
The world of cinema, gaming, and digital media has been revolutionized by Visual Effects (VFX), blending reality with imagination to create awe-inspiring visuals. VFX artists are at the forefront of this transformative industry, using cutting-edge technology and creativity to bring fantastical ideas to life.
From blockbuster movies to immersive video games and advertising campaigns, their work shapes how we experience visual storytelling. As VFX continues to gain prominence in global media, these artists have become some of the most sought-after professionals, leading to a surge in specialized job profiles across the industry.
Hence, I have drafted this article on the Top 10 VFX Artist Job Profiles, so that aspiring VFX artists like you can choose your career wisely. Here, you will find insights into their roles, responsibilities, required skills, and industry demand. Let’s begin!
Table of contents
- What is VFX and Why is it Trending?
- What are VFX Artist Job Profiles?
- Top 10 VFX Artist Job Profiles
- Compositor
- 3D Modeler
- VFX Supervisor
- Texture Artist
- Matte Painter
- Roto Artist
- Lighting Artist
- FX Artist
- Animation Artist
- Previsualization Artist
- Steps to Become a VFX Artist
- Concluding Thoughts…
- FAQs
- What is VFX job profile?
- What is the role of a VFX artist?
- Is VFX a high-paying job?
- Does VFX involve coding?
- How much do Netflix VFX artists make?
What is VFX and Why is it Trending?
Visual Effects (VFX) refers to the process of creating, enhancing, or manipulating imagery in films, television, games, and other multimedia projects using specialized software and techniques. It enables artists to create visually stunning environments, characters, and scenes that would be impossible or too expensive to achieve in real life.

Why is VFX Trending?
- High Demand in Entertainment: With the rise of big-budget films, TV shows, and streaming platforms, VFX has become an integral part of storytelling.
- Technological Advancements: Tools like Unreal Engine and AI-driven software have made VFX more accessible and efficient.
- Expansion Beyond Movies: VFX is now widely used in advertising, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and gaming industries.
- Audience Expectations: Modern audiences demand realistic and immersive visual experiences, pushing the need for high-quality VFX.
- Global Career Opportunities: The field offers lucrative roles across the globe, with increasing remote work opportunities.
What are VFX Artist Job Profiles?
VFX (Visual Effects) artist job profiles are the specialized roles within the visual effects industry that bring imaginative visuals to life for movies, television, video games, and advertisements. These professionals combine creativity with technical expertise to produce computer-generated imagery (CGI), integrate 3D elements with live-action footage, and enhance storytelling through simulations, animations, and digital artistry.
Each VFX role focuses on a specific task—compositing, lighting, or 3D modeling—and contributes to the visually captivating results audiences see on screen. VFX job profiles are critical for industries where digital effects elevate the visual narrative, such as Hollywood films, OTT platforms, and gaming.
The demand for VFX artists is rapidly growing as entertainment content becomes more CGI-heavy, leading to increased opportunities for professionals in India and worldwide. VFX artist job profiles are ideal for artistic and technologically inclined individuals.
Top 10 VFX Artist Job Profiles
After understanding what VFX is and what its job profiles mean, I have drafted a list of the top 10 VFX Artist job profiles, where we will be discussing what they do, their responsibilities, the skills needed for the role, what your career would look like should you choose it and the salaries as well so that you can make your career decisions with ease.
1. Compositor
Compositors are responsible for merging multiple visual elements from various sources, including live-action footage, 2D/3D animations, and effects, into a single cohesive frame. They ensure color grading, lighting, and shadows are seamlessly integrated to create realistic visuals.
Their work involves refining green screen footage, eliminating errors, and adding depth to the scene, ensuring a polished final output that aligns with the director’s vision.
Key Responsibilities:
- Blending different layers of images and effects.
- Adjusting color grading, lighting, and shadows for consistency.
- Identifying and fixing visual discrepancies.
Skills Needed:
- Expertise in software like Nuke, Adobe After Effects.
- Strong eye for detail and artistic sense.
- Knowledge of color theory and 2D/3D compositing.
Career Progression:
- Entry Level: Junior compositor assisting in basic layering and color corrections.
- Mid-Level: Lead compositor overseeing entire sequences.
- Senior Level: Supervisor roles, managing teams and ensuring creative alignment with directors.
Average Salary: ₹4–12 LPA
2. 3D Modeler
3D Modelers design detailed and realistic 3D assets, including characters, objects, environments, and props, which form the foundation of VFX. They use specialized software like Maya or Blender to create models that can be animated, textured, and lit.
Their creations require an eye for detail and a deep understanding of form, scale, and aesthetics to ensure models blend seamlessly into the final visuals.
