
What is Prompt Engineering?
Feb 18, 2025 5 Min Read 2683 Views
(Last Updated)
In the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence, prompt engineering has emerged as a game-changing skill. Now, what is prompt engineering? Prompt engineering is the process of designing and refining input prompts to guide AI models, particularly large language models (LLMs), like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), to produce accurate, relevant, and context-specific outputs.
It plays a crucial role in AI, especially in natural language processing (NLP), by ensuring that the models understand the user’s intent and deliver results that meet specific requirements. In this article, you’ll discover the inner workings of prompt engineering, core concepts and techniques, prompt engineer skills, applications and much more.
Table of contents
- What is Prompt Engineering?
- Core Concepts
- Importance in AI
- How Prompt Engineering Works
- Step-by-Step Breakdown of Prompt Engineering:
- Prompt Engineering Techniques
- System Prompts vs. User Prompts
- Key Prompting Techniques
- Skills Required for Prompt Engineering
- Applications of Prompt Engineering
- Challenges in Prompt Engineering
- Concluding Thoughts…
- FAQs
- What are the responsibilities of a prompt engineer?
- How much does a prompt engineer earn annually in India?
- Can you explain the method used in prompt engineering?
- Is it challenging to become proficient in prompt engineering?
What is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering is the art and science of crafting precise instructions to guide AI models in generating desired outputs. It involves structuring natural language text that describes the task an AI should perform.
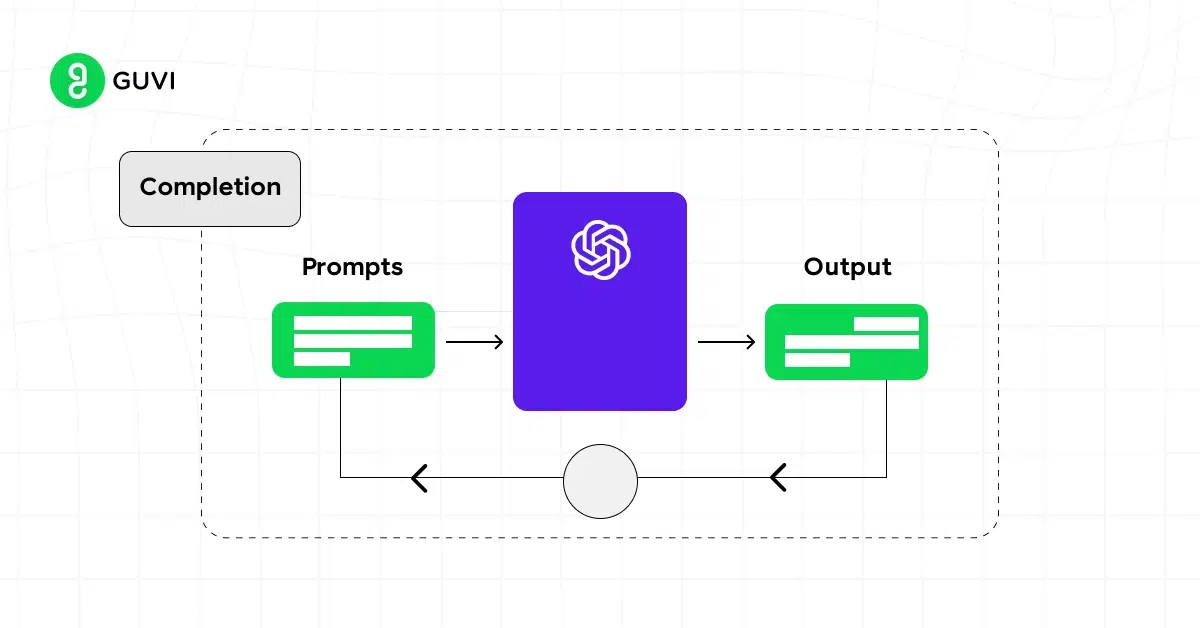
You can think of it as the interface between human intent and machine output, similar to teaching a child through well-phrased questions.
