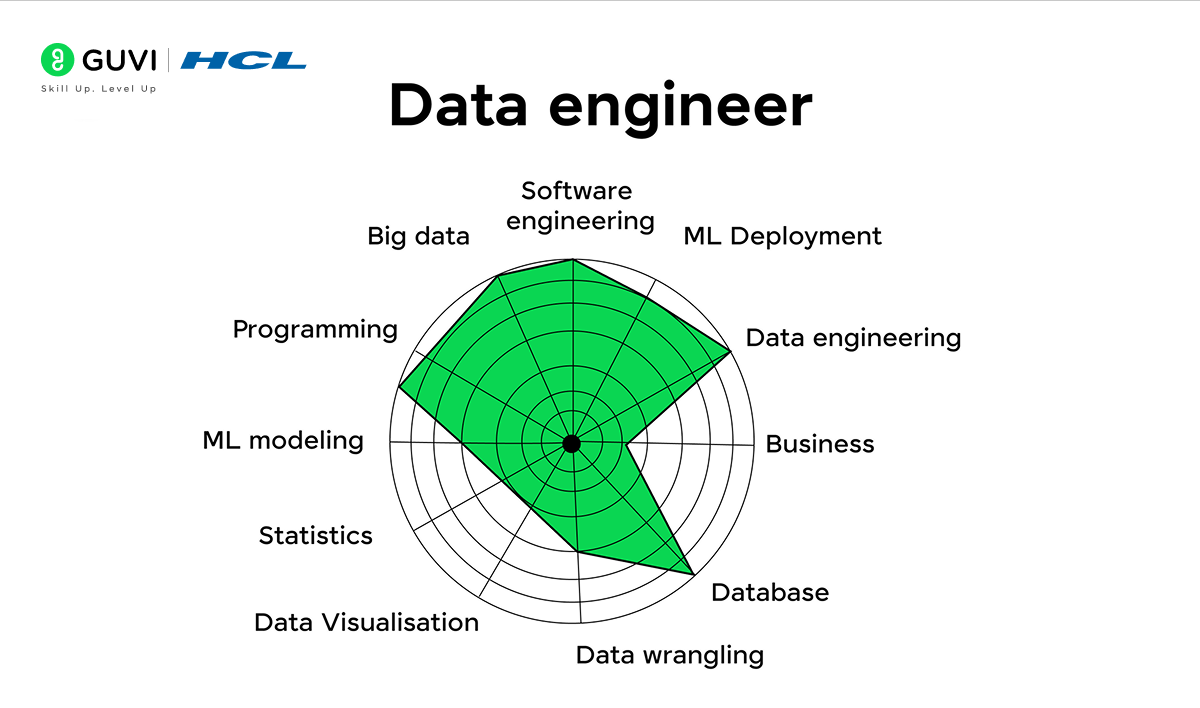
A Data Engineer spends most of their day writing code. They create data pipelines, run tests, and fix problems in systems that are already in use. But being good at talking to others matters just as much.
At a company like Meta, a Data Engineer in the analytics program would have to:
- Design and oversee the data architecture for several big projects while weighing design and operational trade-offs in systems.
- Build and add to frameworks that boost the effectiveness of data logging, teaming up with data infrastructure to sort out and fix problems.
- Team up with engineers, product managers, and Data Scientists to get what data they need and show key data insights in a clear way.
Data Science vs. Data Engineering: What’s the Difference?
Data Science and Data Engineering have some things in common and even might sound the same, but they have different main goals and jobs.
Data Science tries to get insights from data and create models that predict things. Data Engineering makes sure a company’s data systems work well, including getting data ready for Data Scientists to use.
| Aspect | Data Scientist | Data Engineer |
| Primary Focus | Analyzing data to generate insights | Building and maintaining data infrastructure |
| Goal | Create models and guide decisions | Ensure reliable, scalable data systems |
| Core Skills | Statistics, ML, data visualization, Python, R | SQL, ETL, big data tools, cloud engineering |
| Tools | Jupyter, Tableau, scikit-learn | Spark, Hadoop, Airflow, Kafka, Snowflake |
| Output | Reports, dashboards, ML models | Data pipelines, APIs, databases |
| Collaboration | Works with business and product teams | Works with data scientists and dev teams |
| Mindset | Analytical and research-focused | Engineering and system-focused |
Things to Consider When Choosing Your Career
Choosing between Data Science and Data Engineering is up to you. You should think about what you like, what you’re good at, and what you want from your career. Here are some important things to consider:
1. What You Love and Find Interesting
- If you love to analyze data, create predictive models, and find useful insights, Data Science might be perfect for you.
