
Learning the basics of Ethical Hacking: A Guide
Apr 10, 2025 6 Min Read 4602 Views
(Last Updated)
Ever wondered how companies like Meta, which have tons of data, are safe from hackers? The transition to the digital world not only eases our lives but also puts us at risk of our data being exposed if the system gets hacked. But who keeps our data secure? That’s where ethical hacking comes into play.
With the increasing reliance on digital infrastructure, cybersecurity has become a number one concern for organizations across the globe. From protecting sensitive financial data to safeguarding personal user information, the role of ethical hackers, also known as white-hat hackers, has become more vital than ever.
Still confused about how a hacker protects us from hackers? Worry not, this article is designed to walk you through the basics of ethical hacking, how it differs from malicious hacking, what roles you can pursue, the salary trends in India, and how to start your journey in this exciting and impactful field. So, without further ado, let us get started!
Table of contents
- What is Ethical Hacking?
- Types of Ethical Hacking
- Web Application Hacking
- Network Hacking
- System Hacking
- Wireless Network Hacking
- Social Engineering
- The Ethical Hacking Process
- Reconnaissance (Information Gathering)
- Scanning
- Gaining Access
- Maintaining Access
- Clearing Tracks (Optional/Simulated)
- Reporting
- Average Salary of Ethical Hacker in India
- How to Start Your Ethical Hacking Journey?
- Build a Strong Foundation in IT and Networking
- Learn Key Programming and Scripting Languages
- Understand Cybersecurity Fundamentals
- Set Up a Practice Lab (Legally and Safely)
- Earn Industry-Recognized Certifications
- Join Cybersecurity Communities
- Start Small, Stay Ethical, and Keep Learning
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is ethical hacking?
- How can I become an ethical hacker?
- Is ethical hacking legal?
- Do ethical hackers need programming skills?
- Can I become an ethical hacker at 40?
What is Ethical Hacking?

Ethical hacking is the practice of legally breaking into computers and devices to test an organization’s defenses. It’s also referred to as penetration testing, white-hat hacking, or offensive security.
Unlike malicious hackers, ethical hackers work with authorization to identify security flaws and help organizations fix them before bad actors can exploit them.
To put it simply, ethical hacking mimics the mindset and techniques of cybercriminals, but the intent is constructive, not destructive. The goal is to proactively assess risks, uncover vulnerabilities, and strengthen the overall cybersecurity posture of the system or network.
Why is Ethical Hacking Important?
With businesses increasingly relying on digital infrastructure, cyber threats have also evolved. Data breaches, ransomware attacks, and unauthorized access can cause financial loss, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
Ethical hackers act as the first line of defense. Their job is to identify the same loopholes that a malicious hacker might exploit, but to fix them before it’s too late.
Some real-world examples of ethical hacking include:
- Testing web applications for SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS)
- Check network ports for unauthorized access points
- Attempting to bypass authentication systems
- Simulating phishing or social engineering attacks
If you are keen on learning more about why ethical hacking is essential in today’s data-driven world, read the blog – 15 Reasons Why You Should Learn Ethical Hacking
Types of Ethical Hacking
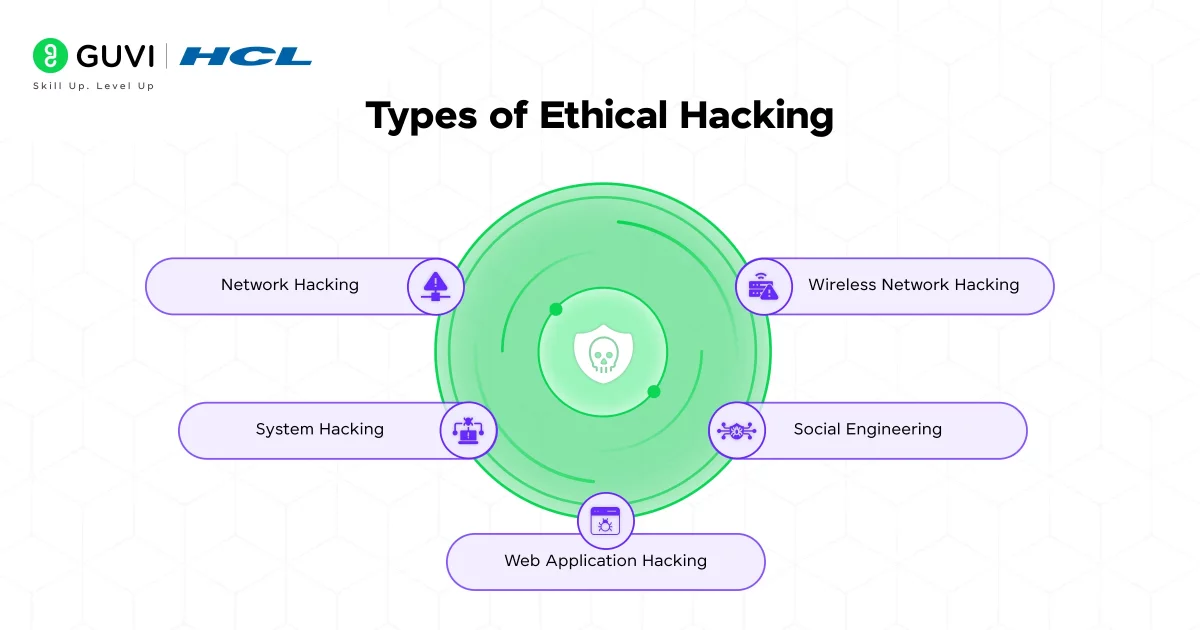
Ethical hacking is not a one-size-fits-all discipline, it spans a wide range of domains, each targeting different aspects of an organization’s digital infrastructure. Ethical hacking can be categorized based on the target system or environment. Here are the main types:
1. Web Application Hacking
This type focuses on testing the security of web-based applications by identifying vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and insecure authentication mechanisms. Ethical hackers simulate attacks to prevent data breaches, session hijacking, and unauthorized access through web interfaces.
Focuses on testing web applications for vulnerabilities like:
- SQL Injection
- Cross-site scripting (XSS)
- Broken authentication
- Insecure APIs
Goal: Ensure secure coding and prevent unauthorized access or data leaks.
2. Network Hacking
Network hacking involves assessing the security of an organization’s network infrastructure. Ethical hackers scan for open ports, unpatched systems, and weaknesses in firewalls or routers, helping to secure data transmission and prevent intrusions like man-in-the-middle or denial-of-service attacks.
Involves identifying weaknesses in network infrastructure:
- Unsecured ports
- Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks
- Packet sniffing
- Firewall bypass
Goal: Strengthen network configurations and block potential entry points for attackers.
3. System Hacking
System hacking targets operating systems and endpoint devices like computers or servers. Ethical hackers attempt to exploit system-level vulnerabilities, elevate privileges, or bypass authentication to identify and patch weaknesses that malicious attackers could abuse.
- Privilege escalation
- Malware injection
- Password cracking
Goal: Secure systems against unauthorized internal or external access.
4. Wireless Network Hacking
This involves analyzing the security of wireless communication protocols such as Wi-Fi. Ethical hackers attempt to crack encryption (like WEP/WPA), test for rogue access points, and exploit signal vulnerabilities to ensure that only authorized users can connect to the wireless network.
Involves testing Wi-Fi networks for vulnerabilities:
- WEP/WPA cracking
- Rogue access points
- Deauthentication attacks
Goal: Ensure secure encryption and prevent eavesdropping or unauthorized device access.
5. Social Engineering
Social engineering relies on manipulating people rather than technology. Ethical hackers test human vulnerabilities by simulating phishing emails, baiting, or impersonation tactics to evaluate how susceptible employees are to psychological manipulation and to enhance awareness training.
Focuses on manipulating humans rather than systems:
- Phishing emails
- Pretexting
- Baiting
Goal: Educate employees to recognize and respond to deception tactics.