Core Concepts
At its core, prompt engineering focuses on selecting appropriate words, phrases, sentence structures, and punctuation to create optimal textual input for AI models. It’s enabled by in-context learning, which is an AI model’s ability to temporarily learn from prompts. This skill becomes more effective as models grow larger.
Key aspects of prompt engineering include:
- Providing sufficient context
- Framing inputs effectively
- Specifying styles or roles for the AI
- Refining prompts for better performance
Importance in AI
Prompt engineering has a significant impact on how we interact with and harness the power of generative AI. It’s crucial for:
- Improving AI model performance
- Ensuring effective human-AI communication
- Developing AI-driven solutions like chatbots and content generators
- Mitigating prompt injection attacks
As AI becomes more prevalent in various industries, prompt engineering serves as the bridge between human needs and AI capabilities. It’s not just about getting the right answer; it’s about ensuring AI understands the context, nuances, and intent behind every query.
This makes prompt engineering an essential skill in the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence.
How Prompt Engineering Works
Prompt engineering works by manipulating the input prompt provided to an AI model, thereby shaping the output. The prompt can include various elements, such as specific instructions, examples, constraints, or even contextual information.
The AI model, in turn, processes this input to generate text that aligns as closely as possible with the desired outcome.
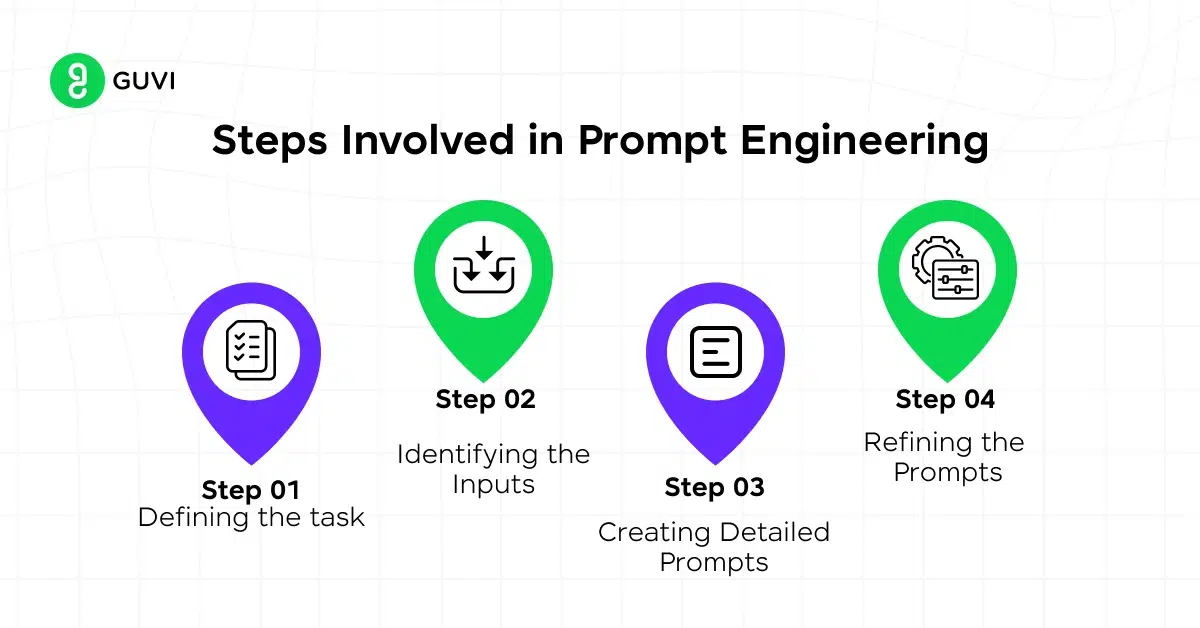
Step-by-Step Breakdown of Prompt Engineering:
- Identify the Task: Define the specific task or question that the AI needs to address.