Responsibilities:
- Designing 3D models using software like Maya, Blender, or ZBrush.
- Collaborating with animators and texture artists.
- Optimizing models for animation and rendering.
Skills Needed:
- Proficiency in 3D modeling tools.
- Strong understanding of form, anatomy, and topology.
- Artistic creativity combined with technical precision.
Career Progression:
- Entry Level: Assistant VFX supervisor or team lead.
- Mid-Level: On-set supervisor working on high-budget projects.
- Senior Level: Studio-level supervision, shaping entire projects or heading VFX departments.
Average Salary: ₹5–15 LPA
3. VFX Supervisor
The VFX Supervisor leads the creative and technical teams throughout the production process. They collaborate with directors, producers, and artists to ensure the visual effects align with the storytelling and technical requirements.
Supervisors also manage budgets, schedules, and resources while troubleshooting complex challenges, ensuring the VFX is visually compelling and delivered on time.
Responsibilities:
- Leading VFX teams and coordinating with directors.
- Reviewing shots and providing feedback.
- Managing budgets and production timelines.
Skills Needed:
- Extensive knowledge of VFX pipelines and tools.
- Leadership and communication skills.
- Problem-solving and decision-making abilities.
Career Progression:
- Entry Level: Modeling artist creating assets for smaller projects.
- Mid-Level: Specialist in character/environment modeling.
- Senior Level: Lead modeler or creative director for asset design.
Average Salary: ₹15–30 LPA
4. Texture Artist
Texture Artists add surface details to 3D models, such as skin textures, metallic finishes, or fabric weaves, to make them visually believable. Using software like Substance Painter, they map realistic textures onto objects, ensuring consistency with lighting and scene requirements. Their work enhances the visual depth and realism of the models.
Responsibilities:
- Creating realistic textures for characters, props, and environments.
- Using tools like Substance Painter and Photoshop.
- Collaborating with lighting and rendering teams.
Skills Needed:
- Strong artistic skills and attention to detail.
- Knowledge of UV mapping and PBR workflows.
- Understanding of material properties like metalness and roughness.
Career Progression:
- Entry Level: Junior artist working on simple lighting setups.
- Mid-Level: Senior artist handling complex scenes and styles.
- Senior Level: Lighting supervisor ensuring scene consistency across large projects.
Average Salary: ₹4–10 LPA
5. Matte Painter
Matte painters create highly detailed and realistic digital or traditional backdrops for scenes that cannot be filmed practically. These backdrops can include landscapes, cityscapes, or even alien worlds.
Their work ensures consistency in perspective, lighting, and color. Matte painters are vital for building immersive environments, saving production costs, and bringing imaginative worlds to life in films, games, and commercials.
Responsibilities:
- Designing complex landscapes and cityscapes.
- Integrating 2D/3D elements into scenes.
- Ensuring visual consistency across shots.
Skills Needed:
- Proficiency in Photoshop and digital painting techniques.
- Strong understanding of perspective and lighting.
- Creativity and storytelling abilities.
Career Progression:
- Entry-Level: Junior Matte Painter, creating static or semi-static backgrounds.
- Mid-Level: Advanced Matte Painter, responsible for high-detail, layered environments for film or AAA games.
- Senior-Level: Lead Matte Painter, overseeing large-scale projects and collaborating with directors.
Average Salary: ₹3–8 LPA
6. Roto Artist
Roto artists meticulously trace and isolate elements in live-action footage, frame by frame, using software like Nuke or Silhouette. This isolation, or “rotoscoping,” is used to mask objects, track movements, or integrate digital assets with filmed scenes.
Precision is crucial, as their work enables seamless blending of CGI and live-action, such as adding effects to specific areas or replacing backgrounds. Roto artists are foundational to the VFX pipeline, ensuring all elements align perfectly in the final composition.
Responsibilities:
- Creating masks and mattes for object isolation.
- Collaborating with compositors for seamless integration.
- Fixing motion blur and edge details.
Skills Needed:
- Precision and attention to detail.
- Expertise in rotoscoping software like SilhouetteFX.
- Understanding of VFX workflows.
Career Progression:
- Entry Level: Junior artist working on basic UV mapping and textures.
- Mid-Level: Specialist in photorealistic textures for complex models.
- Senior Level: Lead texture artist or technical director focusing on innovations in texturing.
Average Salary: ₹3–6 LPA
7. Lighting Artist
Lighting artists design and implement lighting setups in virtual scenes to create the desired mood, depth, and realism. They replicate real-world lighting conditions using software like Maya or Houdini while also ensuring consistency across shots.

By manipulating shadows, reflections, and highlights, they enhance the emotional impact of scenes. Their work directly affects how audiences perceive environments and characters, making lighting one of the most critical elements of a visually cohesive production.