The Ethical Hacking Process
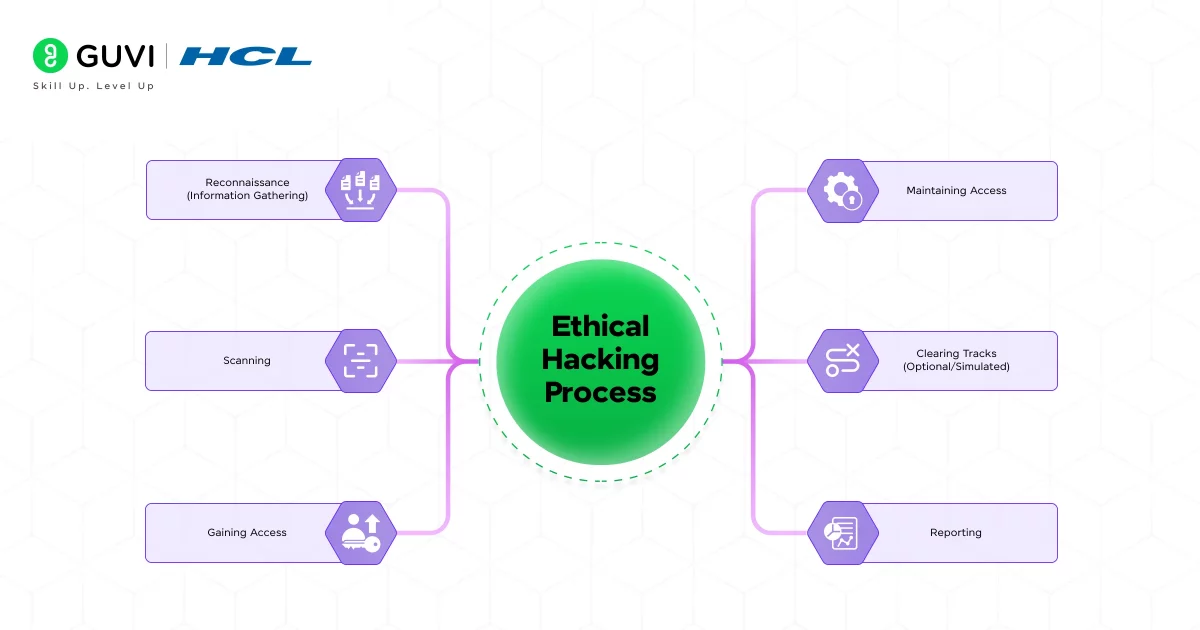
No matter the type, ethical hacking always follows a structured, step-by-step process that mirrors the path a real attacker might take. Understanding the standard process behind it is essential for anyone looking to build a strong foundation in cybersecurity.
Here are the key phases:
1. Reconnaissance (Information Gathering)
This initial phase involves collecting information about the target system or network to understand its structure and identify potential vulnerabilities. Ethical hackers use both passive methods (like public records) and active probing (like pinging servers) to prepare for deeper analysis.
- Passive Reconnaissance: Collect data without directly interacting with the target (e.g., using public websites or WHOIS data).
- Active Reconnaissance: Directly engage with the system (e.g., ping sweeps, port scans).
Goal: Understand the system’s structure, technologies, and potential weak spots.
2. Scanning
In the scanning phase, ethical hackers use tools to identify live hosts, open ports, and running services. This technical footprint helps pinpoint possible entry points and is essential for mapping the system’s external and internal attack surfaces.
- Techniques: Network scanning, port scanning, vulnerability scanning
- Tools Used: Nmap, Nessus, OpenVAS, Nikto
Goal: Create a blueprint of the system to identify potential attack vectors.
3. Gaining Access
Here, the ethical hacker exploits discovered vulnerabilities to gain entry into the system. This step mimics a real attacker’s intrusion and can involve techniques like brute force attacks, buffer overflows, or injection flaws to test the effectiveness of security defenses.
- Common Exploits: SQL injection, brute-force attacks, buffer overflows, misconfigurations
- Tools Used: Metasploit, SQLmap, Hydra
Goal: Gain authorized control of the system to evaluate its defenses.
4. Maintaining Access
Once access is gained, this phase tests whether a hacker can maintain that access undetected over time. Ethical hackers may simulate installing backdoors or Trojans to evaluate if and for how long an attacker could persist within the system without triggering alerts.
- Methods: Installing rootkits, creating new admin accounts, placing custom shells
- Purpose: To simulate what a real attacker would do to stay inside the system undetected.
