Psychology of UX Design: 3 Important Keys to Understand
Jan 16, 2025 4 Min Read 2896 Views
(Last Updated)
When you think about the psychology of UX design, you’re delving into a world that goes far beyond just making things look good. It’s about tapping into emotions, creating connections, and understanding what drives user behavior.
This is where design psychology and UX psychology come into play, transforming how you experience digital products. Because emotional design in UX is not just a bonus; it’s a necessity.
Every detail in a design—from the color palette to the layout—can influence how you feel and interact with a product. But why is this so crucial?
Have you ever visited a website or used an app that just felt right? Chances are, the designers behind it mastered the art of emotional design. They knew how to evoke the right feelings, making your experience memorable and enjoyable.
This emotional connection is key to user engagement. It’s what turns a one-time visitor into a loyal user. And here’s where the magic of UX psychology comes in—it gives designers the tools to understand and influence these emotional responses.
So, as we explore the three important keys to unlocking the psychology of UX design, remember: it’s all about creating experiences that resonate on a deeper, emotional level. Let’s get started.
Table of contents
- Understanding the Psychology of UX Design
- Leveraging Color Psychology to Produce Emotions
- Building Emotional Engagement Through Micro-Interactions
- Using Personalization to Foster Strong Connections
- Wrapping Up
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the first steps in applying psychology to UX design?
- Can psychology in UX design improve website conversion rates?
- Are there any specific tools used in UX psychology for emotion analysis?
- What is a common mistake in using psychology in UX design?
- How does UX psychology address accessibility concerns?
- Can UX psychology principles apply to mobile app design?
- Is there a certification for UX designers in psychology?
Understanding the Psychology of UX Design

Grasping the psychology of UX design means dissecting the human brain— comprehending the intricate dance between emotion and decision-making.
Every click, swipe, or scroll is more than just a physical action; it’s a decision driven by underlying emotions. That’s where design psychology and UX psychology truly shine, revealing the ‘why?‘ behind user actions.
But what psychological principles are at play here? It boils down to a few core concepts.
Firstly, there’s the principle of the aesthetic-usability effect, which suggests that users often perceive aesthetically pleasing designs as more usable. Then, there’s the emotional contagion theory, which explains how we unconsciously mirror the emotions conveyed by a design. And last, the cognitive load theory, which reminds us that an overwhelmed mind is less likely to make positive decisions.
So, when you blend these psychological insights into your design process, you’re not just creating something that looks good but crafting an experience that feels good. And that feeling is what turns users into advocates for your design.
Let’s explore the three key elements to deciphering the psychology of UX design:
1. Leveraging Color Psychology to Produce Emotions
The power of color is undeniable. Colors do much more than fill space; they produce a range of emotions and responses. They can transform a user’s experience from average to memorable. Hence, understanding color psychology becomes a crucial aspect of design psychology and UX psychology.
Think about the emotional impact of color choices in your designs. Each color carries its emotional weight:
Blues can convey trust and security, often seen in banking apps.
Reds can create a sense of urgency or excitement, commonly used in clearance sales banners.

Greens are associated with tranquility and health, a go-to for wellness apps.
By choosing the right color palette, you’re not just decorating a space; you’re setting a mood, provoking a feeling, and guiding decision-making.
Think of how social media platforms like Instagram use a mix of warm and cool tones, striking a balance between excitement and calm, encouraging users to both post content and browse.
Or how eCommerce sites often use contrasting colors for call-to-action buttons, making them stand out and nudging users to click.
Incorporating color psychology into UX design isn’t about picking your favorite hues; it’s a strategic decision that can significantly affect how users perceive and interact with your design.
So, next time you pick a palette, ask yourself: what emotion do I want to evoke? Your answer could be the key to creating an engaging and effective user experience.
Also Read: Balancing Between Creativity and Functionality in UI/UX Design Projects [2024]
2. Building Emotional Engagement Through Micro-Interactions
In the psychology of UX design, micro-interactions play the role of unsung heroes. These small, functional interactions are fundamental elements of design psychology, greatly enhancing the user experience through subtle emotional engagement.
So, what exactly are micro-interactions?
They are those tiny, almost invisible interactions in a user interface that occur when you perform a task.
Think of the satisfying ‘ping‘ sound when you refresh your email…
…the playful animation when you ‘like‘ a social media post 💓…
or the haptic feedback when you set an alarm on your phone. ⏰
These brief moments create a sense of accomplishment and engagement, transforming mundane tasks into delightful experiences.
Consider the ‘pull-to-refresh‘ feature initially introduced by Twitter.
This simple, intuitive gesture not only made information retrieval effortless but also added a playful element to the user’s interaction with the app.
Another example is the animation of a heart ‘bursting‘ when you double-tap an Instagram photo.
Doing so offers immediate feedback and a small burst of joy, encouraging more interaction.
Micro-interactions are more than just decorative elements; they are critical tools in creating an emotionally resonant user experience. They bridge the gap between the user and the interface, making digital interactions feel more human and personal.
In the psychology of UX design, these tiny details can make a big difference, turning an ordinary experience into something memorable.
Explore Minimalism in UI/UX Design: Role and Importance for Design Career
3. Using Personalization to Foster Strong Connections
Personalization is more than just a trend these days; it’s a profound approach within UX psychology that forges stronger connections between users and digital products.
Personalization in UX involves tailoring the user experience to meet individual needs and preferences. It’s the art of making users feel like the product or service speaks directly to them.
This could be through customized content, relevant recommendations, or individualized user interfaces. When users see that a product understands and anticipates their needs, it creates a sense of belonging and emotional attachment.
Implementing personalized experiences, however, requires thoughtful strategies. It begins with data — understanding user behaviors, preferences, and pain points. Tools like user analytics and feedback systems come into play here, providing the insights needed for personalization.
Then, it’s about applying these insights to create user-centric design solutions. For instance, a music streaming service that curates playlists based on listening habits makes users feel understood and valued.

