
Top Roles and Responsibilities of a Business Analyst
Apr 25, 2025 5 Min Read 2260 Views
(Last Updated)
Business analysts are the link between ideas and execution. In a time where we need to make decisions fast and backed by facts, they step in to align the business needs with practical solutions. From streamlining clunky processes to turning goals into working features, they help teams move forward with clarity.
This role isn’t about attending meetings for the sake of it or drafting endless documents. It’s about solving real problems, shaping smart decisions, and being the one people rely on when the direction is unclear. Here’s a closer look at the roles and responsibilities of a business analyst.
Table of contents
- Who is a Business Analyst?
- Key Roles and Responsibilities of a Business Analyst
- Requirement Gathering and Analysis
- Stakeholder Management
- Process Mapping and Optimization
- Data Analysis and Reporting
- Solution Design and Validation
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation
- Implementation and Support
- Functional Specifications and Documentation
- Skills Needed for a Business Analyst
- Wrapping Up
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the daily tasks of a business analyst?
- Is coding required for a business analyst role?
- What industries hire business analysts?
- Which tools should a business analyst learn?
- Is a certification important to become a business analyst?
- Can business analysts work remotely?
- What is the average salary of a business analyst in India?
Who is a Business Analyst?
A business analyst analyzes how a company works, identifies what isn’t working well, and determines how to improve things. This could mean improving a process, fixing a communication gap, or recommending a tech-based solution that helps teams work faster and smarter. The work is structured, grounded in research, and tied closely to the company’s goals.
Depending on the industry, a business analyst might be called a systems analyst, product owner, requirements manager, or management consultant. But the core remains the same – translating business needs into solutions that work in the real world.
Whether it’s fine-tuning internal processes, gathering requirements, supporting clients, or driving better sales strategies, the roles of business analysts often touch every corner of an organization.
Key Roles and Responsibilities of a Business Analyst
The responsibilities of a business analyst can vary depending on the industry, project scope, or team structure. However, some tasks are consistent across most roles. From the early planning stages to solution delivery and support, these professionals help turn goals into outcomes.
Below is a breakdown of the top business analyst roles and responsibilities that define this position across organizations.
Requirement Gathering and Analysis
A business analyst begins by understanding what the business needs. This involves working with stakeholders through interviews, workshops, or surveys to gather clear input. The focus isn’t just on what’s said outright but also on uncovering hidden expectations or pain points.
These findings are documented in user stories, specifications, or process diagrams. This step sets the direction for the project, ensuring everyone is aligned from the start.
Primary responsibilities include:
- Working with stakeholders to understand business needs through interviews, workshops, or surveys.
- Documenting functional and non-functional requirements in formats like user stories or process diagrams.
- Refining and validating requirements throughout the project lifecycle to maintain alignment with goals.
Stakeholder Management
One of the key roles of a business analyst is to act as the link between business stakeholders, technical teams, and end-users. They ensure everyone stays aligned with the project goals. This means facilitating clear communication, understanding differing needs, and bridging the gap between strategic vision and technical execution.
A business analyst also manages expectations, resolves conflicts, and encourages open dialogue, helping projects progress without delays or confusion.
Strong stakeholder management is essential to the business analyst roles and responsibilities, especially in cross-functional teams where miscommunication can lead to costly setbacks.
Primary responsibilities include:
- Acting as a bridge between business users, development teams, and management to ensure clear communication.
- Facilitating discussions to align everyone on objectives and timelines.
- Managing feedback loops and expectations throughout the project.
Process Mapping and Optimization
To improve efficiency, a business analyst reviews how things currently work. It includes digging into existing processes to find what slows teams down or creates confusion. Using visual tools like flowcharts, swimlane diagrams, or process maps, business analysts highlight what needs fixing and suggest ways to streamline operations.
These improvements involve automation, restructured workflows, or removing repetitive tasks. This is one of the core responsibilities of a business analyst: to make sure systems and teams work smarter, not harder.
Primary responsibilities include:
- Analyzing current workflows to identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
- Using process maps and visual tools to document existing and improved flows.
- Recommending changes or automation to boost speed, accuracy, and team productivity.
Data Analysis and Reporting
Business analysts turn raw data into something teams can use. They gather information from different sources, run the numbers, and spot patterns that help drive smarter decisions. Whether it’s sales data, customer feedback, or operational metrics, they break it down to uncover what matters.
Using top business analytics tools like Excel, SQL, Power BI, or Tableau, they create dashboards and reports that give stakeholders a clear picture. Data isn’t just numbers; it’s evidence. And making sense of it is a crucial part of the roles and responsibilities of a business analyst.
Primary responsibilities include:
- Collecting and analyzing data to support business decisions.
- Creating reports and dashboards using tools like Excel, Power BI, and Tableau.
- Sharing insights with teams in clear, visual, and actionable ways.
Solution Design and Validation
Once the requirements are clear, a business analyst works with technical teams to shape a solution that fits the business need. This might involve designing mockups, drafting process flows, or collaborating on prototypes that reflect how the final system should function.