Goal: Assess the system’s ability to detect and remove intruders.
5. Clearing Tracks (Optional/Simulated)
Although ethical hackers don’t erase evidence for real, this phase simulates methods attackers use to avoid detection, like altering logs or deleting footprints, helping organizations understand how to improve monitoring and response mechanisms.
- Activities: Deleting logs, altering timestamps, removing malware traces
- Purpose: Help the organization improve its logging, monitoring, and incident detection systems.
Goal: Help teams understand how attacks can go unnoticed and how to improve monitoring systems.
6. Reporting
After the 5-phase process, the ethical hacker prepares a comprehensive Vulnerability Assessment Report, which includes:
- Discovered vulnerabilities
- Risk levels (Low, Medium, High, Critical)
- Exploitation method
- Screenshots and Proof-of-Concepts
- Recommendations for mitigation
This report is then submitted to the concerned IT/security teams for remediation.
Average Salary of Ethical Hacker in India
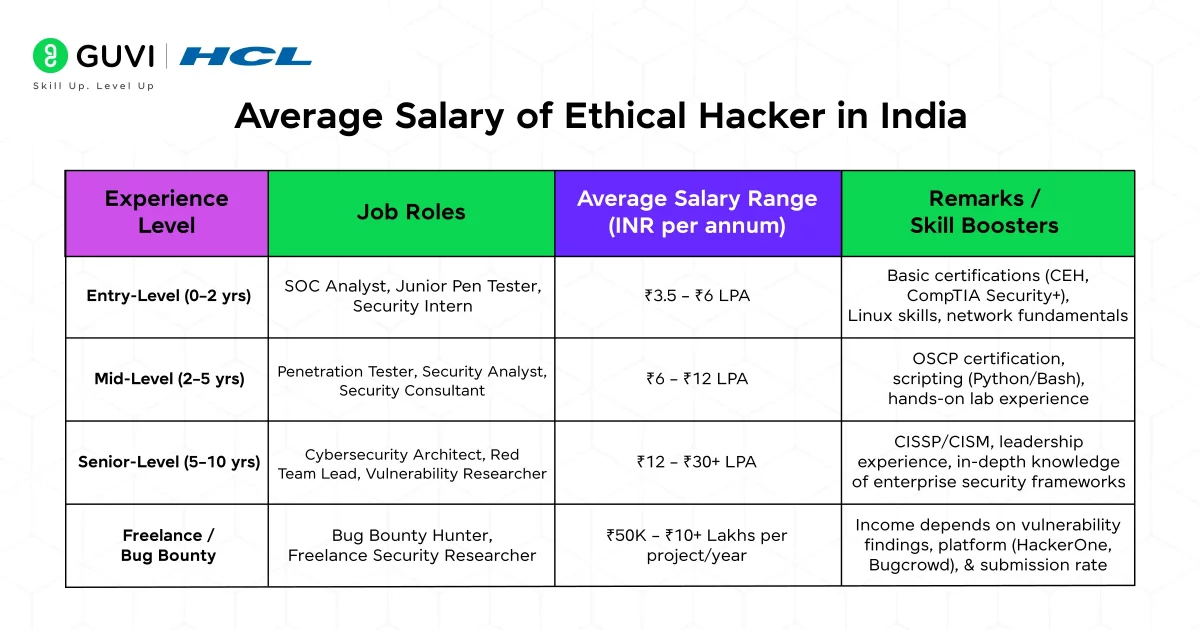
India is emerging as one of the largest hubs for cybersecurity talent. Ethical hackers with the right skills and certifications are handsomely rewarded, and the demand is only growing with the economy’s digitalization and increased data protection awareness.
