
The Art and Mind of Design: Connecting Through Psychology
Jan 29, 2025 3 Min Read 1279 Views
(Last Updated)
How does design transcend functionality to forge deep emotional connections with users? Why do certain products leave us delighted while others leave us indifferent? The secret lies in the psychology of design, how elements like color, typography, and interactions evoke emotions, shape perceptions, and create lasting impressions.
By understanding these psychological principles, designers can move beyond creating mere tools and craft experiences that resonate deeply with users. Let’s dive deeper and explore the art and mind of design.
Table of contents
- How Design Shapes Emotions
- Cognitive Principles Behind Design
- Cultural Sensitivity in Design
- Designing for Emotional Impact
- Why Emotional Design Matters
- How Tech Giants Leverage Design Psychology
- Apple: The Pinnacle of Minimalist Design
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is design psychology, and why is it important?
- What role does typography play in influencing user perceptions?
- What is the significance of visual hierarchy in design?
How Design Shapes Emotions
- Color Psychology: Colors directly impact mood and perception.
Real-world examples include:
Yellow (Optimism and Warmth): Bumble uses yellow in its branding to create a friendly, optimistic vibe for its users.
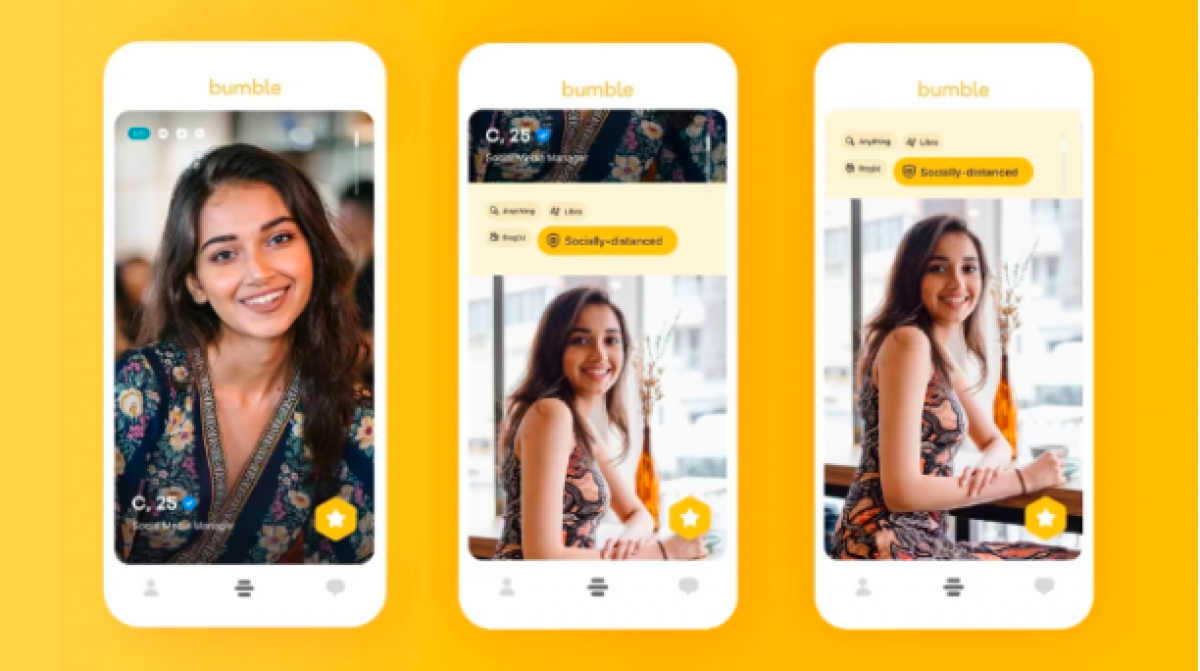
Purple (Creativity and Luxury): The iconic purple wrapper of Cadbury chocolates signifies indulgence and luxury, creating an emotional connection with premium quality.

Green (Balance and Growth): Spotify’s green logo and interface signify balance and harmony, aligning with its focus on music as a form of personal growth and well-being.

Selecting the right colors helps evoke emotions aligned with your product’s purpose.
2. Typography’s Emotional Tone: Typography subtly influences user perceptions.
For instance:
- Medium employs a clean, serif typeface that emphasizes readability and professionalism, catering to its audience of readers and writers.

- Coca-Cola uses a flowing, cursive font in its logo, evoking feelings of nostalgia and tradition.