Validation is just as important. The business analyst ensures the solution goes through testing, verifying that it works and solves the right problem. This step is central to many business analyst roles and responsibilities, especially when aligning product outcomes with business goals.
Primary responsibilities include:
- Working with developers to build solutions that meet defined business requirements.
- Creating prototypes, wireframes, or mockups to visualize the proposed system.
- Validating the final product through user testing and feedback collection.
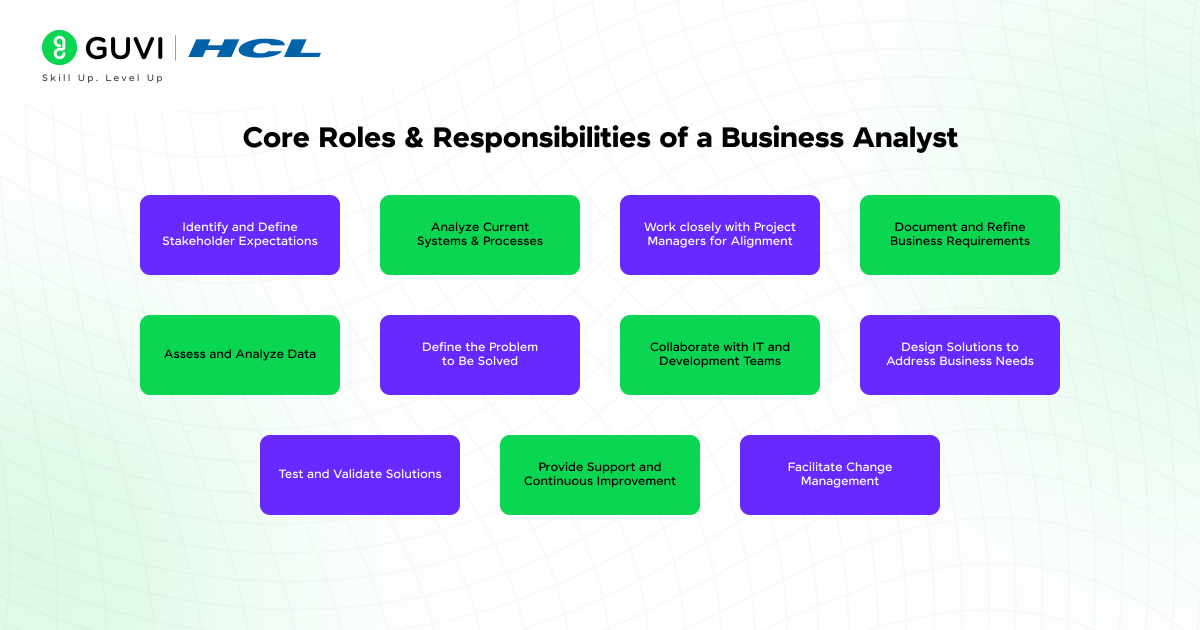
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Every project has risks, such as missed deadlines, budget overruns, and unclear priorities. A business analyst helps spot these issues before they become roadblocks. Working closely with teams, they assess what might go wrong and prepare strategies to reduce the damage.
This proactive mindset is an important part of the roles and responsibilities of a business analyst, especially when dealing with high-stakes projects or shifting timelines.
Primary responsibilities include:
- Identifying potential project risks across budget, scope, and timelines.
- Developing backup plans and mitigation strategies.
- Regularly reviewing risk factors and adjusting plans as the project evolves.
Know More: Top 15 Business Analyst Interview Questions With Answers
Implementation and Support
A business analyst stays involved beyond the planning phase. During implementation, they help roll out the solution, which includes coordinating with teams, answering questions, and ensuring everything runs smoothly. They also support training efforts, so end-users know how to work with the new system.
Even after launch, the responsibilities of a business analyst include gathering feedback, troubleshooting issues, and helping teams adjust to changes. Their continued involvement ensures the solution delivers lasting value.
Primary responsibilities include:
- Supporting deployment by coordinating with teams and managing handovers.
- Assisting with user training to ensure successful adoption.
- Providing post-launch support and gathering feedback for future improvements.
Read more: Top 11 Business Analytics Courses and Certifications in India
Functional Specifications and Documentation
Clear documentation keeps everyone aligned and prevents confusion later. A business analyst creates detailed functional specifications that outline what the system should do, how it should behave, and what’s expected from the development side. These documents act as a reference point throughout the project.
This part of the job may not grab headlines, but it’s one of the most practical business analyst responsibilities, helping ensure that no detail slips through the cracks.
Primary responsibilities include:
- Creating detailed functional specifications for development teams.
- Maintaining documentation for project scope, changes, and business rules.
- Serving as the go-to reference for technical and non-technical stakeholders.
Skills Needed for a Business Analyst
A successful business analyst blends analytical thinking, technical know-how, and strong communication to turn business needs into workable solutions.
Below are the top business analyst skills that support their roles and responsibilities across industries.