- Contextualize the Prompt: Provide background information or context that the model needs to understand the task. This is crucial for ensuring that the model generates a response that is both relevant and accurate.
- Use Clear Instructions: Craft the prompt using clear and direct language to minimize ambiguity and reduce the chances of the model producing irrelevant or incorrect information.
- Example-based Prompting (Few-shot Prompting): Provide examples within the prompt to guide the AI on how to handle similar tasks. This is particularly useful for complex or nuanced requests.
- Iterate and Refine: After reviewing the output, refine the prompt to improve its clarity or specificity, and iterate this process until the desired result is consistently achieved.
Prompt Engineering Techniques
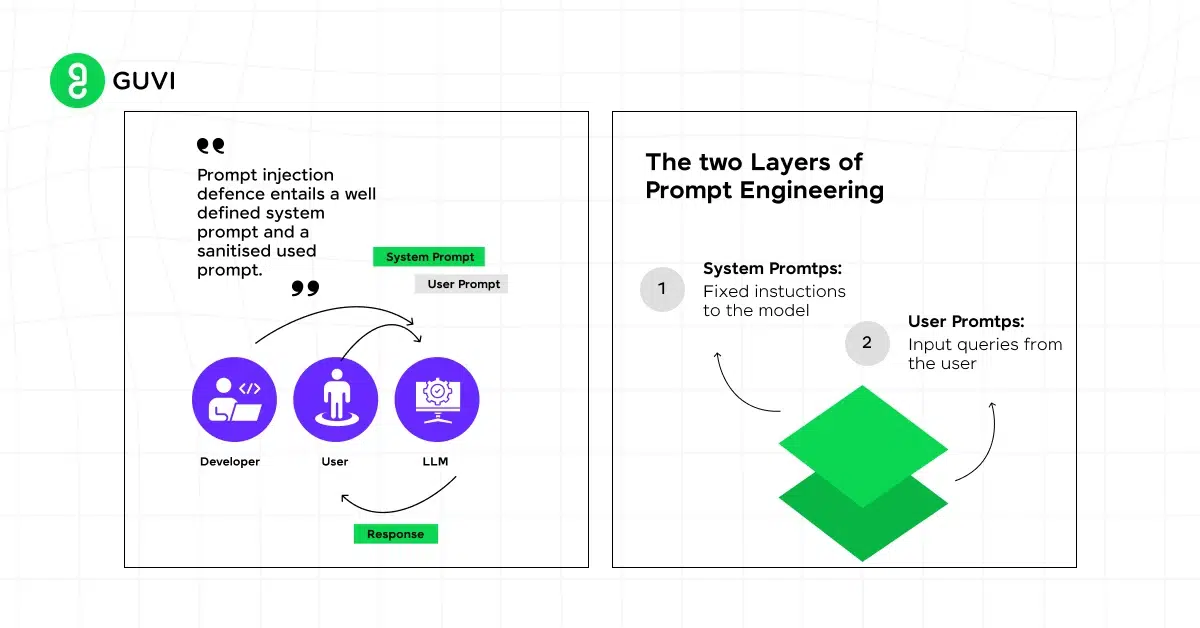
System Prompts vs. User Prompts
- System Prompts: These are the underlying instructions programmed into the AI model that dictates its general behavior. For example, a system prompt might tell the AI to avoid generating harmful content or to prioritize factual accuracy.