- But if you enjoy designing efficient data systems, making pipelines better, and keeping data reliable, Data Engineering could be your thing.
2. Salary Comparison
Here’s a salary comparison table between data engineers and data scientists in India:
| Experience Level | Data Engineer (INR per annum) | Data Scientist (INR per annum) |
| Entry-Level (0-2 years) | 4 – 7 lakhs | 5 – 8 lakhs |
| Mid-Level (2-5 years) | 7 – 15 lakhs | 8 – 18 lakhs |
| Senior-Level (5+ years) | 15 – 30 lakhs | 18 – 35 lakhs |
| Lead/Managerial | 30+ lakhs | 35+ lakhs |
Note: Salaries can vary significantly based on factors such as company size, industry, location, and individual qualifications.
3. Skill Alignment
- Look at your current skills and see where you excel. If you’re great with computer science, coding, and managing data, Data Engineering might suit you well.
- On the flip side, if you excel in applied math, stats, and machine learning, Data Science could be right up your alley.
- Go through the above sections where we discuss both data science and data engineering skill sets at length.
4. Career Goals and Opportunities
A) Data Science
Opportunities:
- Data Analyst: Entry-level role responsible for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to provide actionable insights.
- Data Scientist: Engages in advanced data analysis, statistical modeling, and the development of machine learning algorithms.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Specializes in creating and deploying machine learning models.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Analyst: Focuses on leveraging data to support business decisions and strategy development.
- AI Research Scientist: Works on developing cutting-edge artificial intelligence techniques and applications.
Growth Path:
- Junior Data Scientist: Start by working on data cleaning, exploratory data analysis, and basic model development.
- Data Scientist: Progress to handling more complex data problems, leading projects, and refining predictive models.
- Senior Data Scientist: Take on strategic responsibilities, mentor junior data scientists, and lead data-driven business initiatives.
- Lead Data Scientist/Principal Data Scientist: Oversee large-scale projects, shape data strategy, and influence business decisions at a high level.
- Chief Data Scientist: Define the data vision for the organization, guide data science teams, and drive innovation across the company.
B) Data Engineering
Opportunities:
- Data Engineer: Focuses on designing, building, and maintaining the data infrastructure and pipelines required for data processing and analysis.
- Big Data Engineer: Specializes in handling large-scale data processing frameworks and tools like Hadoop and Spark.
- Data Architect: Designs and manages data frameworks and systems that support data storage, processing, and retrieval.
- ETL Developer: Works on Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL) processes to integrate data from various sources.
- Database Administrator (DBA): Manages and optimizes databases to ensure data availability, performance, and security.
Growth Path:
- Junior Data Engineer: Begin by learning data integration techniques, building data pipelines, and understanding database management.
- Data Engineer: Advance in designing scalable data solutions, optimizing data pipelines, and working with big data technologies.
- Senior Data Engineer: Lead complex data projects, mentor junior engineers, and ensure the efficiency and scalability of data systems.
- Lead Data Engineer/Architect: Oversee data architecture design, manage data engineering teams, and drive improvements in data infrastructure.
- Chief Data Officer (CDO): Shape the organization’s overall data strategy, manage data governance, and lead data-centric initiatives across the enterprise.
Both data science and data engineering offer rewarding career paths with significant growth potential.
5. Learning Preferences
- Start your learning journey by enrolling in online certification programs that don’t just help you upskill but also add major value to your resume, such as the GUVI Data Science Course.
- Data Science training focuses on stats, machine learning, coding in Python or R, and showing data.
- Data Engineering training, on the flip side, covers databases (SQL, NoSQL), big data tech, coding languages (Python, C++, Scala), and cloud computing.
- Think about how you want to learn, the traditional way by enrolling in a CS degree or upskilling with updated syllabi through online certifications and begin your journey, refer to our Blog Space for more questions you may have.
Data Engineer and Data Scientist – Who Gets Hired More?
As data continues to power everything from personalized recommendations to business forecasting, companies across industries are investing heavily in hiring both Data Engineers and Data Scientists.
Companies Hiring Data Scientists
Data Scientists are key players when it comes to modeling business problems, building predictive algorithms, and communicating insights. These professionals are highly sought after in industries like tech, healthcare, finance, retail, and logistics.
