
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Jul 14, 2025 5 Min Read 1389 Views
(Last Updated)
Have you ever wondered how companies manage to process thousands of invoices, respond to customer queries instantly, or update massive databases without hiring a small army?
The answer lies in Robotic Process Automation (RPA), a technology that’s quietly transforming how modern businesses operate behind the scenes.
In this article, we’ll explore what RPA is, how it works, where it’s used, and why it’s becoming a critical tool for every company out there that is driving toward digital efficiency and scale.
Table of contents
- What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
- Why Does Robotic Process Automation Matter in Today’s Workplaces?
- Increased Productivity
- Cost Savings
- Improved Accuracy
- Scalability Without Complexity
- Enhanced Compliance and Audit Trails
- How is RPA Different from Traditional Automation?
- How Does RPA Work in Practice?
- Step 1: Identify Suitable Processes
- Step 2: Map Out the Process
- Step 3: Build the Bot
- Step 4: Test in a Controlled Environment
- Step 5: Deploy and Monitor
- Use Cases of Robotic Process Automation
- Banking and Finance
- Healthcare
- Human Resources (HR)
- Retail and E-commerce
- Benefits and Challenges of RPA
- Benefits of RPA
- Challenges of RPA
- Is RPA the Same as AI?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
- What types of tasks are best suited for RPA?
- How is RPA different from traditional automation?
- Do I need coding skills to use RPA tools?
- What are the main benefits of RPA?
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?

Robotic Process Automation refers to the use of software robots or “bots” that are programmed to carry out structured, repetitive tasks that are usually performed by humans. These bots work across applications and systems, replicating the way a person interacts with a digital environment.
Imagine a bot that logs into your company’s accounting software, downloads reports, copies the numbers into an Excel sheet, and emails it to your finance manager without missing a beat. That’s RPA in action.
Unlike AI, which learns and evolves, RPA strictly follows predefined rules. It doesn’t make decisions. It simply executes tasks quickly and accurately, based on the instructions it’s given. We will see more on how RPA is different from AI in the upcoming sections!
Why Does Robotic Process Automation Matter in Today’s Workplaces?
In an age where businesses are striving for faster, leaner, and more reliable operations, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) plays a critical role. It’s not just a technical solution, it’s a strategic lever for digital transformation.
Let’s break down the key reasons why RPA is becoming indispensable:
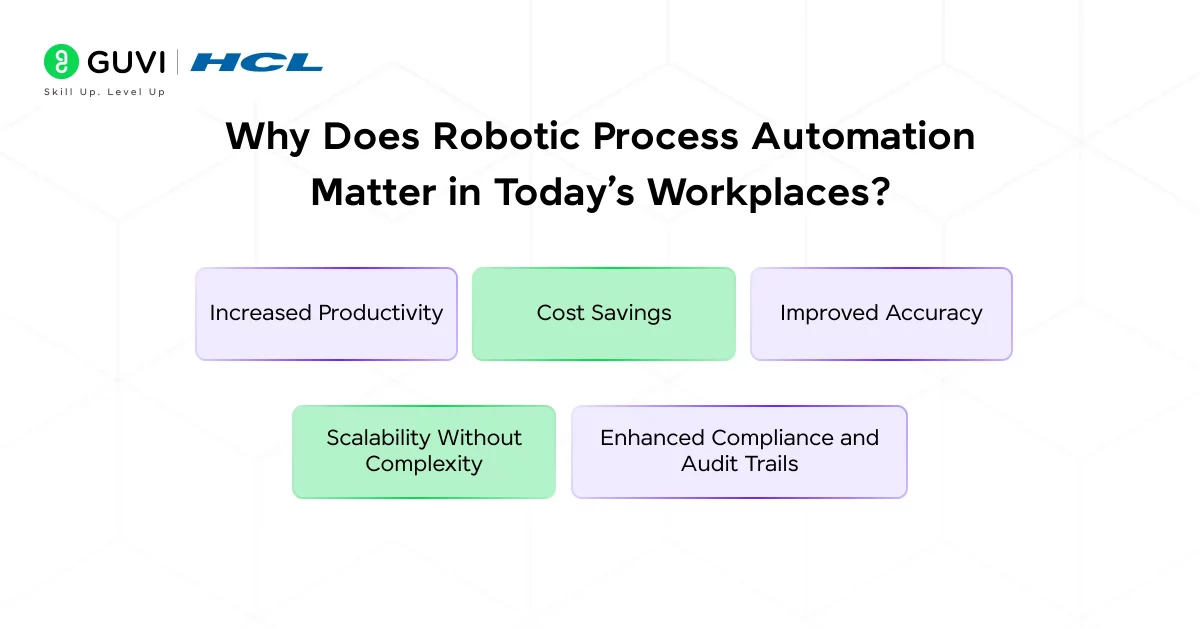
1. Increased Productivity
Manual, repetitive tasks like data entry, report generation, or copying files between systems can consume hours of employee time each week. With RPA, these tasks can be completed in seconds, allowing teams to shift their focus to higher-value work.