- User Prompts: These are the specific inputs provided by users for particular tasks. The effectiveness of user prompts largely depends on how well they communicate the user’s intent to the model.
| Prompt Type | Description | Example |
| System Prompt | Internal instructions guiding overall AI behavior | “Prioritize factual accuracy in all responses.” |
| User Prompt | Specific instructions given by the user for a task | “Summarize the following article in 100 words.” |
Key Prompting Techniques
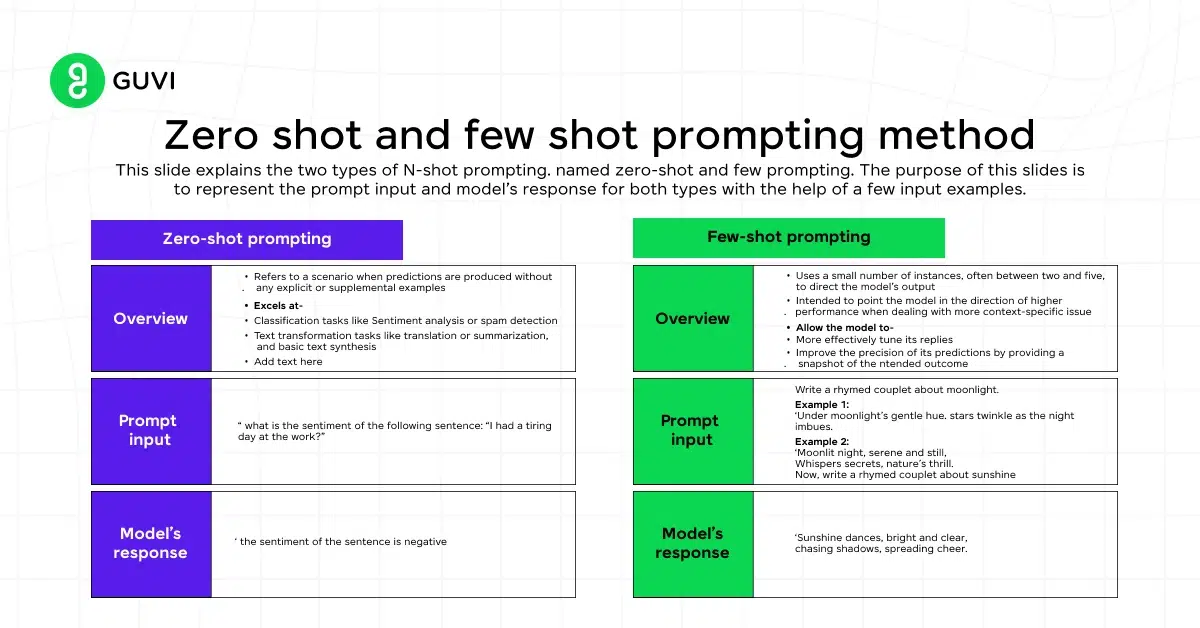
- Zero-shot and Few-shot Prompting:
- Zero-shot Prompting: The model is asked to perform a task without being given any prior examples or guidance. This approach relies entirely on the model’s training and understanding of the language to generate the desired output.
- Few-shot Prompting: The model is provided with a few examples within the prompt. These examples serve as a guide, helping the model understand how to approach the task at hand.
| Technique | Description | Example |
| Zero-shot | Task performed without examples | “Translate the following text into Spanish: ‘The weather is nice.'” |
| Few-shot | Task performed with a few examples provided within the prompt | “Translate the following text into Spanish: ‘Hello’ -> ‘Hola’, ‘Yes’ -> ‘Sí'” |
- Chain-of-Thought (CoT) Prompting: Chain-of-Thought prompting involves breaking down complex tasks into a series of smaller, logical steps. This method helps the AI model generate more accurate and well-reasoned outputs by guiding it through a structured thought process.
