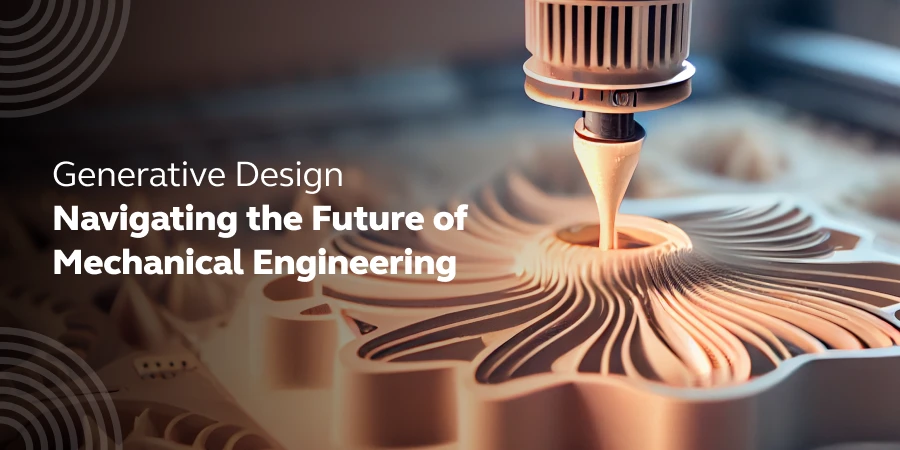
Generative Design: Navigating the Future of Mechanical Engineering
Apr 01, 2025 4 Min Read 4841 Views
(Last Updated)
Is generative design poised to change the landscape of mechanical engineering? This question, far from being mere speculation, taps into the heart of a constantly evolving field where creativity meets computational power.
The concept of generative design, emerging at the intersection of artificial intelligence, advanced software, and engineering expertise, is not just a fleeting trend; it’s a paradigm shift in how we approach problem-solving and design in engineering.
The genesis of generative design can be traced back to the beginning of computer-aided design (CAD) systems, yet it transcends traditional boundaries. Originally, CAD marked a significant leap from drawing boards to digital screens, enabling engineers to create and manipulate designs with remarkable precision. However, generative design pushes this envelope further.
It’s not just about drafting a design; it’s about letting an advanced algorithm explore many possibilities, learning and evolving with each iteration. This method, born from the fusion of machine learning and computational geometry, has opened doors to designs that were once considered unattainable or too complex for human minds.
Let’s understand further what generative design means specifically for mechanical engineering, where accuracy, efficiency, and innovation are not just goals but necessities.
Table of contents
- What is Generative Design?
- Generative Design Explained: Key Features and Benefits
- Methodologies and Technologies
- Key Features of Generative Design
- Benefits of Generative Design
- The Future of Generative Design in Mechanical Engineering
- Future Predictions and Potential Changes
- Wrapping Up
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What role does AI play in generative design?
- What are the limitations of adopting generative design in engineering?
- How Does generative design integrate with 3D printing technology?
- How is generative design transforming the automotive industry?
- What skills are required to specialize in generative design engineering?
What is Generative Design?

Generative design is an iterative design process that harnesses the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud computing to co-create designs alongside human engineers. It’s a symbiotic relationship where engineers define design goals and constraints, and the AI algorithms generate many design alternatives.
This process begins with inputting parameters such as materials, cost limits, manufacturing methods, and performance requirements. The generative design software then explores all feasible permutations of a solution, rapidly generating numerous design alternatives.
This is not a linear path but a dynamic exploration, with each iteration refining and evolving towards the most optimized design. The beauty of this approach lies in its ability to reveal solutions that are not immediately obvious, offering innovative and often more efficient alternatives than traditional methods.
Before we move on to the next part, you should have a deeper knowledge of key mechanical engineering concepts. You can consider enrolling yourself in GUVI’s CAD Program for Mechanical Engineers, which lets you gain practical experience by developing real-world projects and covers technologies including AutoCAD, Solidworks, CATIA, Ansys, GD & T, etc.
Additionally, if you would like to explore AutoCAD for Mechanical Engineering through a self-paced course, you can take GUVI’s AutoCAD Mechanical Certification Course.
Generative Design Explained: Key Features and Benefits
Generative design is reshaping the engineering domain by introducing groundbreaking features and benefits. It is more than just a new tool in the engineer’s arsenal: it’s a new way to think about design.
Let’s explore the specifics of generative design, understanding its methodologies, technologies, and the numerous advantages it offers.
Methodologies and Technologies
Algorithms, machine learning, and cloud computing are at the heart of generative design. This powerful trio works in unison to explore various design possibilities.
- Algorithms: Generative design algorithms are sophisticated pieces of code that can simulate various design conditions and generate multiple solutions based on predefined criteria.
- Machine learning: Machine learning allows the system to learn from each design iteration. It recognizes patterns, adapts to changes, and continuously improves the design outcomes.