For example, an HR team that previously spent days processing new hire paperwork can automate it to free up time for employee engagement initiatives.
2. Cost Savings
Deploying RPA bots is significantly more cost-effective than hiring additional staff to handle growing workloads. Bots work 24/7, don’t require benefits, and don’t take breaks.
A single bot can often perform the work of three or more full-time employees handling routine digital tasks.
3. Improved Accuracy
Unlike humans, bots don’t make typographical errors, forget steps, or misinterpret instructions if they’re programmed correctly. This leads to more consistent, reliable output and fewer reworks.
In industries like banking or insurance, this level of accuracy is crucial to avoid regulatory fines or service disruptions.
4. Scalability Without Complexity
Need to scale operations during a peak season or after a business expansion? With RPA, you can deploy additional bots quickly without overhauling your existing infrastructure.
For seasonal industries like retail or logistics, this flexibility offers a clear competitive edge.
5. Enhanced Compliance and Audit Trails
RPA bots keep detailed logs of every step they perform, which makes audits simpler and more transparent. Processes can be designed to follow compliance rules by default, reducing risk.
Think about regulatory reporting in the finance sector, bots can prepare and submit accurate filings without delays.
How is RPA Different from Traditional Automation?
At this point, you might wonder why RPA sounds very much similar to traditional automation methods. But there is a clear distinction between them.
While both RPA and traditional automation aim to improve efficiency by reducing manual effort, they differ in how they are implemented and what they can automate.
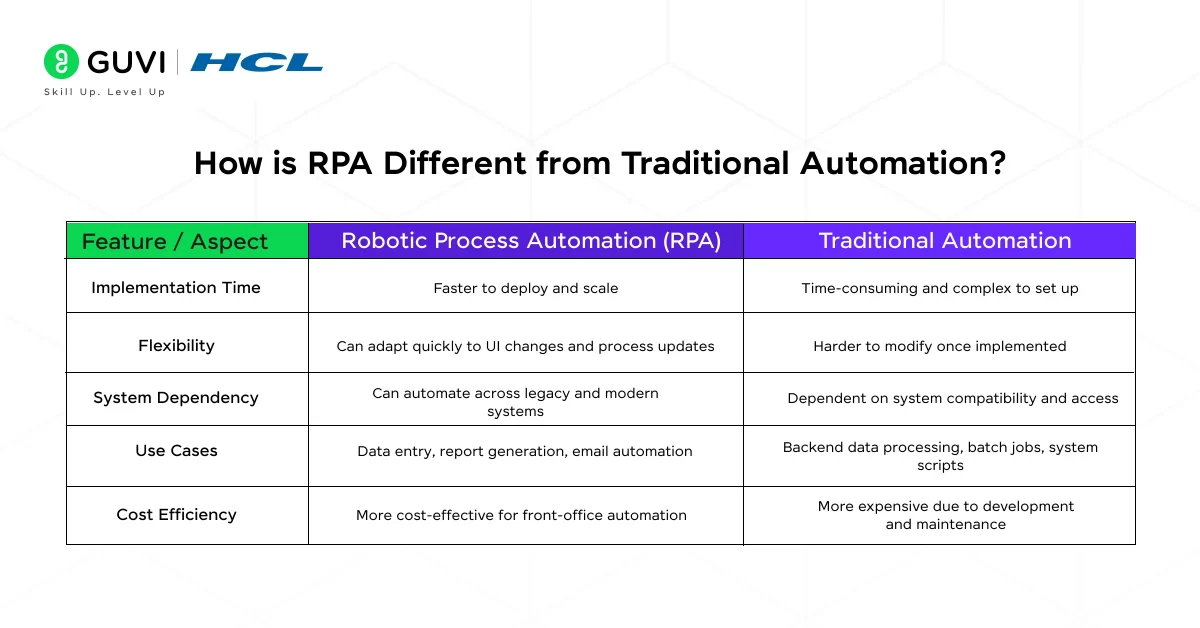
| Feature / Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Traditional Automation |
| Approach | Works at the user interface (UI) level | Works at the backend/system level |
| Integration | No deep system integration required | Requires integration via APIs, scripts, or custom code |
| Coding Requirement | Low-code or no-code platforms | Heavy coding and development efforts needed |
| Process Type | Ideal for rule-based, repetitive, multi-app tasks | Suited for structured, single-system processes |
| Implementation Time | Faster to deploy and scale | Time-consuming and complex to set up |
| Flexibility | Can adapt quickly to UI changes and process updates | Harder to modify once implemented |
| System Dependency | Can automate across legacy and modern systems | Dependent on system compatibility and access |
| Use Cases | Data entry, report generation, email automation | Backend data processing, batch jobs, system scripts |
| Cost Efficiency | More cost-effective for front-office automation | More expensive due to development and maintenance |
Summary: RPA is quicker, more flexible, and business-friendly, while traditional automation is more rigid, technical, and suited for deeper system-level processes.