Here’s a detailed look at what you can expect to earn based on experience and skill level:
| Experience Level | Job Roles | Average Salary Range (INR per annum) | Remarks / Skill Boosters |
| Entry-Level (0–2 years) | SOC Analyst, Junior Pen Tester, Security Intern | ₹3.5 – ₹6 LPA | Basic certifications (CEH, CompTIA Security+), Linux skills, network fundamentals |
| Mid-Level (2–5 years) | Penetration Tester, Security Analyst, Security Consultant | ₹6 – ₹12 LPA | OSCP certification, scripting (Python/Bash), hands-on lab experience |
| Senior-Level (5–10 years) | Cybersecurity Architect, Red Team Lead, Vulnerability Researcher | ₹12 – ₹30+ LPA | CISSP/CISM, leadership experience, in-depth knowledge of enterprise security frameworks |
| Freelance / Bug Bounty | Bug Bounty Hunter, Freelance Security Researcher | ₹50K – ₹10+ Lakhs per project/year | Income depends on vulnerability findings, platform (HackerOne, Bugcrowd), and submission rate |
Source: Fynd Things
Additional Tips:
- Metro cities like Bangalore, Hyderabad, Pune, and Delhi offer higher pay scales due to demand.
- Certifications significantly influence starting salaries and career growth.
- Experienced ethical hackers with niche skills (cloud security, reverse engineering, mobile security) can command premium packages.
How to Start Your Ethical Hacking Journey?
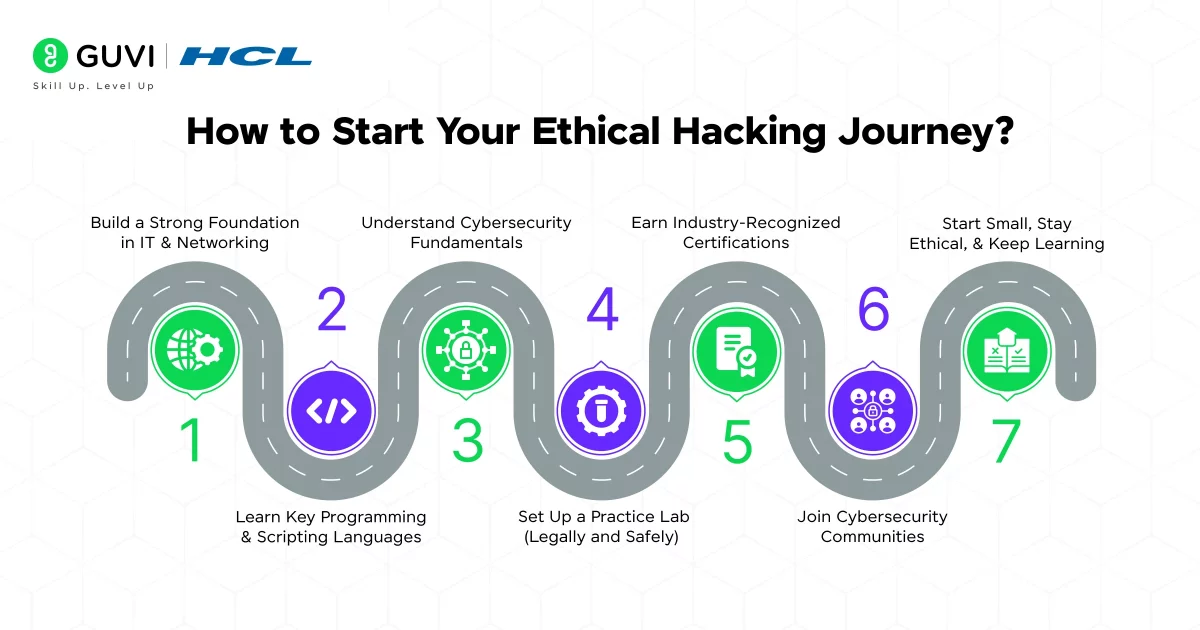
If you’re fascinated by cybersecurity and want to protect systems from cyber threats, ethical hacking is a rewarding path. But where do you begin?
The journey to becoming a successful ethical hacker requires a combination of foundational knowledge, technical skills, hands-on experience, and continuous learning.
Here’s a structured roadmap to help you get started:
1. Build a Strong Foundation in IT and Networking
Before diving into ethical hacking, it’s crucial to understand how computers, networks, and systems work. This includes:
- Operating Systems: Learn how Windows, Linux, and macOS function internally.
- Networking Basics: Understand TCP/IP, DNS, HTTP/S, firewalls, proxies, and ports.
- System Architecture: Know how software communicates with hardware.