Responsibilities:
- Designing and adjusting light setups in scenes.
- Collaborating with rendering and compositing teams.
- Ensuring consistency in lighting across frames.
Skills Needed:
- Knowledge of light physics and rendering engines.
- Artistic sense for mood and storytelling.
- Proficiency in software like Houdini, Maya.
Career Progression:
- Entry-Level: Junior Lighting Artist, handling minor lighting adjustments and scene optimization.
- Mid-Level: Senior Lighting Artist, responsible for lighting entire sequences or films.
- Senior-Level: Lighting Supervisor, managing creative and technical aspects of lighting pipelines.
Average Salary: ₹4–12 LPA
8. FX Artist
FX artists specialize in creating dynamic simulations, such as explosions, water splashes, fire, and smoke. Using advanced tools like Houdini, Maya, or Blender, they simulate natural phenomena and stylized effects with a high degree of realism.
Their work often involves physics-based algorithms to mimic real-world behavior. FX artists play a crucial role in action sequences and fantasy genres, delivering the visual spectacle that captivates audiences and defines modern blockbuster entertainment.
Responsibilities:
- Designing realistic simulations using Houdini, RealFlow.
- Collaborating with animators and compositors.
- Ensuring effects align with the director’s vision.
Skills Needed:
- Expertise in physics-based simulations.
- Creativity and technical knowledge.
- Problem-solving and optimization skills.
Career Progression:
- Entry-Level: Junior FX Artist, working on basic simulations like smoke or fire.
- Mid-Level: Senior FX Artist, crafting complex simulations for major sequences.
- Senior-Level: FX Supervisor, leading teams and collaborating on innovative effects.
Average Salary: ₹5–15 LPA
9. Animation Artist
Animation artists breathe life into digital characters, objects, and environments through movement and expressions. They handle everything from character motion to complex creature animations using software like Maya or Blender.
Their work includes realistic physics, emotional gestures, and choreography, ensuring seamless integration with storylines. Animation artists are essential for creating relatable and dynamic visuals in films, games, and advertisements, bridging the gap between storytelling and visual engagement.
Responsibilities:
- Animating characters, creatures, and props.
- Collaborating with rigging and modeling teams.
- Ensuring fluid and believable motion.
Skills Needed:
- Proficiency in animation principles and software like Maya.
- Creativity and timing sense.
- Attention to detail and storytelling.
Career Progression:
- Entry-Level: Junior Animator, creating simple character or object animations.
- Mid-Level: Senior Animator, producing advanced animations with lifelike detail.
- Senior-Level: Animation Supervisor, overseeing multiple teams and style continuity.
Average Salary: ₹4–10 LPA
10. Previsualization Artist
Previsualization artists, or “previz” artists, create rough 3D representations of scenes to visualize camera angles, motion, and staging before full production. Using tools like Cinema 4D or Maya, they assist directors in planning shots, minimizing production costs, and identifying potential challenges early.

Their work serves as a blueprint for the entire VFX team, ensuring creative alignment and efficient execution. Previz artists are vital for translating abstract concepts into actionable visual plans.
Responsibilities:
- Developing animatics and 3D storyboards.
- Collaborating with directors and VFX teams.
- Experimenting with camera angles and sequences.
Skills Needed:
- Knowledge of cinematography and storytelling.
- Proficiency in 3D tools like Maya, Cinema 4D.
- Creative problem-solving.
Career Progression:
- Entry-Level: Junior Previs Artist, assisting in visualizing basic action sequences.
- Mid-Level: Senior Previs Artist, crafting detailed storyboards and animatics for films.
- Senior-Level: Previs Supervisor, bridging communication between directors and VFX teams.
Average Salary: ₹3–8 LPA
Steps to Become a VFX Artist
Now that we’ve learned about the top VFX Artist job profiles and what they bring to the table, I would like to give you a small brief on the steps needed to become a VFX artist and work with these job profiles so that you know what you’re getting into.