- Cloud computing: Using cloud computing in generative design provides the necessary computational power. It allows for processing large data sets and design variables at incredible speeds.
Key Features of Generative Design
Generative design stands out for its unique features that set it apart from traditional design methods:
- Rapid iteration and exploration: Unlike traditional design processes, generative design can rapidly iterate through thousands of design options, exploring alternatives that might not be immediately apparent.
- Complex geometry and lightweight designs: The ability to create complex, lightweight designs that are both structurally sound and material-efficient is one of the hallmarks of generative design.
- Customization: Generative design allows for high levels of customization, catering to specific requirements and constraints in ways traditional methods cannot.
Benefits of Generative Design
The implications of these features of generative design are profound, offering numerous benefits:
- Optimization: Generative design excels at finding the most optimized solution for a given set of constraints, often yielding results that are stronger, lighter, and more efficient.
- Efficiency: The speed and ability to evaluate multiple options simultaneously significantly shorten the design cycle.
- Innovation: By pushing the boundaries of traditional design, generative design encourages innovation, leading to functional and aesthetically unique solutions.
- Sustainability: With an emphasis on material efficiency and waste reduction, generative design aligns well with sustainable engineering practices.
- Integration with advanced manufacturing: Generative design complements advanced manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing, enabling the production of complex designs that were previously not feasible.
The Future of Generative Design in Mechanical Engineering
At present, generative design is riding a wave of technological advancement, integrating with cutting-edge technologies to enhance its capabilities:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Integrating AI and machine learning continues to refine the generative design, making it more intuitive and capable of producing increasingly sophisticated designs.
- Internet of Things (IoT) and Big Data: As IoT devices proliferate and big data becomes more accessible, generative design benefits from a larger pool of real-world data, leading to more informed and practical design solutions.
- Advanced Materials Science: Exploring new materials and composites with generative design opens possibilities for creating lighter, more robust, and more sustainable products.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): These technologies can enhance the generative design process by enabling engineers to visualize and interact with designs in a more immersive way.
Also read | Best Ways to Learn Mechanical Engineering
Future Predictions and Potential Changes
Generative design is poised to bring about significant changes in various areas of engineering. Some of the predicted changes include:
- Customization and personalization: As the demand for personalized and custom-engineered solutions grows, generative design will be pivotal in catering to specific customer needs and preferences.
- Sustainability and eco-friendly designs: Generative design’s ability to optimize material usage aligns perfectly with the growing emphasis on sustainability, potentially leading to more eco-friendly engineering practices.
- Complexity and innovation in design: The future might see increased adoption of generative design in creating complex, innovative designs, particularly in industries like aerospace, automotive, and biomedical engineering.
- Democratization of design: With generative design software becoming more user-friendly and accessible, there is potential for democratization of design, enabling a more comprehensive range of professionals to contribute to innovative engineering solutions.
Find Out the Promising Scope of Mechanical Engineering in India in 2024
Kickstart your career by enrolling in GUVI’s CAD Career Program for Mechanical Engineers where you will master technologies including AutoCAD, Solidworks, CATIA, Ansys, GD & T, etc, and build interesting real-life mechanical projects.
Alternatively, if you would like to explore AutoCAD for Mechanical Engineering through a self-paced course, you can take GUVI’s AutoCAD Mechanical Certification Course.
Wrapping Up
According to Market Data Forecast, the global market for generative design is set to grow at 20.4 % annually from 2023 to 2028, pointing towards a robust demand across domains shortly.
With its roots in the convergence of AI, machine learning, and cloud computing, generative design has already begun redefining the boundaries of mechanical engineering. It transcends traditional design methodologies, introducing a dynamic, iterative process that yields optimized, efficient, and often groundbreaking solutions.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of generative design points towards a more inclusive, collaborative, and innovative engineering landscape. It promises a future where design limitations are continuously challenged and redefined, giving rise to engineering solutions that are as sustainable as they are revolutionary.
Overall, the future of generative design in mechanical engineering is bright, and it is undoubtedly one to watch with anticipation and excitement. If you’re an aspiring mechanical engineer, explore our Autodesk & IIT-M Pravartak-certified course in CAD design and simulation.
Also read | Generating Concepts for Product Design: Step-by-Step Guide [2024]
Frequently Asked Questions
AI enables generative design to iterate and optimize solutions rapidly, leveraging machine learning for innovative and efficient outcomes.
The key limitations include the need for high computational power, steep learning curves, and integration challenges with existing systems.
Generative design pairs with 3D printing to create complex, optimized structures unachievable through traditional manufacturing methods.
Generative design is transforming automotive engineering by enabling lighter, more robust components and accelerating design processes.
Specializing in generative design requires skills in CAD, AI, and machine learning and a strong foundation in engineering principles.

























Did you enjoy this article?