Pairing fonts thoughtfully enhances the emotional depth of your design.
3. Visual Hierarchy: Proper alignment, spacing, and contrast guide user focus, reducing cognitive load and creating a seamless experience.
Real-world example: Amazon prominently displays the search bar and deals section on its homepage, ensuring users can quickly find what they’re looking for without distraction.
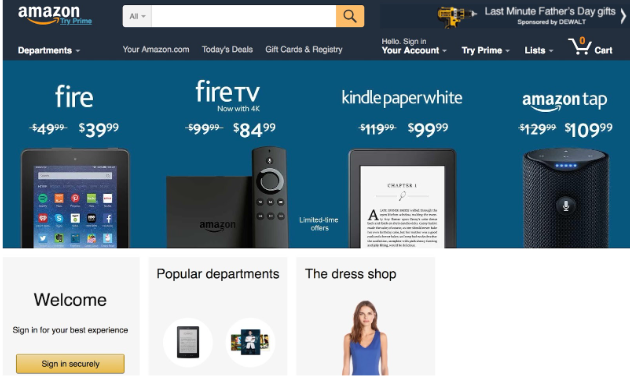
When users feel less overwhelmed, their overall interaction becomes more positive.
Cognitive Principles Behind Design
- The Peak-End Rule Users remember the peak emotional moment and the ending of their interaction.
Example:
- Starbucks leaves users with a personalized touch by writing their name on the cup, creating a positive emotional connection at the end of their purchase.

2. The Von Restorff Effect Distinctive elements stand out and are more memorable.
Example:
- Canva highlights its unique templates and one-click features to make its design tools both intuitive and memorable.

3. Anchoring Bias First impressions matter.
Example:
- Zomato’s homepage features appetizing images of food, immediately drawing users into the experience of ordering delicious meals.
Cultural Sensitivity in Design
Understanding cultural nuances is essential to ensuring designs resonate globally.
For example:
- Blue signifies trust and stability in Western cultures but is associated with mourning in some Eastern traditions.
- Gold often represents wealth and prosperity in many cultures but can also signify excessive opulence in certain contexts.
Designing for Emotional Impact
- Empathy-Led Research Dive deep into user motivations, frustrations, and aspirations. Understanding these emotional triggers helps create designs that resonate on a personal level.
- Microinteractions that Delight Subtle animations or feedback loops—like the progress bar animation in Duolingo—can motivate users to complete their tasks while adding a fun element.
3. Consistency and Trust: A consistent design system fosters trust by ensuring users know what to expect.
Example:
Figma’s interface consistently delivers a collaborative and intuitive experience, making design work seamless and reliable.
Why Emotional Design Matters
- Increased Engagement: Designs that spark joy or curiosity keep users coming back.
- Brand Loyalty: Emotional resonance builds a connection that transcends mere usability.
- Improved Usability: When designs reduce friction and make tasks enjoyable, users feel more accomplished.
How Tech Giants Leverage Design Psychology
Companies like Apple, Google, and Airbnb have mastered the art of leveraging design psychology to create iconic products and services. Let’s explore how Apple achieves this:
Apple: The Pinnacle of Minimalist Design
Minimalist Aesthetic:
Apple’s minimalist design philosophy, characterized by clean lines, simple interfaces, and a focus on functionality, appeals to our innate desire for simplicity and order.
The iPhone’s sleek design and the straightforward layout of macOS are perfect examples of how minimalism creates lasting appeal.
The Power of the Unboxing Experience:
Apple elevates unboxing to an art form. From the soft-close box lid to the neatly arranged accessories, every detail is meticulously crafted to evoke anticipation and excitement.
This isn’t just packaging—it’s an experience that transforms opening a product into an emotional connection, leaving users with a lasting positive impression.
The Halo Effect:
Apple’s unwavering commitment to quality across its product range—whether it’s the iPhone, Apple Watch, or AirPods—has solidified its reputation as a trusted brand.
This “halo effect” ensures that customers associate the excellence of one product with the entire brand, making them more likely to explore and purchase other offerings with confidence.
Conclusion
Design is more than aesthetics or usability; it’s a gateway to human emotions. By harnessing principles like color psychology, cognitive biases, and empathy-led research, we can create designs that inspire joy, trust, and loyalty.
Tech giants like Apple and Spotify exemplify the power of design to connect with users on a personal level. As designers, we have the opportunity to create not just functional products but meaningful experiences that users treasure.
Unlock the full potential of user-centered design with our expert-driven UI/UX course. Our comprehensive curriculum covers everything from design principles to real-world applications. Learn how to create intuitive, visually stunning, and user-friendly experiences that make an impact. Join us today and start mastering the art of UI/UX design!
Frequently Asked Questions
Design psychology explores how design elements like color, typography, and interactions influence user emotions, perceptions, and behavior. It helps create designs that evoke emotional connections, build trust, and improve usability, ultimately enhancing user experience and brand loyalty.
Typography sets the tone and enhances the emotional depth of a design:
Serif fonts, like those on Medium, emphasize professionalism and readability.
Cursive fonts, like Coca-Cola’s, evoke nostalgia and tradition.
Pairing fonts thoughtfully can shape how users perceive a brand.
Visual hierarchy organizes content to guide user focus and reduce cognitive load. For instance, Amazon prominently displays the search bar and deals section to enhance usability and create a seamless experience.










![What Does a UI/UX Designer Do? [Career Guide] 17 What does a UI/UX designer do?](https://www.guvi.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/UX-Designer-Do_.webp)




![How To Switch Career In UI/UX Design? Easy or Hard? [2025] 20 how_to_switch_to_a_career_in_ui_ux_design_](https://www.guvi.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/how_to_switch_to_a_career_in_ui_ux_design_.webp)

Did you enjoy this article?