Here are some top companies actively hiring Data Scientists:
- Netflix – for recommendation engines and user behavior modeling
- Amazon – for fraud detection, inventory forecasting, and Alexa NLP
- Meta (Facebook) – for social graph analysis, user engagement prediction
- Spotify – for music recommendation and personalization algorithms
- IBM – for AI-driven solutions in enterprise and healthcare
- JP Morgan Chase – for financial risk analysis and trading models
- Zomato / Swiggy / Uber Eats – for delivery time predictions and customer analytics
Companies Hiring Data Engineers
Data Engineers are essential for designing, maintaining, and scaling data infrastructure. From ingesting raw data to ensuring it’s clean, structured, and accessible, data engineers are foundational to data operations.
Top companies hiring Data Engineers include:
- Google – for managing large-scale data lakes and ML platform pipelines
- Airbnb – for building real-time data infrastructure for pricing, listings, and search
- Uber – for ensuring data reliability across global mobility services
- Snowflake – for core engineering of cloud-based data platforms
- LinkedIn – for powering analytics, feeds, and personalization engines
- PayPal – for real-time fraud detection and transaction monitoring pipelines
- Flipkart / Myntra / Amazon India – for large-scale e-commerce data flow management
Startups & Mid-Sized Companies Hiring
In addition to big names, there’s explosive growth in startups, SaaS companies, and mid-sized enterprises looking to expand their data teams:
- Fintech: Razorpay, Stripe, Groww
- Healthtech: Practo, 1mg, Flatiron Health
- Edtech: BYJU’S, Coursera, Chegg
- SaaS: Freshworks, Zoho, HubSpot
Data Scientist vs. Data Engineer: Which Is Best for You?
Choosing between a career as a Data Scientist or a Data Engineer depends on your strengths, interests, and long-term goals. While both roles are part of the same data ecosystem, they attract very different types of thinkers.
Choose Data Science if you:
- Enjoy analyzing data to uncover patterns and insights
- Are fascinated by machine learning, AI, and statistics
- Like solving business problems through data-driven decision-making
- Want to spend your day building models, visualizations, and presentations
- Have strong skills in Python/R, math, and storytelling with data
Best for: Those who love research, experimentation, and communicating findings to drive business strategy.
Choose Data Engineering if you:
- Enjoy building systems and working on the technical backbone of applications
- Like writing efficient code, designing data pipelines, and managing databases
- Prefer working behind the scenes to ensure data is clean, fast, and accessible
- Are passionate about data architecture, ETL, and cloud infrastructure
- Have strong skills in SQL, Python/Scala/Java, and big data technologies
Best for: Those who love system design, backend engineering, and making sure everything “just works” at scale.
Can You Switch Between the Two?
Yes! Many professionals start in one role and eventually pivot. A Data Engineer may pick up analytics and move into Data Science, while a Data Scientist might deepen their coding and infrastructure skills and take on more engineering-focused tasks. The skills are complementary and companies increasingly value hybrid profiles that blend both.
Takeaways…
As the world becomes increasingly data-driven, the demand for skilled professionals in Data Science and Data Engineering will continue to soar. By carefully evaluating your interests, strengths, and career aspirations, you can make an informed decision that sets you on a rewarding path in this exciting and rapidly evolving field.
Remember, the journey to becoming a Data Scientist or Data Engineer is not a linear one. With the right education and experience, you can always pivot and explore alternative paths within the data ecosystem, such as Data Architecture, or even combine multiple disciplines.
The future belongs to those who can harness the power of data, and by choosing the path that resonates with you, you’ll be well-equipped to make a lasting impact in this data revolution.
FAQ’s
It depends on your interests. Data engineers focus on building and maintaining data infrastructure, while data scientists analyze and interpret complex data to provide insights. Choose based on your skills and career goals.
Typically, data engineers(₹3.5–20.9 lakhs) earn slightly more than data scientists, (₹ 4.0 Lakhs to ₹ 23.0 Lakhs)though this can vary based on location, experience, and industry.
Switching from data engineer to data scientist is possible but requires gaining expertise in statistical analysis, machine learning, and domain-specific knowledge.
Yes, a data engineer can become a data scientist. Transitioning involves acquiring skills in statistical analysis, machine learning, and data visualization, as well as gaining experience in data science projects.
















![10 Impressive Data Visualization Project Ideas [With Source Code] 7 Data Visualization Project Ideas](https://www.guvi.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/best_data_visualization_project_ideas_with_source_code_.webp)






Did you enjoy this article?