How Does RPA Work in Practice?

While RPA may seem complex on the surface, the actual implementation process is structured and straightforward, especially with modern RPA tools that require minimal coding.
Here’s how a typical RPA workflow unfolds:
Step 1: Identify Suitable Processes
Not every task is ideal for RPA. The best candidates are:
- Rule-based (clear steps with no ambiguity)
- Repetitive and high-volume
- Stable (systems and processes don’t change frequently)
- Involve structured data (like forms, spreadsheets, or databases)
For instance, copying leads from a CRM to an email marketing tool is a great candidate for automation.
Step 2: Map Out the Process
Once a task is identified, business analysts or automation specialists break it down step by step. This includes:
- Every screen the bot needs to access
- Every field must be filled out
- Decision points in the workflow
This step ensures that the automation logic mirrors the exact behavior of a human user.
Step 3: Build the Bot
Using RPA platforms like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, or Blue Prism, developers (or even non-tech users with basic training) design the automation.
These tools offer:
- Drag-and-drop interfaces
- Prebuilt activity libraries
- Integration with desktop and web apps
- Options for triggering bots on a schedule or in real-time
For example, a bot might be built to scrape invoice data from emails and feed it into an ERP system.
If you are someone who’s preparing to crack a job in a platform like UiPath, read the blog – Top 20 RPA UiPath Interview Questions and Answers
Step 4: Test in a Controlled Environment
Before going live, the bot is tested under real-world conditions to:
- Verify that it handles edge cases correctly
- Check that it doesn’t interfere with other systems
- Ensure error-handling mechanisms are in place
This “UAT” phase (User Acceptance Testing) is essential for preventing automation failures post-deployment.
Step 5: Deploy and Monitor
Once the bot is validated, it’s moved into production. From here, the focus shifts to:
- Monitoring bot performance
- Logging errors or exceptions
- Making iterative improvements if the process changes
Some organizations set up dashboards that track bot activity in real time for transparency and control.
By combining structured analysis, smart design, and modern low-code tools, RPA makes it possible to automate complex workflows with surprising speed and simplicity.
Use Cases of Robotic Process Automation
Robotic Process Automation is not confined to a single industry or department; it’s being adopted across sectors wherever routine digital tasks exist. Whether it’s a multinational bank or a local logistics company, RPA can unlock major operational efficiencies.
Let’s look at some common use cases of RPA:
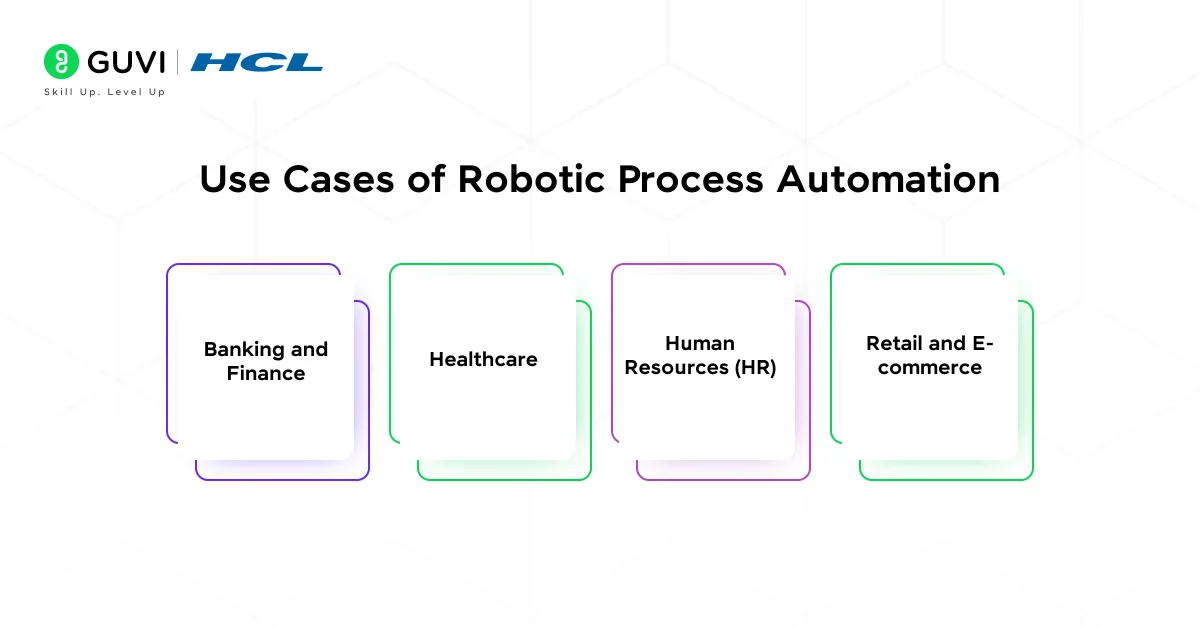
1. Banking and Finance
Financial institutions are early adopters of RPA due to the large volume of rule-based, repetitive tasks.