Or consider an online store that remembers past purchases and sizes, suggesting relevant products — it’s like walking into a familiar store where the staff knows you.
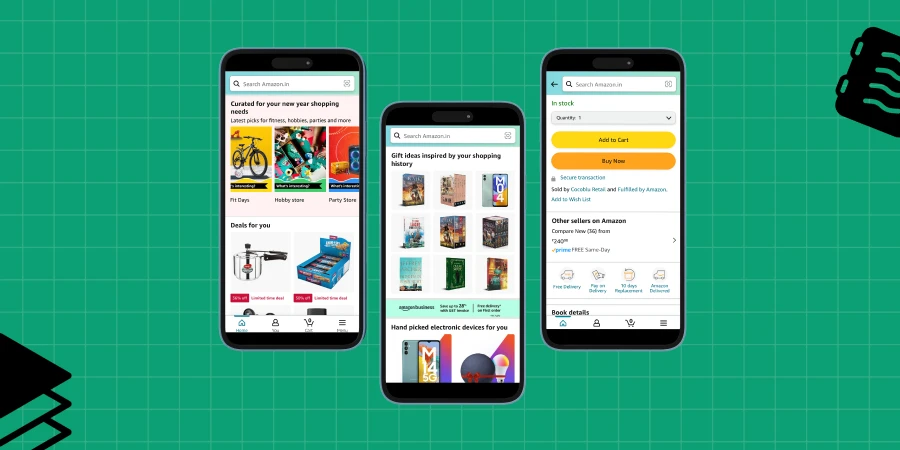
Personalization is not just about using technology to predict user behavior; it’s about using that technology to create a more humane and empathetic user experience.
If you also want to create exquisite UI/UX designs, then you must join GUVI’s Professional UI/UX Design Course with Skill India certification. Get Placement Assistance within 3 months!
Wrapping Up
The emotional dimension of UX design is not just an aspect but the essence of creating meaningful and lasting user experiences. It helps bring out the best in digital products by focusing on the human side of technology.
Reflecting on our key takeaways, we see that color psychology, micro-interactions, and personalization are not just tools but powerful conduits for emotional engagement. They are the subtle yet potent forces that transform user interfaces from mere points of interaction into spaces of emotional resonance.
As you step forward in your UX design journey, give substantial weightage to these emotional elements. Let the colors you choose paint not just a visual but an emotional landscape; let each micro-interaction be a small but significant step towards greater user satisfaction; let personalization be the path to creating not just a user base, but a community.
Ensure you understand the fundamentals of UI/UX, including heuristic analysis, journey maps, testing, etc. If you want to explore more about it, join GUVI’s UI/UX Course with placement assistance. You’ll also learn about the tools used in UI/UX: AdobeXd, Illustrator, Photoshop, Figma, and many more. Build some fantastic real-time projects to get hands-on experience.
Further, you can even undergo our self-paced certificate course in UX design psychology to master design fundamentals and unlock the secrets of creating satisfying digital experiences.
Also, read: UI UX Design Tools for 2024
Frequently Asked Questions
The first steps include researching user behavior, understanding target audience demographics, and analyzing how different design elements influence emotions and decisions.
Yes, by understanding user psychology, designers can create more engaging and intuitive interfaces that encourage users to take desired actions, potentially increasing conversion rates.
Tools like user emotion tracking software, heatmaps, and user feedback platforms are commonly used in UX psychology to analyze emotional responses.
A common mistake is overgeneralizing user behavior without considering individual differences and diverse user needs.
UX psychology incorporates principles of accessible design to ensure digital products are usable and enjoyable for people with various disabilities.
UX psychology principles are crucial in mobile app design for creating user-friendly, engaging, and efficient mobile experiences.
Yes, specialized courses and certifications are available that focus on the intersection of UX design and psychology, enhancing a designer’s skills in creating psychologically informed user experiences. GUVI’s UX design fundamentals certification course is worth checking out.


















Did you enjoy this article?