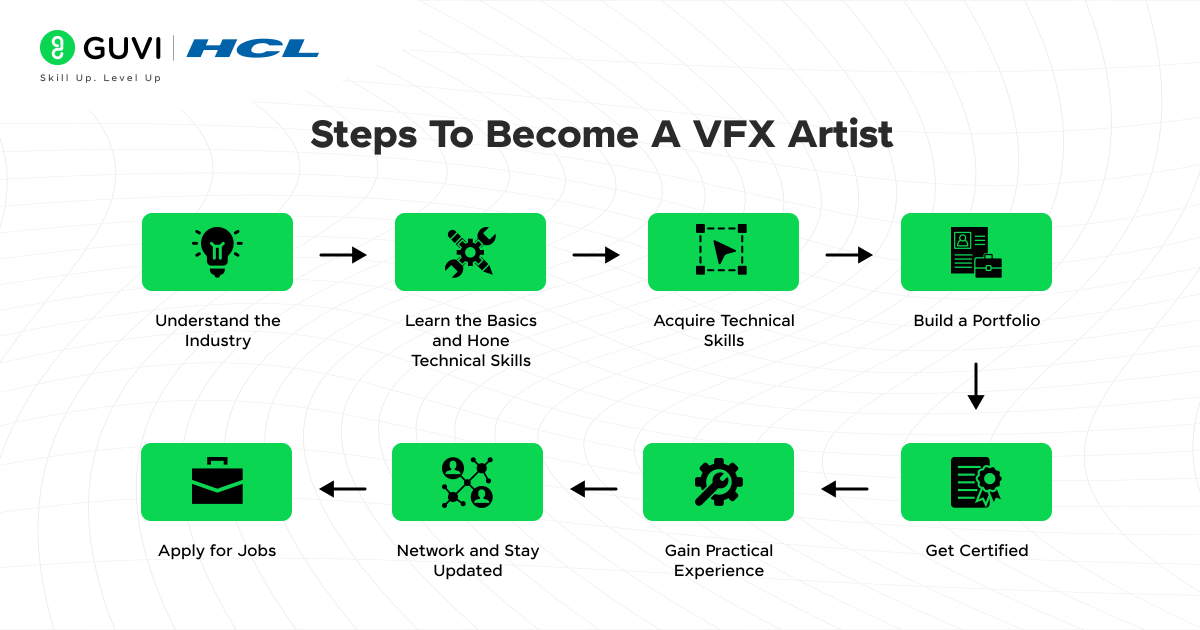
- Understand the Industry: Research various VFX roles and their responsibilities to identify your area of interest.
- Learn the Basics and Hone Technical Skills: Develop a strong foundation in art, design, and storytelling principles. Invest in sought-after learning resources like GUVI’s VFX Course with Generative AI. This program equips aspiring VFX artists with hands-on experience in tools like Unreal Engine, Houdini, and AI-driven design platforms, enabling faster, high-quality production.
You’ll learn industry-relevant skills to create stunning visuals for movies, games, and media, with expert mentorship and job support to launch your dream career in VFX.
- Acquire Technical Skills:
- Master software like Maya, Houdini, Blender, or Nuke.
- Learn programming languages like Python for automation and scripting.
- Build a Portfolio:
- Create high-quality projects showcasing diverse skills.
- Focus on quality over quantity to impress recruiters.
- Get Certified:
- Enroll in specialized VFX courses from reputed institutes or online platforms.
- Obtain certifications in tools like Autodesk Maya or Houdini.
- Gain Practical Experience:
- Intern with VFX studios or participate in collaborative projects.
- Work on personal projects to refine your skills.
- Network and Stay Updated:
- Attend industry events, webinars, and forums.
- Keep up with the latest trends and technologies in VFX.
- Apply for Jobs:
- Tailor your resume and cover letter for specific roles.
- Use job portals, LinkedIn, and networking opportunities to find openings.
Concluding Thoughts…
The VFX industry continues to thrive as visual storytelling evolves into an immersive, boundary-pushing medium. Each VFX artist’s role—whether it’s crafting intricate backgrounds as a matte painter, perfecting scenes as a roto artist, or creating simulations as an FX artist—plays a pivotal role in bringing imagination to life.
With growing opportunities in India, competitive salaries, and clear career progression, aspiring artists can build rewarding careers in this dynamic field. Hence, I hope this article has helped you garner the knowledge you need to build a successful career as a VFX artist.
If you have any doubts about the article, reach out to me through the comments section below.
FAQs
A VFX (Visual Effects) job involves creating realistic or imaginative visuals for films, games, or media using software tools. It includes compositing, animation, modeling, and effects simulation.
A VFX artist designs and integrates computer-generated imagery (CGI) with live-action footage to enhance visual storytelling in movies, TV shows, games, and commercials.
Yes, VFX can be high-paying in India, with salaries ranging from ₹3-8 LPA for entry-level roles and ₹15-30 LPA for experienced professionals in top studios.
While VFX primarily involves artistic work, coding is used in areas like scripting, simulations, and creating custom effects, often requiring knowledge of Python or C++.
Netflix VFX artists in India typically earn between ₹10-25 LPA, depending on experience, specialization, and project scale.































Did you enjoy this article?