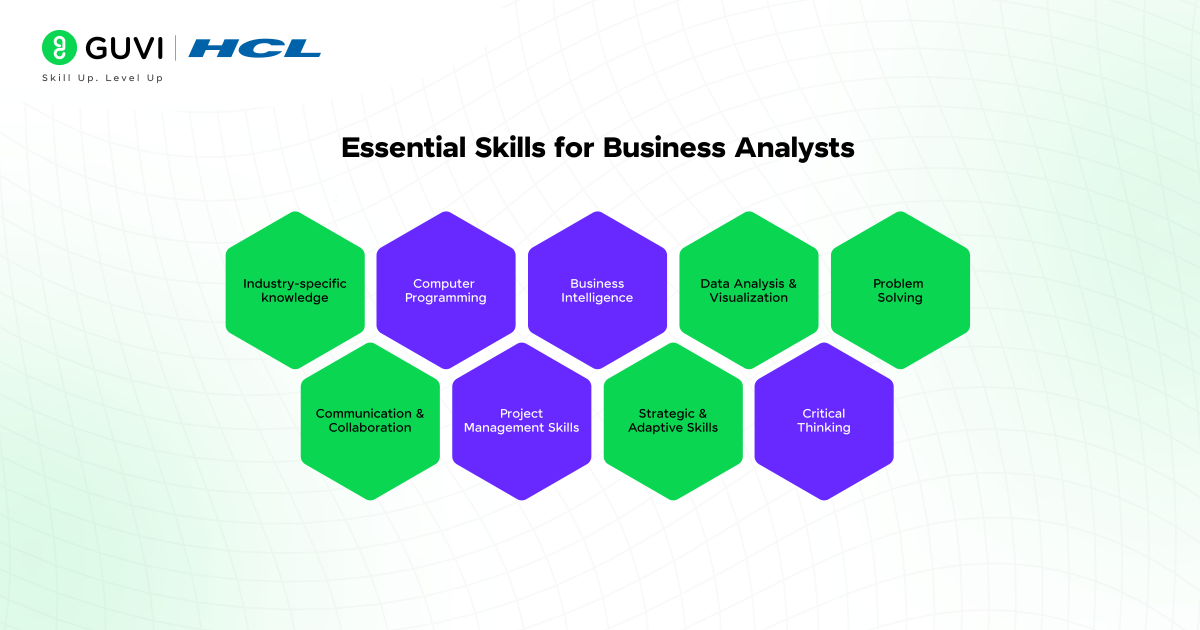
Analytical Thinking
Breaking down data, understanding workflows, and spotting patterns are all part of helping teams make better decisions. A sharp analytical mindset is central to solving problems before they grow.
Technical Proficiency
Knowing how to work with tools like SQL, Excel, or Tableau helps business analysts dig into data and make sense of it. Familiarity with project management platforms or database systems also helps them stay aligned with tech teams.
Communication Skills
Business analysts spend a lot of time talking with stakeholders. They need to explain things clearly, whether it’s a set of requirements or a proposed solution. Good writing and clear presentations are among top business analyst skills that go a long way in this role.
Problem-Solving Ability
When processes break down or teams hit a wall, a business analyst is expected to develop practical fixes. Thinking on your feet and balancing what’s ideal with what’s realistic is part of the job.
Collaboration
From designers to developers to executives, business analysts work with many teams. Their ability to bring everyone together helps projects move faster and stay on track.
Documentation Skills
Creating clear, easy-to-understand documents, such as requirement specs or process maps, is a regular task. It keeps everyone aligned and prevents confusion later on.
GUVI’s Master’s in Business Analytics Course with Marketing is one of the best business analytics courses and certifications to learn these skills online, from industry experts. It integrates business analytics and digital marketing, focusing on data-driven decision-making techniques that can enhance marketing strategies.
Wrapping Up
The roles and responsibilities of a business analyst go far beyond just gathering requirements. It’s a career built on asking the right questions, finding better ways to work, and turning problems into progress.
Whether you’re mapping processes, analyzing data, or bridging communication gaps, every part of the job helps shape smarter decisions across the business.
Business analysis is worth exploring if you enjoy solving real-world challenges and translating ideas into outcomes. Keep learning, stay curious, and focus on building skills that let you grow with the role.
Frequently Asked Questions
The general tasks of business analysts include gathering requirements, documenting processes, analyzing data, attending meetings with stakeholders, and supporting solution implementation.
No, coding isn’t mandatory. However, knowing SQL or basic scripting can be helpful, especially in data-heavy projects.
Business analysts are in demand across IT, finance, healthcare, e-commerce, manufacturing, and consulting firms.
Popular tools include Excel, Tableau, Power BI, JIRA, Confluence, SQL, and business process modeling tools like Lucidchart or Draw.io.
Certifications aren’t compulsory but can boost your chances. Look for business analyst courses and certifications from recognized platforms.
Many organizations offer remote or hybrid roles for business analysts, especially in the IT and consulting sectors.
Entry-level business analysts earn ₹4–6 LPA, while experienced professionals can make ₹10–20 LPA or more depending on the domain.






























Did you enjoy this article?