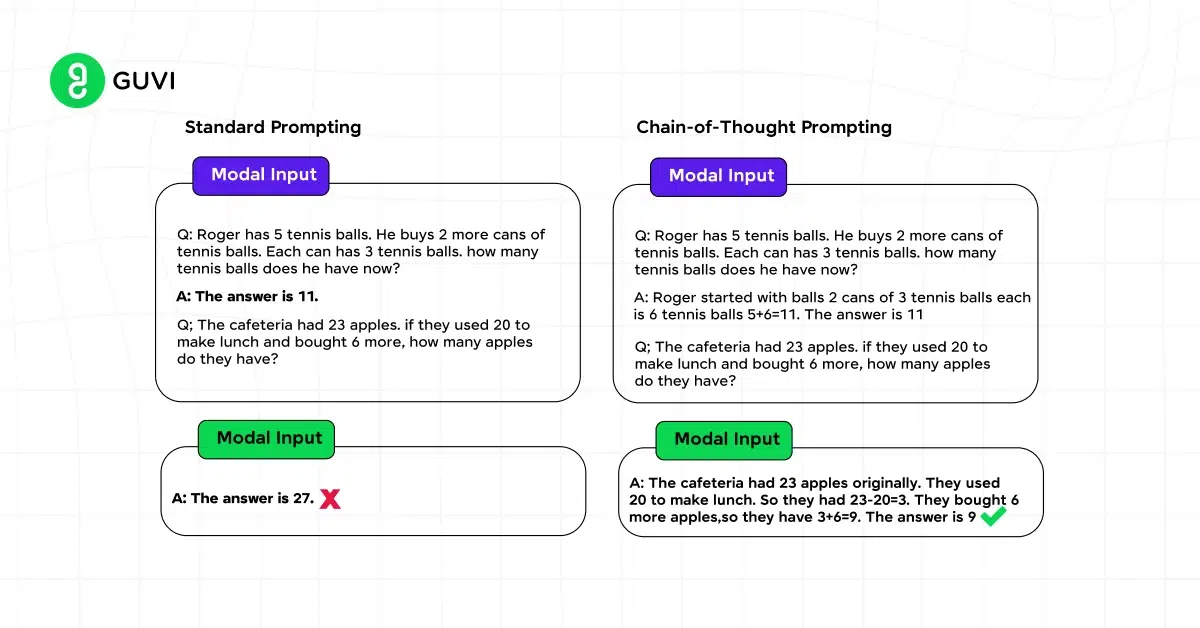
- Meta-Prompts: Meta-prompts are designed to make the AI reflect on its own reasoning process. This technique can be used to enhance the accuracy and reliability of the output by encouraging the model to verify its own conclusions before presenting them.

- Hybrid Prompts: Hybrid prompts combine various prompting techniques to handle more complex or nuanced tasks. For example, a prompt might combine a few-shot example with a Chain-of-Thought approach to ensure both accuracy and reasoning in the output.

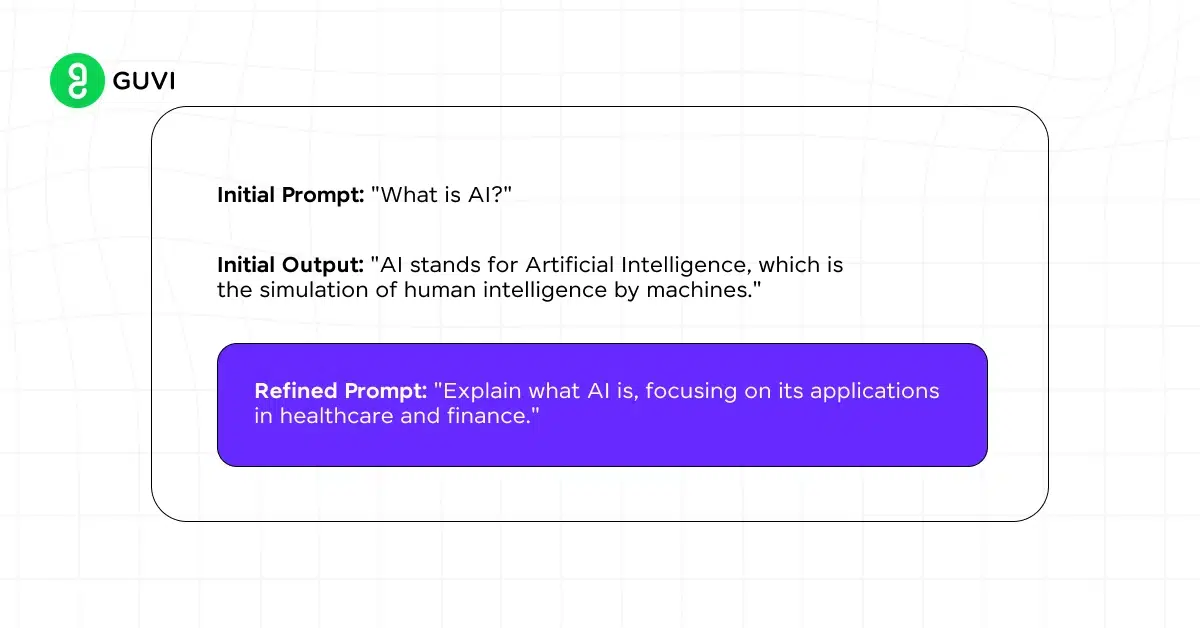
- Iterative Refinement: This technique involves repeatedly refining the prompt based on the AI’s output. Each iteration is analyzed, and the prompt is adjusted to improve clarity, reduce ambiguity, and better align with the desired outcome.
Skills Required for Prompt Engineering
Becoming an expert in prompt engineering requires a diverse set of skills that blend technical expertise with creative problem-solving abilities. Here are the key skills:
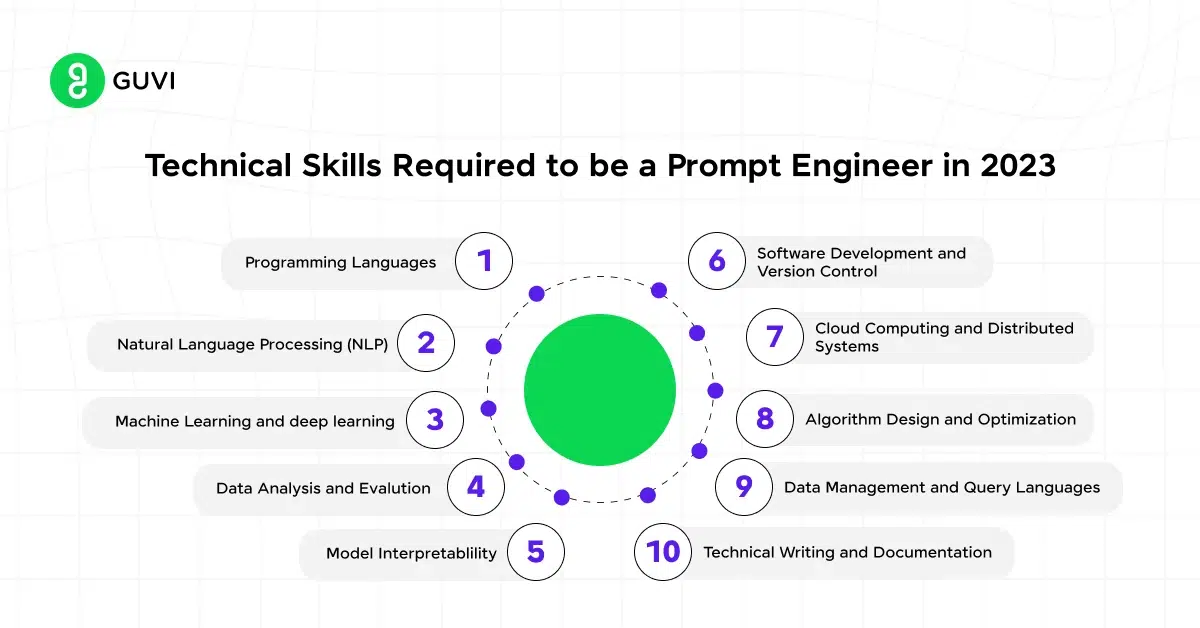
- Deep Understanding of AI Models:
A thorough understanding of how AI models, particularly LLMs like GPT, function is essential. This includes knowledge of their architecture, training processes, strengths, and limitations. - Proficiency in NLP:
A strong foundation in natural language processing is crucial, as it allows the prompt engineer to craft prompts that effectively communicate with the AI model. This involves understanding linguistic nuances, context, and the model’s ability to process and generate text. - Analytical Problem-Solving:
Prompt engineering often involves diagnosing issues with AI outputs and devising strategies to improve them. Analytical skills help in identifying the root cause of problems and in designing prompts that guide the model toward better performance. - Iterative Testing and Refinement:
The ability to systematically test and refine prompts is key to successful prompt engineering. This requires patience, attention to detail, and a willingness to experiment with different approaches. - Creative Thinking:
Innovation is at the heart of prompt engineering. Creative thinking enables the engineer to develop novel prompts that push the boundaries of what the AI can achieve, whether it’s in generating content, solving problems, or creating art.