Use cases include:
- Automating loan application processing
- Handling account reconciliation
- Generating regulatory compliance reports
- Fraud detection through rule-based data checks
For example, a bank may use an RPA bot to validate customer documents during onboarding and flag inconsistencies in real-time.
2. Healthcare
In healthcare, accuracy and speed are critical. RPA helps reduce administrative burden and allows professionals to focus more on patient care.
Common applications:
- Patient registration and record management
- Medical billing and claims processing
- Appointment scheduling
- Inventory management of medical supplies
Hospitals can use bots to extract patient data from scanned forms and feed it into electronic health record (EHR) systems.
3. Human Resources (HR)
HR departments often deal with high-volume tasks that are perfect for automation.
Automated processes may include:
- Employee onboarding and offboarding
- Leave and attendance tracking
- Payroll processing
- Resume screening and interview scheduling
An RPA solution can onboard a new employee end-to-end, from sending welcome emails to provisioning system access.
4. Retail and E-commerce
Retailers use RPA to streamline backend operations and customer experience.
Key use cases:
- Inventory updates across systems
- Processing orders and returns
- Updating product catalogs
- Customer query responses
For e-commerce brands, RPA bots can process thousands of return requests daily without manual intervention.
Benefits and Challenges of RPA
Like any technology, RPA brings clear advantages, but it also comes with limitations that must be managed carefully. Understanding both sides helps you implement RPA with realistic expectations.
Benefits of RPA
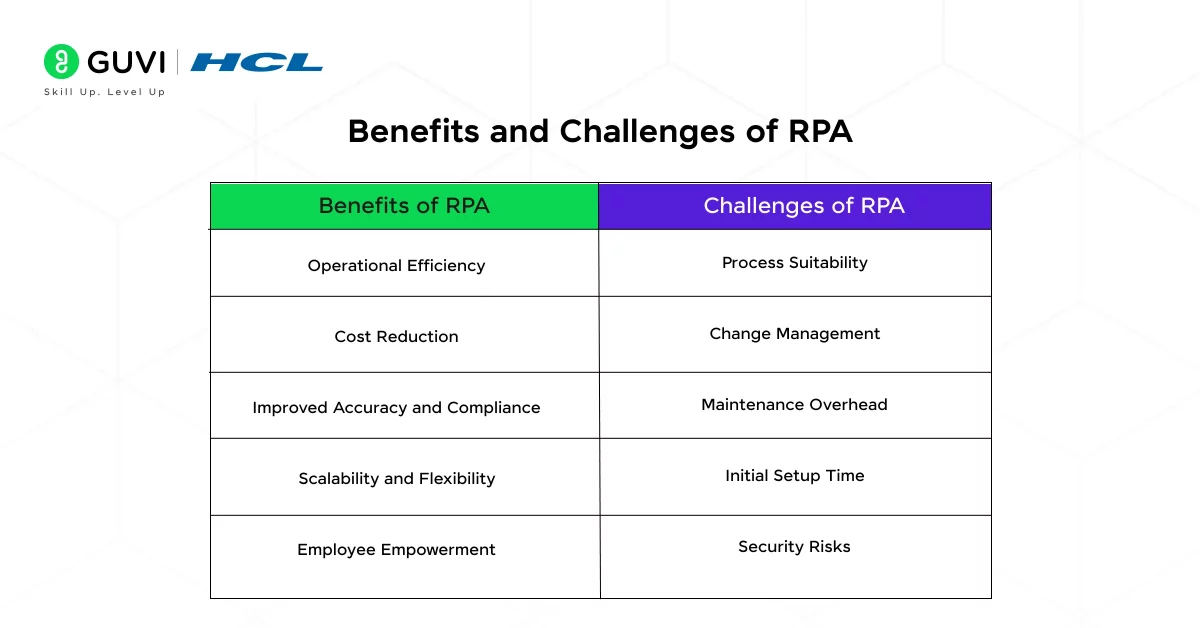
1. Operational Efficiency
RPA bots work faster than humans, and they can operate 24/7. This increases overall process throughput without adding to your workforce.