Resources to start with:
- CompTIA Network+ or Cisco CCNA (networking)
- Linux essentials (Ubuntu, Kali Linux, or Parrot OS)
2. Learn Key Programming and Scripting Languages
While you don’t need to be a software developer, having a working knowledge of programming helps you understand vulnerabilities at the code level.
Start with:
- Python – For scripting and automation
- HTML & JavaScript – For understanding web vulnerabilities like XSS
- C/C++ – For low-level system interaction and buffer overflow attacks
- SQL – For testing injection flaws in databases
Tip: Python is considered the most beginner-friendly and versatile language for ethical hackers.
3. Understand Cybersecurity Fundamentals
Learn about core cybersecurity principles, such as:
- Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA Triad)
- Types of malware and cyber threats
- Encryption and hashing
- Security controls and frameworks
Explore platforms like:
- Cybrary
- Coursera
- edX
- GUVI’s Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking course
4. Set Up a Practice Lab (Legally and Safely)
Never test your skills on real systems without permission. Instead, create your home lab using tools like:
- VirtualBox or VMware to run VMs
- Metasploitable and DVWA (Damn Vulnerable Web App) to practice exploits
Or use online platforms:
- Hack The Box
- TryHackMe
- PortSwigger Labs
- CTF (Capture The Flag) Challenges
5. Earn Industry-Recognized Certifications
Certifications help validate your knowledge and can significantly boost your employability. Start with beginner-friendly ones and progress to advanced levels:
- CompTIA Security+ – Entry-level cybersecurity fundamentals
- CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker) – Globally recognized ethical hacking certification
- OSCP (Offensive Security Certified Professional) – Hands-on advanced certification
- eLearnSecurity, GIAC, or CISSP – For specialized areas
6. Join Cybersecurity Communities
Be part of the ethical hacking community to learn, collaborate, and grow. Join:
- Reddit (r/netsec, r/ethicalhacking)
- Discord and Telegram groups
- Bug bounty platforms like HackerOne, Bugcrowd, Synack
Networking with like-minded professionals can open up internships, mentorships, and job leads.
7. Start Small, Stay Ethical, and Keep Learning
As you gain confidence, apply for internships, freelance on bug bounty platforms, or contribute to open-source security projects. Most importantly, never engage in unauthorized hacking, even for “practice.”
Ethical hacking is all about the responsible use of knowledge.
In case you want to upskill your Ethical Hacking game by wanting to learn advanced in-depth concepts, consider enrolling in GUVI’s Advanced Ethical Hacking Online Course, by the end of this course, you’ll not only grasp a hacker’s mindset but also gain practical expertise through hands-on projects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ethical hacking is more than just a career, it’s a commitment to making the digital world safer for everyone. As cyber threats continue to evolve, so will the demand for skilled professionals who can anticipate, detect, and prevent attacks.
With the right mindset, technical foundation, and continuous learning, you can position yourself as a trusted cybersecurity expert.
Whether you’re aiming for a full-time role, freelancing through bug bounties, or contributing to national cyber defense, the opportunities in ethical hacking are not just promising, they’re essential.
FAQs
Ethical hacking involves authorized attempts to penetrate computer systems, networks, or applications to identify and fix security vulnerabilities. Unlike malicious hacking, ethical hacking is performed with the system owner’s consent to enhance security.
To become an ethical hacker, start by building a strong foundation in IT and networking. Learning programming languages like Python and understanding cybersecurity fundamentals are crucial. Gaining hands-on experience through labs and earning certifications such as CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker) can significantly boost your career prospects.
Yes, ethical hacking is legal when performed with proper authorization from the system owner. Ethical hackers adhere to a code of conduct and operate within the boundaries of the law to improve system security.
While not always mandatory, programming skills are highly beneficial for ethical hackers. Knowledge of languages like Python, C/C++, and JavaScript can help in understanding vulnerabilities and developing custom tools for security testing.
Yes, age is not a barrier to becoming an ethical hacker. With dedication, continuous learning, and practical experience, individuals of any age can acquire the skills and knowledge required to enter the field of ethical hacking.





























Did you enjoy this article?