Applications of Prompt Engineering
Prompt engineering is utilized across a wide range of domains, each requiring unique strategies and approaches. Here are some key applications:
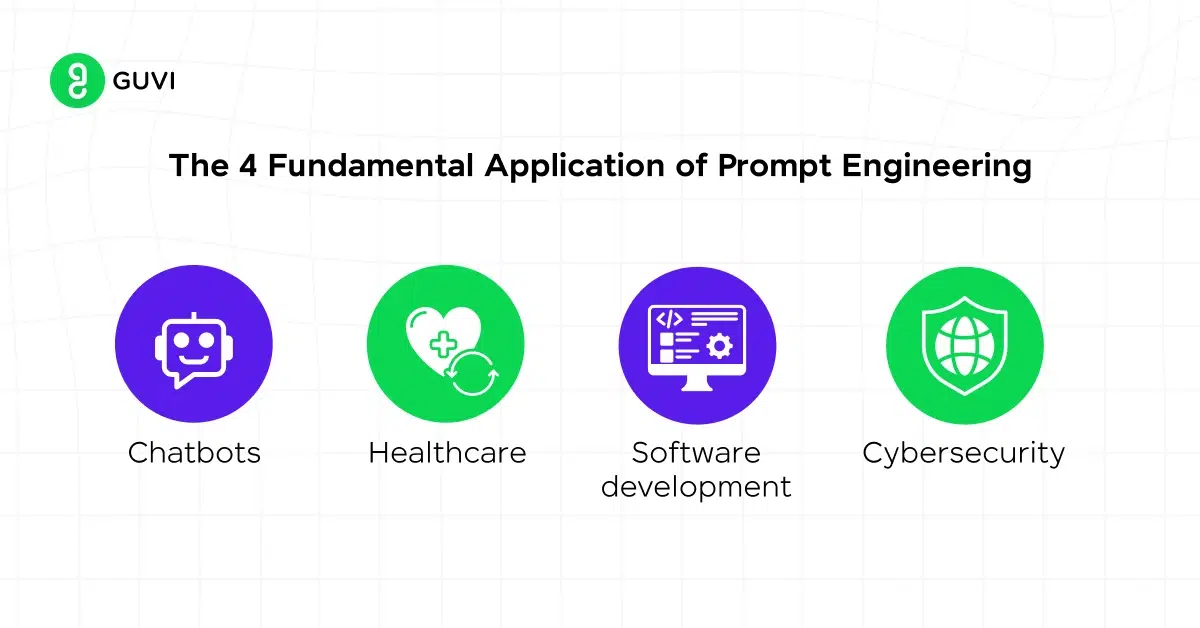
- Chatbots:
- Use Case: In customer service, prompt engineering is used to direct chatbots to provide precise, relevant responses. For example, prompts can be tailored to guide the chatbot in prioritizing certain types of inquiries or directing users to appropriate resources.