2. Cost Reduction
Organizations save significantly on operational costs by automating labor-intensive processes, especially at scale.
3. Improved Accuracy and Compliance
By following predefined rules, bots eliminate human errors. They also log every action, which helps in maintaining clear audit trails for regulatory compliance.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
Once a bot is created, it can be cloned and scaled across departments with minimal overhead.
5. Employee Empowerment
By taking over monotonous tasks, RPA allows employees to focus on strategic, creative, and customer-facing activities.
Challenges of RPA
1. Process Suitability
Not all tasks are ideal for automation. RPA works best with structured, rule-based processes. Dynamic or judgment-based tasks still require human involvement.
2. Change Management
RPA introduces new workflows and roles. Without proper change management, employees might resist adoption due to the fear of job displacement.
3. Maintenance Overhead
While bots are efficient, they are not immune to changes. If your software interfaces or processes change frequently, bots may need regular updates.
4. Initial Setup Time
Although coding is minimal, the setup involves detailed process mapping, testing, and integration, which can take time upfront.
5. Security Risks
If not governed properly, bots with system access could become a security vulnerability. Proper role-based access control and audit trails are essential.
Is RPA the Same as AI?
As we discussed at the start of this blog, RPA and AI might sound similar at first hear but it is not! While Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are both automation technologies, they are not the same, but they can complement each other.
- RPA is rule-based. It follows predefined instructions to perform repetitive, structured tasks—like copying data, clicking buttons, or sending emails.
- AI is data-driven and adaptive. It mimics human intelligence by analyzing data, learning patterns, and making decisions. This includes technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision.
In short:
- RPA does the work.
- AI thinks about work.
When combined, they create Intelligent Automation where RPA handles structured tasks and AI deals with unstructured data or decision-making, like understanding customer queries or analyzing scanned documents.
If you want to learn more about how RPA works and how to get started with it, consider enrolling in GUVI’s Robotic Process Automation(RPA) Course tied up with UiPath, where you get to master everything related to RPA and also provides you with an industry-grade certification!
Conclusion
In conclusion, Robotic Process Automation is no longer a futuristic concept, it’s a practical, accessible solution that’s already reshaping industries.
By automating rule-based, repetitive tasks, not only reduces manual effort and errors but also empowers teams to focus on what truly matters: creativity, strategy, and innovation.
As organizations continue to adapt to digital demands, embracing RPA isn’t just an option, it’s a competitive advantage.
FAQs
RPA is a technology that uses software bots to automate repetitive, rule-based digital tasks by mimicking human interactions on a computer. It helps streamline operations, reduce manual effort, and boost productivity across various functions.
RPA is ideal for tasks that are repetitive, rules-driven, and involve structured data, such as data entry, invoice processing, and form submissions. If a task follows a predictable pattern, it’s likely a good candidate for automation.
Unlike traditional automation, which requires backend integration and heavy coding, RPA works at the user interface level, simulating how a human interacts with software. This makes it faster to implement and more adaptable to changing systems.
Most modern RPA platforms are designed for non-developers, offering intuitive, drag-and-drop interfaces that require little to no coding. However, having some scripting knowledge can be helpful for more advanced customizations.
RPA boosts efficiency, reduces operational costs, and minimizes human error. It allows employees to focus on higher-value work while bots handle routine tasks, resulting in faster turnaround and improved process accuracy.





















![How to Become a Robotics Engineer: A Beginner's Guide [2025] 8 robotics engineer](https://www.guvi.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/How-to-Become-a-Robotics-Engineer.png)
![Best Project Ideas for Robotic Applications - Including All 3 Levels [2025] 9 Feature image - Best Project Ideas for Robotic Applications - Including All 3 Levels](https://www.guvi.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/0-project_ideas_for_robotic_applications.webp)

![Top 20 RPA UiPath Interview Questions and Answers [2025] 10 rpa uipath interview questions](https://www.guvi.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Top-20-RPA-UiPath-Interview-Questions-and-Answers.png)





Did you enjoy this article?