- Impact: Enhances user experience by ensuring that the chatbot remains focused and responsive to specific queries, leading to faster resolution times.
- Content Creation:
- Use Case: AI-driven content creation tools use prompt engineering to generate articles, reports, and creative writing that align with specified guidelines. For instance, a prompt might instruct the AI to write an article in a particular tone or style.
- Impact: Ensures that the generated content meets quality and relevance standards, reducing the need for extensive post-editing.
- Software Development:
- Use Case: In automated coding, prompt engineering helps AI models generate code snippets, debug existing code, or even suggest improvements. For example, a prompt can be designed to instruct the AI to refactor code to improve performance.
- Impact: Speeds up the software development process by reducing manual coding tasks and allowing developers to focus on more complex challenges.
- Image Generation:
- Use Case: In fields like design and media, prompt engineering allows AI models to create custom images based on textual descriptions. For instance, a designer might use a prompt to generate a logo concept by describing the desired elements.
- Impact: Reduces the time and effort required to produce visual content, enabling rapid prototyping and creative exploration.
| Application | Example | Impact |
| Chatbots | Handling customer support queries | Improved user experience and faster issue resolution |
| Content Creation | Generating marketing copy with a specified tone | Ensures consistency and relevance in content production |
| Software Development | Automated generation of code snippets | Reduces manual workload, speeds up development cycle |
| Image Generation | Creating illustrations based on detailed textual descriptions | Enhances creativity and speeds up the design process |
Challenges in Prompt Engineering
Despite its potential, prompt engineering is not without challenges. Some of the key issues include:
- Model Limitations: AI models are prone to generating incorrect or nonsensical information, known as “hallucinations.” These errors can occur when the model’s training data is insufficient or when the prompt is ambiguous. Engineers must carefully design prompts to minimize these risks.
- Ethical Considerations: Bias in AI outputs is a significant concern, and prompt engineering plays a role in mitigating these biases. Engineers must be vigilant in ensuring that their prompts are subtle and can occur unconsciously. Engineers must carefully design prompts to promote fairness and accuracy, actively avoiding perpetuating harmful stereotypes or misinformation.
- Complexity of System Prompts: System prompts, which dictate the AI’s overall behavior, can sometimes conflict with user prompts, leading to unexpected or suboptimal results. For example, if a system prompt emphasizes factual accuracy but the user prompt asks for creative storytelling, the AI might struggle to balance these conflicting directives.
- Iterative Nature: Achieving the desired output often requires multiple iterations of prompt refinement. This process can be time-consuming and requires meticulous attention to detail to identify what changes in the prompt lead to improvements in the output.
Would you like to learn all about prompt engineering and master this high-income AI skill?
Learn Artificial Intelligence and Machine learning and bag an industry certificate to enhance your skills and resume, enroll in GUVI’s IIT-M Pravartak certified Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Courses!
Concluding Thoughts…
Prompt engineering has emerged as a game-changing skill in the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence. This cutting-edge field has a significant influence on how we interact with and harness the power of generative AI, causing a revolution in AI applications across various industries.
By mastering the art and science of crafting precise instructions, prompt engineers play a crucial role in shaping the future of AI technology, bridging the gap between human intent and machine output.
FAQs
A prompt engineer specializes in crafting inputs that guide AI tools to generate desired outcomes. This involves designing and tweaking prompts that help AI systems understand and execute tasks more effectively.
In India, the average annual salary for an AI Prompt Engineer is approximately ₹9.7LPA.
Prompt engineering involves providing specific instructions to generative AI systems to achieve targeted results. Although these AI systems are designed to mimic human behavior, they require clear and precise directions to produce outputs that are both high-quality and relevant.
Becoming skilled in prompt engineering is not overly difficult. It involves learning a few standard techniques initially, and with practice, one can explore and develop additional methods that may be more suited to specific needs or scenarios.
























Did you enjoy this article?